Introduction to Classical Mechanics 1 HISTORY
... a small ball and drop it. Then it falls with the same acceleration as a more massive stone. ...
... a small ball and drop it. Then it falls with the same acceleration as a more massive stone. ...
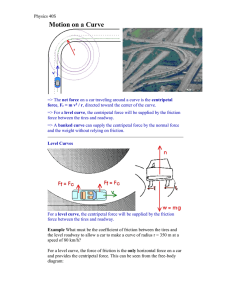
Uniform Circular Motion PP
... 2nd Law tells us there must be a net force directed toward the center of the circle as well. This type of force, known as a centripetal force, can be a gravitational force, a tension, an applied force, or even a frictional force. • NOTE: When dealing with circular motion problems, it is important to ...
... 2nd Law tells us there must be a net force directed toward the center of the circle as well. This type of force, known as a centripetal force, can be a gravitational force, a tension, an applied force, or even a frictional force. • NOTE: When dealing with circular motion problems, it is important to ...
Kinematics Unit Outline - Hicksville Public Schools
... 2.25 newtons of force to be constantly applied to keep it moving at a constant velocity. If a force of 10.25 newtons were applied to the same block the result ...
... 2.25 newtons of force to be constantly applied to keep it moving at a constant velocity. If a force of 10.25 newtons were applied to the same block the result ...
香港考試局
... Two identical light springs are connected with two masses of 2.0 kg and 0.5 kg as shown. Which of the following statements is/are correct ? (1) The tension in the upper spring is four times that in the lower spring. (2) The force acting on the ceiling by the whole system is 25 N. (3) The tension in ...
... Two identical light springs are connected with two masses of 2.0 kg and 0.5 kg as shown. Which of the following statements is/are correct ? (1) The tension in the upper spring is four times that in the lower spring. (2) The force acting on the ceiling by the whole system is 25 N. (3) The tension in ...
Chapter 8 Rotational Dynamics conclusion
... Right-Hand Rule: Grasp the axis of rotation with your right hand, so that your fingers circle the axis in the same sense as the rotation. ...
... Right-Hand Rule: Grasp the axis of rotation with your right hand, so that your fingers circle the axis in the same sense as the rotation. ...
Interpret The Graph Below
... Describe Acceleration Deceleration is also called negative acceleration - it means an object is slowing down When acceleration is calculated, it may be a negative number ...
... Describe Acceleration Deceleration is also called negative acceleration - it means an object is slowing down When acceleration is calculated, it may be a negative number ...
Moments of INERTIA
... • Who is harder to spin in a circle with a rotational speed of 1 RPM; a 10 g point moving with a radius of 20 cm, or a 10 g point moving with a radius of 1 m? • Since both points complete 1 circle in the same amount of time the outside point must travel 5x faster than the inside point, which means i ...
... • Who is harder to spin in a circle with a rotational speed of 1 RPM; a 10 g point moving with a radius of 20 cm, or a 10 g point moving with a radius of 1 m? • Since both points complete 1 circle in the same amount of time the outside point must travel 5x faster than the inside point, which means i ...
Exam 2
... A) No, because the object has constant speed. B) No, because the force and the displacement of the object are perpendicular. C) Yes, since a force acts and the object moves, and work is force times distance. D) Yes, since it takes energy to turn an object. 40) A 3.0-kg object moves to the right at 4 ...
... A) No, because the object has constant speed. B) No, because the force and the displacement of the object are perpendicular. C) Yes, since a force acts and the object moves, and work is force times distance. D) Yes, since it takes energy to turn an object. 40) A 3.0-kg object moves to the right at 4 ...
Document
... Calculate the Acceleration of the Cart Note: This formula will work because the Cart started with a velocity of zero and accelerated at an (approximately) constant rate. In this particular case, the final velocity is the average velocity x 2. ...
... Calculate the Acceleration of the Cart Note: This formula will work because the Cart started with a velocity of zero and accelerated at an (approximately) constant rate. In this particular case, the final velocity is the average velocity x 2. ...
CE-PHY II - MECHANICS
... An object starts from rest and moves with uniform acceleration along a straight line. Which of the following graphs concerning the motion of the object is/are correct ? ...
... An object starts from rest and moves with uniform acceleration along a straight line. Which of the following graphs concerning the motion of the object is/are correct ? ...
lectures 2015
... absolute quantities. We think that we can define a point in ‘absolute’ space and ‘absolute’ time, and that space and time are the same for everyone, no matter how they are moving with respect to each other. These ideas obviously work very well in everyday life, but need closer examination. (e) We ca ...
... absolute quantities. We think that we can define a point in ‘absolute’ space and ‘absolute’ time, and that space and time are the same for everyone, no matter how they are moving with respect to each other. These ideas obviously work very well in everyday life, but need closer examination. (e) We ca ...
Understeer and Oversteer
... Then Newton’s law can be applied to each component separately, as ax=Fx/m, etc. (Fx and ax are the magnitudes of the components of F and a in the x-direction.) Acceleration is the rate of change of the velocity vector v. Velocity can change in either magnitude or direction, or both. In two-dimension ...
... Then Newton’s law can be applied to each component separately, as ax=Fx/m, etc. (Fx and ax are the magnitudes of the components of F and a in the x-direction.) Acceleration is the rate of change of the velocity vector v. Velocity can change in either magnitude or direction, or both. In two-dimension ...
3 - CSUN.edu
... H. None of these choices can be suitably fill in this blank. 8. In a collision, an object experiences an impulse. This impulse can be determined by ____. Enter the two answers alphabetically with no commas or spaces between the letters. A. Multiplying the force on the object by the time over which t ...
... H. None of these choices can be suitably fill in this blank. 8. In a collision, an object experiences an impulse. This impulse can be determined by ____. Enter the two answers alphabetically with no commas or spaces between the letters. A. Multiplying the force on the object by the time over which t ...
FBD practice solutions - knotts
... Absolutely. When you rode the hovercraft, the two forces on you (gravitational and normal) resulted in a net force of zero. When the net force is zero on an object, it travels at constant speed in a straight line as described by Newton's first law. d. A body accelerates without exerting forces on an ...
... Absolutely. When you rode the hovercraft, the two forces on you (gravitational and normal) resulted in a net force of zero. When the net force is zero on an object, it travels at constant speed in a straight line as described by Newton's first law. d. A body accelerates without exerting forces on an ...
Chapter 12: Forces in Motion
... • Why does a projectile follow a curved path? What Is a Force? • A force can cause a resting object to _________, or it can accelerate a moving object by changing the object’s speed or direction. • A __________ or a ___________ ...
... • Why does a projectile follow a curved path? What Is a Force? • A force can cause a resting object to _________, or it can accelerate a moving object by changing the object’s speed or direction. • A __________ or a ___________ ...