Forces - SchoolRack
... air resistance When two objects or materials do not need to be touching for a force to have an effect, it is a non-contact force. Examples: gravity ...
... air resistance When two objects or materials do not need to be touching for a force to have an effect, it is a non-contact force. Examples: gravity ...
Fulltext PDF - Indian Academy of Sciences
... Force: States of motion are affected by forces. When we consider the variety of motions a legitimate question that could arise is, what causes such variety? In other words, why do some bodies remain unchanging in motion, altering neither speed nor direction, while others – indeed most that we ordina ...
... Force: States of motion are affected by forces. When we consider the variety of motions a legitimate question that could arise is, what causes such variety? In other words, why do some bodies remain unchanging in motion, altering neither speed nor direction, while others – indeed most that we ordina ...
Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... So far we have covered aspects of motion relating displacement, velocity, acceleration and time. We will now look at what causes the motion. Specifically, we will look at what causes the acceleration to get items moving, slow items down and change the direction of the velocity. A force is described ...
... So far we have covered aspects of motion relating displacement, velocity, acceleration and time. We will now look at what causes the motion. Specifically, we will look at what causes the acceleration to get items moving, slow items down and change the direction of the velocity. A force is described ...
Stabilization of Inverted, Vibrating Pendulums
... vertical than it did toward the vertical in case #1 ...
... vertical than it did toward the vertical in case #1 ...
When the net force that acts on a hockey puck is 10 N, the puck
... about the forces acting on your car? A) The forces acting to make the car go in the forward direction must be greater than the forces acting to make the car go in the backward direction, or the car would not go forward. B) The forces acting to make the car go in the forward direction must be equal t ...
... about the forces acting on your car? A) The forces acting to make the car go in the forward direction must be greater than the forces acting to make the car go in the backward direction, or the car would not go forward. B) The forces acting to make the car go in the forward direction must be equal t ...
HW7
... As can be seen from the diagram, the component of the force of gravity that is perpendicular to the rod is mg sin . If is the length of the rod, then the torque associated with this force has magnitude mg sin (0.75)(9.8)(1.25) sin 30 4.6 N m . For the position shown, the torque is co ...
... As can be seen from the diagram, the component of the force of gravity that is perpendicular to the rod is mg sin . If is the length of the rod, then the torque associated with this force has magnitude mg sin (0.75)(9.8)(1.25) sin 30 4.6 N m . For the position shown, the torque is co ...
IHS ppt 092710 ISA
... Speed and distance are _________ (a quantity that can be added, subtracted, multiplied, and divided like an ordinary number). Velocity and acceleration are considered ________ quantities, because they take the direction of the motion into account in addition to magnitude. They cannot simply be treat ...
... Speed and distance are _________ (a quantity that can be added, subtracted, multiplied, and divided like an ordinary number). Velocity and acceleration are considered ________ quantities, because they take the direction of the motion into account in addition to magnitude. They cannot simply be treat ...
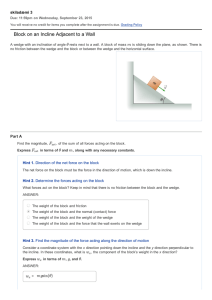
Block on an Incline Adjacent to a Wall
... Hint 2. Determine the force causing acceleration Whenever you see uniform circular motion, there is a real force that causes the associated centripetal acceleration. In this problem, what force causes the centripetal acceleration? ANSWER: normal force static friction weight of cylinder a force o ...
... Hint 2. Determine the force causing acceleration Whenever you see uniform circular motion, there is a real force that causes the associated centripetal acceleration. In this problem, what force causes the centripetal acceleration? ANSWER: normal force static friction weight of cylinder a force o ...
File - Mrs. Hart`s Science Place
... A. The soccer ball is moving and the basketball is not moving. If the soccer ball is moving to the right and hits the basketball, in which direction will the basketball move? The basketball will move to the right B. The basketball has a mass of 10 kg. If it is accelerating at a rate of 3 m/s/s, what ...
... A. The soccer ball is moving and the basketball is not moving. If the soccer ball is moving to the right and hits the basketball, in which direction will the basketball move? The basketball will move to the right B. The basketball has a mass of 10 kg. If it is accelerating at a rate of 3 m/s/s, what ...
PHYSICS
... website and Moodle to keep up if you are out. You are expected to be aware of what was missed during an absence prior to returning to class. Notebook suggestions: Your notebook should be a three-ring binder of about 1.5-inch width. The notebook is not graded, however, the course is cumulative in nat ...
... website and Moodle to keep up if you are out. You are expected to be aware of what was missed during an absence prior to returning to class. Notebook suggestions: Your notebook should be a three-ring binder of about 1.5-inch width. The notebook is not graded, however, the course is cumulative in nat ...
Are You suprised
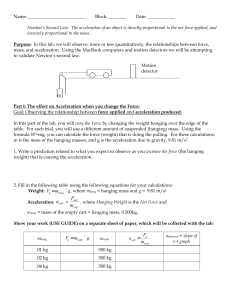
... mass, and acceleration. Using the MacBook computers and motion detectors we will be attempting to validate Newton’s second law. Motion detector ...
... mass, and acceleration. Using the MacBook computers and motion detectors we will be attempting to validate Newton’s second law. Motion detector ...
實驗3:轉動-剛體的轉動運動Lab. 3 : Rotation
... a rotating object is analogous to KELinear and can be expressed in terms of the moment of inertia and angular velocity. The total kinetic energy of an extended object can be expressed as the sum PhysicsNTHU of the translational kinetic energy of the center of mass and the rotational MFTai-戴明鳳 kine ...
... a rotating object is analogous to KELinear and can be expressed in terms of the moment of inertia and angular velocity. The total kinetic energy of an extended object can be expressed as the sum PhysicsNTHU of the translational kinetic energy of the center of mass and the rotational MFTai-戴明鳳 kine ...