Why study geography?
... People move around to different places throughout the world because their resources (raw materials) are spread unevenly around the world. Resources are things that we get from the Earth to help us survive, such as trees, water and fish. People need these resources to build their houses and survive. ...
... People move around to different places throughout the world because their resources (raw materials) are spread unevenly around the world. Resources are things that we get from the Earth to help us survive, such as trees, water and fish. People need these resources to build their houses and survive. ...
Document
... 2. Describe the stages involved in Nebula hypothesis including the abundant elements involved in the early formation of the universe. ...
... 2. Describe the stages involved in Nebula hypothesis including the abundant elements involved in the early formation of the universe. ...
Chapter 1
... Prime Meridian: the meridian of 0 degrees longitude which runs through the original site of the Royal Observatory at Greenwich, England, and from which other longitudes are measured east or west. Greenwich, England was selected by international agreement in an 1884 treaty. – Greenwich Mean Time (GMT ...
... Prime Meridian: the meridian of 0 degrees longitude which runs through the original site of the Royal Observatory at Greenwich, England, and from which other longitudes are measured east or west. Greenwich, England was selected by international agreement in an 1884 treaty. – Greenwich Mean Time (GMT ...
Unit 1: GeoTrekkers in the Western Hemisphere
... study of Earth and how people live on Earth and use its resources grasslands flat or rolling areas of land covered with grasses If located in North America, they are called prairies. In South America they are called pampas. grid system the pattern of lines that help locate places on a map or globe; ...
... study of Earth and how people live on Earth and use its resources grasslands flat or rolling areas of land covered with grasses If located in North America, they are called prairies. In South America they are called pampas. grid system the pattern of lines that help locate places on a map or globe; ...
Primary geography curriculum - Campaign for Real Education
... Yorks Moors, Peak District, Scottish Highlands and Lowlands, Snowdonia, European countries and the world: continents, oceans (Panama and Suez canals), seas, rivers, lakes, capital cities More atlas and map work including scales, symbols, contours, grid references Ordnance Survey maps, magnetic varia ...
... Yorks Moors, Peak District, Scottish Highlands and Lowlands, Snowdonia, European countries and the world: continents, oceans (Panama and Suez canals), seas, rivers, lakes, capital cities More atlas and map work including scales, symbols, contours, grid references Ordnance Survey maps, magnetic varia ...
IntroBasics
... We have point A latitude at 30 South. Next we need to determine longitude by using the Prime Meridian as a reference point. Then count degrees east or west. Point A is 60 West of the Prime Meridian. This is written like this ...
... We have point A latitude at 30 South. Next we need to determine longitude by using the Prime Meridian as a reference point. Then count degrees east or west. Point A is 60 West of the Prime Meridian. This is written like this ...
Monday, June 13, 2016 INNER PLANET DELIGHT: MERCURY AND
... Kinczyk M. J. * Prockter L. M. Byrne P. K. Denevi B. W. Ostrach L. R. Head J. W. III Fassett C. I. Whitten J. L. Thomas R. J. Buczkowski D. L. Hynek B. M. Blewett D. T. Ernst C. M. Preparing the First Global Geological Map of Mercury [#7027] Previous to the MESSENGER spacecraft mission to Mercury, o ...
... Kinczyk M. J. * Prockter L. M. Byrne P. K. Denevi B. W. Ostrach L. R. Head J. W. III Fassett C. I. Whitten J. L. Thomas R. J. Buczkowski D. L. Hynek B. M. Blewett D. T. Ernst C. M. Preparing the First Global Geological Map of Mercury [#7027] Previous to the MESSENGER spacecraft mission to Mercury, o ...
Name Date
... places on Earth’s surface. F. I can explain what a solstice and equinox is. G. I can explain the differences between map projections and types. H. I can describe differences amongst climate regions in the world. I. I can identify various landforms and waterways on Earth’s surface. ...
... places on Earth’s surface. F. I can explain what a solstice and equinox is. G. I can explain the differences between map projections and types. H. I can describe differences amongst climate regions in the world. I. I can identify various landforms and waterways on Earth’s surface. ...
Maps and Globes are Models of Earth
... The latitude lines are curved slightly, this allows for a more accurate size and shape of some landmasses ...
... The latitude lines are curved slightly, this allows for a more accurate size and shape of some landmasses ...
Summer Assignment AP Human Geography 2017-2018
... can only be achieved if you are willing to put forth college level effort. As an introduction to this course, it is required that you complete this summer assignment in an effort to become more familiar with the areas of study that are covered. Your entire packet is due on the first day of your AP c ...
... can only be achieved if you are willing to put forth college level effort. As an introduction to this course, it is required that you complete this summer assignment in an effort to become more familiar with the areas of study that are covered. Your entire packet is due on the first day of your AP c ...
study guide
... GEOGRAPHY 111 MIDTERM I STUDY GUIDE Midterm I exam will be multiple choice, true/false, and matching. I’m not looking simply for the definitions of terms, but for you to understand their common-sense meanings, and real-life examples of them. INTRODUCTION LECTURE / PARTS OF CHAPTER 1 Human Geography ...
... GEOGRAPHY 111 MIDTERM I STUDY GUIDE Midterm I exam will be multiple choice, true/false, and matching. I’m not looking simply for the definitions of terms, but for you to understand their common-sense meanings, and real-life examples of them. INTRODUCTION LECTURE / PARTS OF CHAPTER 1 Human Geography ...
Island Construction * Topographic Map
... line. (For this model, 1cm is equal to 100 feet). 2. Replace the plastic lid and draw a contour line on top of the lid. 3. Remove the lid and add water up to the 2 cm line. Replace and draw your contour line. 4. Repeat step 3 in 1 cm intervals until the volcano is submerged. 5. When your contour lin ...
... line. (For this model, 1cm is equal to 100 feet). 2. Replace the plastic lid and draw a contour line on top of the lid. 3. Remove the lid and add water up to the 2 cm line. Replace and draw your contour line. 4. Repeat step 3 in 1 cm intervals until the volcano is submerged. 5. When your contour lin ...
Science Curriculum Map
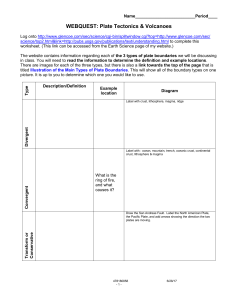
... Six Weeks: __4th and 5th__Time Frame: 4 Weeks TEKS: 8.9 Earth and space. The student knows that natural events can impact Earth systems. The student is expected to: (A) describe the historical development of evidence that supports plate tectonic theory; (B) relate plate tectonics to the formation of ...
... Six Weeks: __4th and 5th__Time Frame: 4 Weeks TEKS: 8.9 Earth and space. The student knows that natural events can impact Earth systems. The student is expected to: (A) describe the historical development of evidence that supports plate tectonic theory; (B) relate plate tectonics to the formation of ...
Chapter 1 Geography, History, and the
... People move around to different places throughout the world because their resources (raw materials) are spread unevenly around the world. Resources are things that we get from the Earth to help us survive, such as trees, water and fish. People need these resources to build their houses and survive. ...
... People move around to different places throughout the world because their resources (raw materials) are spread unevenly around the world. Resources are things that we get from the Earth to help us survive, such as trees, water and fish. People need these resources to build their houses and survive. ...
Geography Handbook Notes
... The student will examine the five themes of geography, explore how they aid geographic observation and analysis, and identify some ways in which the geography of the United States has affected its development. ...
... The student will examine the five themes of geography, explore how they aid geographic observation and analysis, and identify some ways in which the geography of the United States has affected its development. ...
Answers
... (9) A qualitative earthquake scale based on human experience rather than quantitative seismograph measurements is called ...
... (9) A qualitative earthquake scale based on human experience rather than quantitative seismograph measurements is called ...
Internet Webquest
... science/top2.html&link=http://pubs.usgs.gov/publications/text/understanding.html to complete this worksheet. (This link can be accessed from the Earth Science page of my website.) ...
... science/top2.html&link=http://pubs.usgs.gov/publications/text/understanding.html to complete this worksheet. (This link can be accessed from the Earth Science page of my website.) ...
3. Buckingham Quadrangle
... The Virginia landscape is quite diverse in its topography. Our field trips have revealed the influences of geology, climate, and time on the evolution of a landscape. The purpose of this laboratory is to examine topographic maps from the various physiographic provinces of the state and to access the ...
... The Virginia landscape is quite diverse in its topography. Our field trips have revealed the influences of geology, climate, and time on the evolution of a landscape. The purpose of this laboratory is to examine topographic maps from the various physiographic provinces of the state and to access the ...
Unit One Geography: It`s Nature and Perspectives
... – BUT, people have the means/resources to work around these limitations and adjust their environments. ...
... – BUT, people have the means/resources to work around these limitations and adjust their environments. ...
Cartography

Cartography (from Greek χάρτης khartēs, ""map""; and γράφειν graphein, ""write"") is the study and practice of making maps. Combining science, aesthetics, and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality can be modeled in ways that communicate spatial information effectively.The fundamental problems of traditional cartography are to:Set the map's agenda and select traits of the object to be mapped. This is the concern of map editing. Traits may be physical, such as roads or land masses, or may be abstract, such as toponyms or political boundaries.Represent the terrain of the mapped object on flat media. This is the concern of map projections.Eliminate characteristics of the mapped object that are not relevant to the map's purpose. This is the concern of generalization.Reduce the complexity of the characteristics that will be mapped. This is also the concern of generalization.Orchestrate the elements of the map to best convey its message to its audience. This is the concern of map design.Modern cartography is largely integrated with geographic information science (GIScience) and constitutes many theoretical and practical foundations of geographic information systems.