Time, what is it? Dynamical Properties of Time
... Here T ′ = 2 π ω′ is the period of motion of the particle in the frame K′ , t 0′ is an arbitrary instant of time. Determine now the time interval ∆ t in the reference frame K , which corresponds to the half of the period of motion of the particle in the view of the K′ -observer: T ′ +t ′ ...
... Here T ′ = 2 π ω′ is the period of motion of the particle in the frame K′ , t 0′ is an arbitrary instant of time. Determine now the time interval ∆ t in the reference frame K , which corresponds to the half of the period of motion of the particle in the view of the K′ -observer: T ′ +t ′ ...
Vector WS
... 6. An airplane is flying 340 km/hr at 12o East of North. The wind is blowing 40 km/hr at 34o South of East. What is the plane’s actual velocity? 7. You are on an elevator that is plummeting toward the ground at 30.0 m/s and you jump up right before it hits the ground. You jump upward with a velocity ...
... 6. An airplane is flying 340 km/hr at 12o East of North. The wind is blowing 40 km/hr at 34o South of East. What is the plane’s actual velocity? 7. You are on an elevator that is plummeting toward the ground at 30.0 m/s and you jump up right before it hits the ground. You jump upward with a velocity ...
5.3 Friction on level surface
... What is the minimum force of friction between the table and the 150 N block required to hold both blocks in equilibrium? What would the coefficient of static friction between the 150 N block and the table have to be to ensure that both blocks would be held in equilibrium? ...
... What is the minimum force of friction between the table and the 150 N block required to hold both blocks in equilibrium? What would the coefficient of static friction between the 150 N block and the table have to be to ensure that both blocks would be held in equilibrium? ...
newton`s third law of motion—action and reaction
... If we extend the basic idea of a cannon recoiling from the cannonball it launches, we can understand rocket propulsion. Consider air escaping from an untied, blown-up balloon. If the balloon is released and allowed to move as shown in Figure 7.8, it accelerates as the air comes out. A rocket accele ...
... If we extend the basic idea of a cannon recoiling from the cannonball it launches, we can understand rocket propulsion. Consider air escaping from an untied, blown-up balloon. If the balloon is released and allowed to move as shown in Figure 7.8, it accelerates as the air comes out. A rocket accele ...
Dynamics: Newton`s Laws of Motion
... -trap during a soccer match. The ball has a mass of 1.0 kg and Pablo’s face has a mass of 3.0 kg. If the ball strikes Pablo traveling at 20 m/s to the right and leaves traveling at 10 m/s to the left, what is the force on the ball if the collision lasts 0.15s? What is the force on Pablo’s face? ...
... -trap during a soccer match. The ball has a mass of 1.0 kg and Pablo’s face has a mass of 3.0 kg. If the ball strikes Pablo traveling at 20 m/s to the right and leaves traveling at 10 m/s to the left, what is the force on the ball if the collision lasts 0.15s? What is the force on Pablo’s face? ...
MODEL QUESTION PAPER
... 2.9k; and F3 = 8.3i – 6.6j + 5.8k, which are concurrent at the point (2, 2, -5.). The forces are in newtons and the distances are in metres. 2. A force F = (6N)i – (3Nj – (4N)k is acting at a point P whose position vector from the origin ‘O’ of the coordinate axes is (8mm)i + (6mm)j – (4mm)k. Find t ...
... 2.9k; and F3 = 8.3i – 6.6j + 5.8k, which are concurrent at the point (2, 2, -5.). The forces are in newtons and the distances are in metres. 2. A force F = (6N)i – (3Nj – (4N)k is acting at a point P whose position vector from the origin ‘O’ of the coordinate axes is (8mm)i + (6mm)j – (4mm)k. Find t ...
Circular Motion
... but aligned with the radial direction. That’s because we want to determine the component of any force or forces that may act as a centripetal force. We are ignoring friction so the only two forces to consider are the weight mg and the normal force FN . As can be seen only the normal force has an inw ...
... but aligned with the radial direction. That’s because we want to determine the component of any force or forces that may act as a centripetal force. We are ignoring friction so the only two forces to consider are the weight mg and the normal force FN . As can be seen only the normal force has an inw ...
VCE Physics
... Current; ampere [A] It is that current which produces a _____________ of 2 x 10-7 N between two parallel wires which are ______ metre apart in a vacuum. ...
... Current; ampere [A] It is that current which produces a _____________ of 2 x 10-7 N between two parallel wires which are ______ metre apart in a vacuum. ...
Ch 6 ppt
... • Force Pairs Do Not Act on the Same Object A force is always exerted by one object on another object. This rule is true for all forces, including action and reaction forces. • Action and reaction forces in a pair do not act on the same object. If they did, the net force would always be 0 N and noth ...
... • Force Pairs Do Not Act on the Same Object A force is always exerted by one object on another object. This rule is true for all forces, including action and reaction forces. • Action and reaction forces in a pair do not act on the same object. If they did, the net force would always be 0 N and noth ...
FE ANS
... 2.1 a) The gravitational force on an object is its weight. The electromagnetic force that the object exerts on a nearby charged object is zero for the following reason. Each electrically charged particle which goes to make up the object does exert a force on the nearby charge. This force is either r ...
... 2.1 a) The gravitational force on an object is its weight. The electromagnetic force that the object exerts on a nearby charged object is zero for the following reason. Each electrically charged particle which goes to make up the object does exert a force on the nearby charge. This force is either r ...
Eiffel Tower: Internal Forces
... between the ground and ladder base, or if the base was on wheels, the ladder would slide away from the wall. ...
... between the ground and ladder base, or if the base was on wheels, the ladder would slide away from the wall. ...
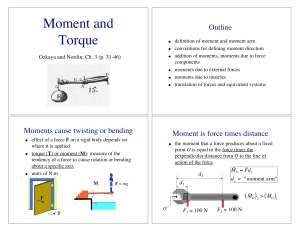
Rotational dynamics
... T is the Torque associated with force F, measured in Newton metres (Nm). ...
... T is the Torque associated with force F, measured in Newton metres (Nm). ...