Forces - Cloudfront.net
... move with a constant velocity. Since velocity is a vector, this means the speed (how fast) and the direction remain unchanged. Example: Take a look at a hockey game. When the puck (small black projectile) is hit, the puck travels at nearly the same speed and in a straight line across the ice. All re ...
... move with a constant velocity. Since velocity is a vector, this means the speed (how fast) and the direction remain unchanged. Example: Take a look at a hockey game. When the puck (small black projectile) is hit, the puck travels at nearly the same speed and in a straight line across the ice. All re ...
Momentum and Impulse
... Newton’s Second Law can be used to relate the momentum of an object to the resultant force acting on it ...
... Newton’s Second Law can be used to relate the momentum of an object to the resultant force acting on it ...
Chpt 4 Quiz Powerpoint
... A very large truck sits on a frozen lake. Assume there is no friction between the tires and the ice. A fly suddenly smashes against the front window. What will happen to the truck? ...
... A very large truck sits on a frozen lake. Assume there is no friction between the tires and the ice. A fly suddenly smashes against the front window. What will happen to the truck? ...
Concept review
... A very large truck sits on a frozen lake. Assume there is no friction between the tires and the ice. A fly suddenly smashes against the front window. What will happen to the truck? ...
... A very large truck sits on a frozen lake. Assume there is no friction between the tires and the ice. A fly suddenly smashes against the front window. What will happen to the truck? ...
AP Clicker Forces
... A very large truck sits on a frozen lake. Assume there is no friction between the tires and the ice. A fly suddenly smashes against the front window. What will happen to the truck? ...
... A very large truck sits on a frozen lake. Assume there is no friction between the tires and the ice. A fly suddenly smashes against the front window. What will happen to the truck? ...
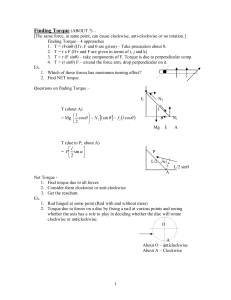
Torque and Motion Relationships
... What is the COM and why is it important? • What is COM (or COG) and why is it important? – It simplifies mechanical analysis of a complicated system – It is the point at which all of the mass of the system may be considered to be located – It is the only point that represents movement of the total ...
... What is the COM and why is it important? • What is COM (or COG) and why is it important? – It simplifies mechanical analysis of a complicated system – It is the point at which all of the mass of the system may be considered to be located – It is the only point that represents movement of the total ...
Honors Physics I - Neshaminy School District
... State Standard 3.2.P.B1: Differentiate among translational motion, simple harmonic motion, and rotational motion in terms of position, velocity, and acceleration. Use force and mass to explain translational motion or simple harmonic motion of ...
... State Standard 3.2.P.B1: Differentiate among translational motion, simple harmonic motion, and rotational motion in terms of position, velocity, and acceleration. Use force and mass to explain translational motion or simple harmonic motion of ...
berncatcaptions1
... C on the chain is replaced by two weightless strings tangent to the curve at A and at C, with a weight equal to the missing chain hanging at their intersection point, then the force at A will be the same as it was in the original whole catenary, and the force at C will be the same as it was in the o ...
... C on the chain is replaced by two weightless strings tangent to the curve at A and at C, with a weight equal to the missing chain hanging at their intersection point, then the force at A will be the same as it was in the original whole catenary, and the force at C will be the same as it was in the o ...
Kinetic Energy and Work
... masses) can be thought of as having two components: kinetic and potential – Kinetic energy is energy of motion – Potential energy is energy of position ...
... masses) can be thought of as having two components: kinetic and potential – Kinetic energy is energy of motion – Potential energy is energy of position ...
04 Newtons Second Law
... facilitate your analysis of data, plot a graph of force vs. acceleration. 3. If the relationship between force and acceleration appears to be linear, fit a straight line to your data. If possible, print a copy of your data table and graph. 4. Write the equation that represents the relationship betwe ...
... facilitate your analysis of data, plot a graph of force vs. acceleration. 3. If the relationship between force and acceleration appears to be linear, fit a straight line to your data. If possible, print a copy of your data table and graph. 4. Write the equation that represents the relationship betwe ...
Physics 11 Assignmen.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 2. We claim that momentum is conserved. Yet most moving objects eventually slow down and stop. Explain. Momentum is conserved if no outside forces are acting on an object. In our everyday experiences outside forces such as friction and air resistance are present to oppose the motion of most moving o ...
... 2. We claim that momentum is conserved. Yet most moving objects eventually slow down and stop. Explain. Momentum is conserved if no outside forces are acting on an object. In our everyday experiences outside forces such as friction and air resistance are present to oppose the motion of most moving o ...
Summary Chapter 05 Newton`s Laws of Motion
... same way with the generating force), if the body moved before, is added or subtracted from the former motion, according as they directly conspire with or are directly contrary to each other; or obliquely joined, when they are oblique, so as to produce a new motion compounded from the determination o ...
... same way with the generating force), if the body moved before, is added or subtracted from the former motion, according as they directly conspire with or are directly contrary to each other; or obliquely joined, when they are oblique, so as to produce a new motion compounded from the determination o ...
Kinematics
... and acceleration vs. time. What the above device shows is that, when looking at a graph of x vs. t, the velocity at some time is found by looking at the slope of the graph at that point. For instance, if I want to know the velocity of an object at t = 5 s, I would determine the slope of the displace ...
... and acceleration vs. time. What the above device shows is that, when looking at a graph of x vs. t, the velocity at some time is found by looking at the slope of the graph at that point. For instance, if I want to know the velocity of an object at t = 5 s, I would determine the slope of the displace ...
Section Check
... , tells you that if you double the force, you will double the same object’s acceleration. If you apply the same force to several different objects, the one with the most mass will have the smallest acceleration and the one with the least mass will have the greatest acceleration. One unit of force ca ...
... , tells you that if you double the force, you will double the same object’s acceleration. If you apply the same force to several different objects, the one with the most mass will have the smallest acceleration and the one with the least mass will have the greatest acceleration. One unit of force ca ...