What is force?
... • Any passenger not wearing a safety belt continues to move forward at the same speed the car was traveling. • Within about 0.02 s (1/50 of a second) after the car stops, unbelted passengers slam into the dashboard, steering wheel, windshield, or the backs of the front seats. ...
... • Any passenger not wearing a safety belt continues to move forward at the same speed the car was traveling. • Within about 0.02 s (1/50 of a second) after the car stops, unbelted passengers slam into the dashboard, steering wheel, windshield, or the backs of the front seats. ...
Do now
... Acceleration is defined as change of velocity over time. Acceleration is caused by net force. ...
... Acceleration is defined as change of velocity over time. Acceleration is caused by net force. ...
Document
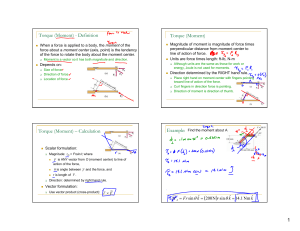
... Where gravity is concerned this point is always through the center of gravity. For muscular force, this point is assumed to be the muscle’s attachment to a bony lever. The point of intersection of the line of force and the mechanical axis of the ...
... Where gravity is concerned this point is always through the center of gravity. For muscular force, this point is assumed to be the muscle’s attachment to a bony lever. The point of intersection of the line of force and the mechanical axis of the ...
Simple harmonic motion
... A TRAMPOLINE exerts a restoring force on the jumper that is directly proportional to the average force required to displace the mat. Such restoring forces provide the driving forces necessary for objects that oscillate with simple harmonic motion. ...
... A TRAMPOLINE exerts a restoring force on the jumper that is directly proportional to the average force required to displace the mat. Such restoring forces provide the driving forces necessary for objects that oscillate with simple harmonic motion. ...
Solutions to Mechanics Problems
... Choosing this option suggests that the candidate realises that the ball has some momentum when released, but that it dissipates as it falls under gravity. It may be, if it has not been stressed initially that air resistance can be ignored, that the candidate has the correct understanding, but assume ...
... Choosing this option suggests that the candidate realises that the ball has some momentum when released, but that it dissipates as it falls under gravity. It may be, if it has not been stressed initially that air resistance can be ignored, that the candidate has the correct understanding, but assume ...
香港考試局
... A small object P of mass 0.5 kg is attached to one end of a light, rigid rod of length 0.7 m, which is free to rotate about the other end O as shown. The object is swung to rotate in a vertical circle so that it attains an angular speed of 6 rad s-1 at its topmost position. What is the force exerted ...
... A small object P of mass 0.5 kg is attached to one end of a light, rigid rod of length 0.7 m, which is free to rotate about the other end O as shown. The object is swung to rotate in a vertical circle so that it attains an angular speed of 6 rad s-1 at its topmost position. What is the force exerted ...
Physics 2nd Six Week Review
... 14. A truck enters the freeway at a velocity of 5.5 m/s and increases its velocity to 14.6 m/s in a time span of 35 seconds. Calculate the acceleration of the truck. 15. A runner starts from rest and accelerates at a constant rate of .58 m/s2 for a distance of 25 meters. What was the runners’ final ...
... 14. A truck enters the freeway at a velocity of 5.5 m/s and increases its velocity to 14.6 m/s in a time span of 35 seconds. Calculate the acceleration of the truck. 15. A runner starts from rest and accelerates at a constant rate of .58 m/s2 for a distance of 25 meters. What was the runners’ final ...
B-field hw3 ANS
... Increase the area of the coil within the magnetic field. Increase the current. ...
... Increase the area of the coil within the magnetic field. Increase the current. ...
Document
... 2. How does fluid displacement relate to buoyant force? 3. What determines if an object sinks or floats? 4.3 The buoyant force acts on objects in fluids. Fluids exert an upward force on objects. Gravity acts on objects in water as it does on ground. Buoyant force - the upward force a fluid exe ...
... 2. How does fluid displacement relate to buoyant force? 3. What determines if an object sinks or floats? 4.3 The buoyant force acts on objects in fluids. Fluids exert an upward force on objects. Gravity acts on objects in water as it does on ground. Buoyant force - the upward force a fluid exe ...
Newton`s 1st Law of Motion
... 8. An object at rest will stay at rest unless an unbalanced force acts on it. An object in motion will move at constant velocity unless an unbalanced force acts on it. 9. If an object has a constant velocity, then no unbalanced forces are pushing on it. 10. A force on an object tends to change it ve ...
... 8. An object at rest will stay at rest unless an unbalanced force acts on it. An object in motion will move at constant velocity unless an unbalanced force acts on it. 9. If an object has a constant velocity, then no unbalanced forces are pushing on it. 10. A force on an object tends to change it ve ...