Chapter 3 Golden Ticket
... 1. The rate at which velocity changes with time; the change may be in magnitude or direction or both. 2. The property of things to resist changes in motion. 3. The quantity of matter in an object. More specifically, it is the measure of the inertia or sluggishness that an object exhibits in response ...
... 1. The rate at which velocity changes with time; the change may be in magnitude or direction or both. 2. The property of things to resist changes in motion. 3. The quantity of matter in an object. More specifically, it is the measure of the inertia or sluggishness that an object exhibits in response ...
Document
... According to Newton’s Third Law, the force of your hand on the table is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the force of the table on your hand. The total force of the table acting on your hand, , is called the contact force. This force has both a normal component to the surface, , calle ...
... According to Newton’s Third Law, the force of your hand on the table is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the force of the table on your hand. The total force of the table acting on your hand, , is called the contact force. This force has both a normal component to the surface, , calle ...
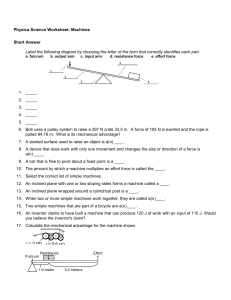
Physica Science Worksheet: Machines Short Answer Label the
... 6. Bob uses a pulley system to raise a 297 N crate 33.5 m. A force of 105 N is exerted and the rope is pulled 94.76 m. What is its mechanical advantage? 7. A slanted surface used to raise an object is a(n) ____. 8. A device that does work with only one movement and changes the size or direction of a ...
... 6. Bob uses a pulley system to raise a 297 N crate 33.5 m. A force of 105 N is exerted and the rope is pulled 94.76 m. What is its mechanical advantage? 7. A slanted surface used to raise an object is a(n) ____. 8. A device that does work with only one movement and changes the size or direction of a ...
Force Diagrams
... Explanation of Support or Normal Force You sit on your chair – and your weight, due to the force of gravity pushes you downward onto the chair, while the chair supports your weight. Support forces are pretty clever – they appear only when they are needed, and only in as much amount as needed. If the ...
... Explanation of Support or Normal Force You sit on your chair – and your weight, due to the force of gravity pushes you downward onto the chair, while the chair supports your weight. Support forces are pretty clever – they appear only when they are needed, and only in as much amount as needed. If the ...
NewtonPart2 - University of Colorado Boulder
... an illusion! There is no outward force on the person. Our intuition is failing us. Our intuition about forces was developed over a lifetime of experiences in inertial (non-accelerating) reference frames. If we are suddenly placed in an accelerating reference frame, our brains (wrongly) interpret our ...
... an illusion! There is no outward force on the person. Our intuition is failing us. Our intuition about forces was developed over a lifetime of experiences in inertial (non-accelerating) reference frames. If we are suddenly placed in an accelerating reference frame, our brains (wrongly) interpret our ...
Chapter 12 Notes
... Gravity is the weakest universal force, but it is the most effective over long distances. Earth’s gravitational force keeps the moon in a nearly circular orbit. The gravitational pull of the moon on the Earth causes ocean tides. ...
... Gravity is the weakest universal force, but it is the most effective over long distances. Earth’s gravitational force keeps the moon in a nearly circular orbit. The gravitational pull of the moon on the Earth causes ocean tides. ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... object continues in a state of rest, or of motion in a straight line at a constant speed, unless it is compelled to change that state by forces exerted upon it. aka the Law of Inertia An object at rest stays at rest; an object in motion stays ...
... object continues in a state of rest, or of motion in a straight line at a constant speed, unless it is compelled to change that state by forces exerted upon it. aka the Law of Inertia An object at rest stays at rest; an object in motion stays ...
L9 - University of Iowa Physics
... some point the block moves this occurs when the push P exceeds the maximum static friction force. • When the block is moving it experiences a smaller friction force called the kinetic friction force • It is a common experience that it takes more force to get something moving than to keep it moving ...
... some point the block moves this occurs when the push P exceeds the maximum static friction force. • When the block is moving it experiences a smaller friction force called the kinetic friction force • It is a common experience that it takes more force to get something moving than to keep it moving ...
Normal Reaction force
... Question 4 Solution Emma is correct and Frank is incorrect. The book is at rest, so, the resultant force on the book is zero. As a result N and mg are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction. N and mg both act on the book and therefore cannot be action and reaction in the sense of Newton's 3 rd ...
... Question 4 Solution Emma is correct and Frank is incorrect. The book is at rest, so, the resultant force on the book is zero. As a result N and mg are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction. N and mg both act on the book and therefore cannot be action and reaction in the sense of Newton's 3 rd ...
Midterm I Solutions ρ
... 7. A ball is thrown horizontally from the top of a 15 m high cliff. If the initial speed of the ball is 10 m/s, what is the speed of the ball when it hits the ground? 10 m/s A) 10 m/s B) 15 m/s 15 m C) 19.8 m/s D) 29.8 m/s E) none of the above The easiest way to get the answer is by conservation of ...
... 7. A ball is thrown horizontally from the top of a 15 m high cliff. If the initial speed of the ball is 10 m/s, what is the speed of the ball when it hits the ground? 10 m/s A) 10 m/s B) 15 m/s 15 m C) 19.8 m/s D) 29.8 m/s E) none of the above The easiest way to get the answer is by conservation of ...
Chapter 6 Study Guide: Newton`s 3rd Law of Motion – Action
... 8. Nellie Newton holds an apple in her hand. If action is Earth pulling on the apple, then reaction is _____. a. her hand providing a normal force on the apple b. her hand pushing up on the apple c. both (a) and (b) d. neither (a) nor (b) 9. As a ball falls, the action force is the pull of Earth’s m ...
... 8. Nellie Newton holds an apple in her hand. If action is Earth pulling on the apple, then reaction is _____. a. her hand providing a normal force on the apple b. her hand pushing up on the apple c. both (a) and (b) d. neither (a) nor (b) 9. As a ball falls, the action force is the pull of Earth’s m ...