* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Fluid dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Density of states wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
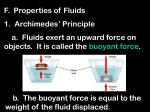
Ch. 4.1 Density is mass per unit of volume. Objects have mass and volume. mass – measure of amount of matter an object contains (units: g, kg) volume - measure of amount of space an object takes up (units: cm3, ml) Rectangular solid: length x width x height (l x w x h) Irregular shaped solid: water displacement, difference between original volume and volume after object placed into container Density is mass divided by volume. density - a measure of the amount of matter present in a given volume of a substance depends on both the mass and the volume of an object density does not change based on the amount of the object present Calculating Density Density = mass volume D=m v Sinking vs. floating Water has a density of 1.0 g/ml (1.0 g/cm3) Something that floats in water, density is less than 1.0 g/ml Something that sinks in water, density is more than 1.0 g/ml 4.3 EQs 1. What is buoyant force? 2. How does fluid displacement relate to buoyant force? 3. What determines if an object sinks or floats? 4.3 The buoyant force acts on objects in fluids. Fluids exert an upward force on objects. Gravity acts on objects in water as it does on ground. Buoyant force - the upward force a fluid exerts on any object in the fluid It acts against the downward force of gravity. Buoyancy exists because of pressure differences in fluids acts on all objects in a fluid, but floats only if buoyant force is greater than the weight of object Buoyancy in gases Like water, gases are fluids and exert buoyant forces The size of the buoyant force equals the weight of the displaced fluid. Archimedes’ Principle buoyant force is equal to the weight of the displaced water Floating and Sinking Buoyant force = force of gravity: neither rise nor sink Buoyant force > force of gravity: object floats Buoyant force < force of gravity: object sinks Something floats when… Density of the object is less than density of liquid Buoyant force = object’s weight Buoyant force is greater than force of gravity Volume of displaced water is = to volume of the portion of the object that is submerged