Friction ppt - Cobb Learning
... Why do sports shoes have more tread on them compared to dress shoes? Because more tread leads to more bumps, which leads to more friction. Athletic shoes need more friction to allow for greater acceleration (rapid sprints, sudden stops, and quick turns), whereas dress shoes do not require the same ...
... Why do sports shoes have more tread on them compared to dress shoes? Because more tread leads to more bumps, which leads to more friction. Athletic shoes need more friction to allow for greater acceleration (rapid sprints, sudden stops, and quick turns), whereas dress shoes do not require the same ...
Circular Motion - Effingham County Schools
... outside. Your inertia resists acceleration. You are not flung out, your body simply wants to keep moving in straight line motion! ...
... outside. Your inertia resists acceleration. You are not flung out, your body simply wants to keep moving in straight line motion! ...
Weeks_4
... believed in “the simplicity and harmonious unity of the universe” (quote page 323 David Burton) I. Each planet moves around the sun in an ellipse, with the sun at one focus. II. The radius vector from the sun to the planet sweeps out equal areas in equal intervals of time. III. The squares of the pe ...
... believed in “the simplicity and harmonious unity of the universe” (quote page 323 David Burton) I. Each planet moves around the sun in an ellipse, with the sun at one focus. II. The radius vector from the sun to the planet sweeps out equal areas in equal intervals of time. III. The squares of the pe ...
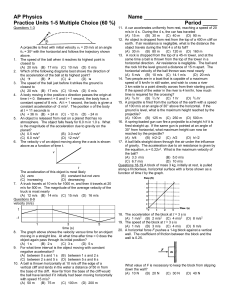
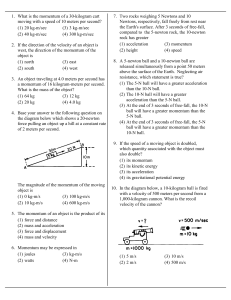
AP Physics
... earth. If air resistance is negligible, what is the distance the object travels during the first 4 s of its fall? (A) 30 m (B) 80 m (C) 120 m (D) 160 m 13. A rock is dropped from the top of a 45-m tower, and at the same time a ball is thrown from the top of the tower in a horizontal direction. Air r ...
... earth. If air resistance is negligible, what is the distance the object travels during the first 4 s of its fall? (A) 30 m (B) 80 m (C) 120 m (D) 160 m 13. A rock is dropped from the top of a 45-m tower, and at the same time a ball is thrown from the top of the tower in a horizontal direction. Air r ...
Lesson 1 - Fair Lawn Schools
... object applies a force on another, the second object applies an equal force in the opposite direction on the first object. • The forces of a force pair do not cancel because they act on different objects. • According to the law of conservation of momentum, momentum is conserved during a collision un ...
... object applies a force on another, the second object applies an equal force in the opposite direction on the first object. • The forces of a force pair do not cancel because they act on different objects. • According to the law of conservation of momentum, momentum is conserved during a collision un ...
Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... you push on a cart, the faster it goes. Is the cart’s velocity related to the force you apply? Or, is the force related to something else? Also, what does the mass of the cart have to do with how the motion changes? We know that it takes a much harder push to get a heavy cart moving than a lighter o ...
... you push on a cart, the faster it goes. Is the cart’s velocity related to the force you apply? Or, is the force related to something else? Also, what does the mass of the cart have to do with how the motion changes? We know that it takes a much harder push to get a heavy cart moving than a lighter o ...
Document
... Any two objects exert gravitational forces on each other, equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. ...
... Any two objects exert gravitational forces on each other, equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. ...
Serway_PSE_quick_ch05
... With twice the force, the object will experience twice the acceleration. Because the force is constant, the acceleration is constant, and the speed of the object (starting from rest) is given by v = at. With twice the acceleration, the object will arrive at speed v at half the time. ...
... With twice the force, the object will experience twice the acceleration. Because the force is constant, the acceleration is constant, and the speed of the object (starting from rest) is given by v = at. With twice the acceleration, the object will arrive at speed v at half the time. ...
香港考試局
... (e) A light spring of force constant 8 N m-1 is fixed vertically below the descending pan as shown in Figure 2.2. A light plate is attached to the upper end of the spring. The descending pan comes into contact with the plate when the two pans are at the same level. The motion of the system becomes s ...
... (e) A light spring of force constant 8 N m-1 is fixed vertically below the descending pan as shown in Figure 2.2. A light plate is attached to the upper end of the spring. The descending pan comes into contact with the plate when the two pans are at the same level. The motion of the system becomes s ...
RevfinQans
... Answer: The tension is zero. By the same v v2 v1 argument as in the question above, one can show that the acceleration is straight down when the mass on the extreme right with the string horizontal. Since the acceleration is straight down, the net force must be straight down, so there can be no ...
... Answer: The tension is zero. By the same v v2 v1 argument as in the question above, one can show that the acceleration is straight down when the mass on the extreme right with the string horizontal. Since the acceleration is straight down, the net force must be straight down, so there can be no ...
I will read the background information about Newton`s Second Law
... cart, the faster it goes. Is the cart’s velocity related to the force you apply? Or does the force just change the velocity? Also, what does the mass of the cart have to do with how the motion changes? We know that it takes a much harder push to get a heavy cart moving than a lighter one. A force se ...
... cart, the faster it goes. Is the cart’s velocity related to the force you apply? Or does the force just change the velocity? Also, what does the mass of the cart have to do with how the motion changes? We know that it takes a much harder push to get a heavy cart moving than a lighter one. A force se ...
Chapter 7 Impulse and Momentum
... Chapter 7 is about the COLLISION of two masses. Both masses are needed to understand their interaction. Newton's 3rd Law plays a very important part. Collisions involve two new concepts: Impulse and Momentum. Impulse concept leads to the Momentum definition. Also applied to two (or more) masses blow ...
... Chapter 7 is about the COLLISION of two masses. Both masses are needed to understand their interaction. Newton's 3rd Law plays a very important part. Collisions involve two new concepts: Impulse and Momentum. Impulse concept leads to the Momentum definition. Also applied to two (or more) masses blow ...