Chapter 4 Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion continued
... of your body parts, mostly at a point of contact. If your body is not stretched or compressed, you will feel like you are floating. Gravity ALONE will not stretch or compress your body. Hanging from the board, the board also pulls up on your arms. Newton’s 3rd law! Standing on the ground, the ground ...
... of your body parts, mostly at a point of contact. If your body is not stretched or compressed, you will feel like you are floating. Gravity ALONE will not stretch or compress your body. Hanging from the board, the board also pulls up on your arms. Newton’s 3rd law! Standing on the ground, the ground ...
Investigation 1
... The following question looks again at linear motion with a constant acceleration but in the downward direction. (Refer to Questions 6 and 7.) The question in the last column is difficult only because the ball changes direction. In order to figure out the answers remember that the upward motion is s ...
... The following question looks again at linear motion with a constant acceleration but in the downward direction. (Refer to Questions 6 and 7.) The question in the last column is difficult only because the ball changes direction. In order to figure out the answers remember that the upward motion is s ...
13-5 Energy Conservation in Oscillatory Motion As a function of time
... 13-2 Simple Harmonic Motion If we call the period of the motion T – this is the time to complete one full cycle – we can write the position as a function of time: ...
... 13-2 Simple Harmonic Motion If we call the period of the motion T – this is the time to complete one full cycle – we can write the position as a function of time: ...
PowerPoint
... Two analysis models using Newton’s Laws of Motion have been developed. The models have been applied to linear motion. Newton’s Laws can be applied to other situations: Objects traveling in circular paths Motion observed from an accelerating frame of reference Motion of an object through a visc ...
... Two analysis models using Newton’s Laws of Motion have been developed. The models have been applied to linear motion. Newton’s Laws can be applied to other situations: Objects traveling in circular paths Motion observed from an accelerating frame of reference Motion of an object through a visc ...
KEY
... 5. If a watermelon thrown off a diving board has the same momentum when hitting the water as one that hits the concrete deck why does the melon burst open on the deck but not on the water? What does this have to do with time? It took longer for the momentum to change in the water. The longer the tim ...
... 5. If a watermelon thrown off a diving board has the same momentum when hitting the water as one that hits the concrete deck why does the melon burst open on the deck but not on the water? What does this have to do with time? It took longer for the momentum to change in the water. The longer the tim ...
Newton`s Second Law
... • According to the second law of motion, when a ball has centripetal acceleration, the direction of the net force on the ball also must be toward the center of the curved path. • The net force exerted toward the center of a curved path is called a centripetal force. ...
... • According to the second law of motion, when a ball has centripetal acceleration, the direction of the net force on the ball also must be toward the center of the curved path. • The net force exerted toward the center of a curved path is called a centripetal force. ...
Part I
... • Circumference = Distance Around= 2πr Speed: v = (2πr/T) = 2πrf Centripetal Acceleration: ...
... • Circumference = Distance Around= 2πr Speed: v = (2πr/T) = 2πrf Centripetal Acceleration: ...
Newton`s second law of motion
... • According to the second law of motion, when a ball has centripetal acceleration, the direction of the net force on the ball also must be toward the center of the curved path. • The net force exerted toward the center of a curved path is called a centripetal force. ...
... • According to the second law of motion, when a ball has centripetal acceleration, the direction of the net force on the ball also must be toward the center of the curved path. • The net force exerted toward the center of a curved path is called a centripetal force. ...
motion in two dimension
... Motion in More Than One Dimension It is an intriguing result that the motion of a particle in one direction does not affect the motion in any perpendicular direction. The classic example is if you shoot a gun level to the ground and drop a bullet at the same time, they hit the ground at the same if ...
... Motion in More Than One Dimension It is an intriguing result that the motion of a particle in one direction does not affect the motion in any perpendicular direction. The classic example is if you shoot a gun level to the ground and drop a bullet at the same time, they hit the ground at the same if ...
Forces and Newton`s Laws
... For example: The acceleration due to gravity The acceleration on the baseball due to the bat The acceleration of car due to friction! When you exert a push or a pull on an object, you say, you are exerting a force on that object. A force cannot be seen, it is only known by its effects on an obje ...
... For example: The acceleration due to gravity The acceleration on the baseball due to the bat The acceleration of car due to friction! When you exert a push or a pull on an object, you say, you are exerting a force on that object. A force cannot be seen, it is only known by its effects on an obje ...
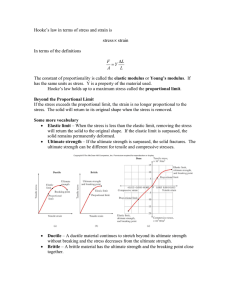
Work - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... 1. What is the impulse given to a golf ball of mass 45.9g if it starts at rest and attains a final velocity of 35m/s? 2. If the golf ball in problem 1 was in contact with the golf club for 0.027s, what force acted on the golf ball? 3. If there is no acceleration is there momentum? Is there impulse? ...
... 1. What is the impulse given to a golf ball of mass 45.9g if it starts at rest and attains a final velocity of 35m/s? 2. If the golf ball in problem 1 was in contact with the golf club for 0.027s, what force acted on the golf ball? 3. If there is no acceleration is there momentum? Is there impulse? ...