National Diploma in Engineering Mechanical Principles for
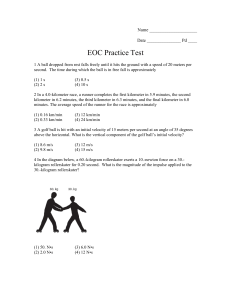
... A block of mass 60kg is pulled up an incline the angle of which is 35° from the horizontal. (See figure 1). There is an opposing friction force of 50 N. If the linear distance from A to B is 12 metres calculate: a) The force required to move the block at a constant velocity, b) The work done moving ...
... A block of mass 60kg is pulled up an incline the angle of which is 35° from the horizontal. (See figure 1). There is an opposing friction force of 50 N. If the linear distance from A to B is 12 metres calculate: a) The force required to move the block at a constant velocity, b) The work done moving ...
ENERGY - Katy Independent School District
... • Other forces, such as friction, convert the work done on an object into heat. • Heat is a form of energy, but not one we can ever use again. Thus some say that the energy is “lost”. • You push a block across a rough floor. Once it stops moving, it does not return on its own to the starting point. ...
... • Other forces, such as friction, convert the work done on an object into heat. • Heat is a form of energy, but not one we can ever use again. Thus some say that the energy is “lost”. • You push a block across a rough floor. Once it stops moving, it does not return on its own to the starting point. ...
Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... the force just change the velocity? Also, what does the mass of the cart have to do with how the motion changes? We know that it takes a much harder push to get a heavy cart moving than a lighter one. A Force Sensor and an Accelerometer will let you measure the force on a cart simultaneously with th ...
... the force just change the velocity? Also, what does the mass of the cart have to do with how the motion changes? We know that it takes a much harder push to get a heavy cart moving than a lighter one. A Force Sensor and an Accelerometer will let you measure the force on a cart simultaneously with th ...
Newtonian Mechanics
... electric and magnetic, and nuclear. All observed forces (e.g., contact, friction, a spring, atomic forces, etc.) are produced in some way by those basic forces. Whatever force is acting in a system, (27) states how that force influences the motion of a mass m (in classical mechanics!). The mass in ( ...
... electric and magnetic, and nuclear. All observed forces (e.g., contact, friction, a spring, atomic forces, etc.) are produced in some way by those basic forces. Whatever force is acting in a system, (27) states how that force influences the motion of a mass m (in classical mechanics!). The mass in ( ...
FORCE What is force?
... 1. There are two bodies, which each has a mass of 2 kg and 5 kg respectively. The two bodies are at the same place. If acceleration due to gravity in that place is 9.8 m/s2, determine the weight of each body. 2. An Astronaut has a weight of 490 N on the earth. If on the moon acceleration due to grav ...
... 1. There are two bodies, which each has a mass of 2 kg and 5 kg respectively. The two bodies are at the same place. If acceleration due to gravity in that place is 9.8 m/s2, determine the weight of each body. 2. An Astronaut has a weight of 490 N on the earth. If on the moon acceleration due to grav ...
Chapter 10
... Every particle on the disc undergoes circular motion about the origin, O Polar coordinates are convenient to use to represent the position of P (or any other point) P is located at (r, q) where r is the distance from the origin to P and q is the measured counterclockwise from the reference line ...
... Every particle on the disc undergoes circular motion about the origin, O Polar coordinates are convenient to use to represent the position of P (or any other point) P is located at (r, q) where r is the distance from the origin to P and q is the measured counterclockwise from the reference line ...
Milestones Master Study 2017
... Weight - a measure of the gravitational force exerted on an object: An object’s weight can change depending on where in the universe it is. A. The SI unit for weight is the Newton (N) Inertia - the tendency of an object to resist being moved or, if the object is moving, to resist a change in speed o ...
... Weight - a measure of the gravitational force exerted on an object: An object’s weight can change depending on where in the universe it is. A. The SI unit for weight is the Newton (N) Inertia - the tendency of an object to resist being moved or, if the object is moving, to resist a change in speed o ...
Lesson 1: Newton`s First Law of Motion
... Newton's Second Law of Motion Newton's Second Law Newton's first law of motion predicts the behavior of objects for which all existing forces are balanced. Objects at equilibrium (the condition in which all forces balance) will not accelerate. According to Newton, an object will only accelerate if t ...
... Newton's Second Law of Motion Newton's Second Law Newton's first law of motion predicts the behavior of objects for which all existing forces are balanced. Objects at equilibrium (the condition in which all forces balance) will not accelerate. According to Newton, an object will only accelerate if t ...
Terminal Velocity Powerpoint
... The speed an object can travel at through a fluid will vary depending upon the drag of the fluid – if the drag is high then this will affect the resultant force so that the terminal velocity of the object is low. If the drag is reduced then the resultant force will increase, allowing for an increase ...
... The speed an object can travel at through a fluid will vary depending upon the drag of the fluid – if the drag is high then this will affect the resultant force so that the terminal velocity of the object is low. If the drag is reduced then the resultant force will increase, allowing for an increase ...
Practice Exam
... (1) stronger and repulsive (2) weaker and repulsive (3) stronger and attractive (4) weaker and attractive 28 A balloon is rubbed against a student’s hair and then touched to a wall. The balloon “sticks” to the wall due to (1) electrostatic forces between the particles of the balloon (2) magnetic fo ...
... (1) stronger and repulsive (2) weaker and repulsive (3) stronger and attractive (4) weaker and attractive 28 A balloon is rubbed against a student’s hair and then touched to a wall. The balloon “sticks” to the wall due to (1) electrostatic forces between the particles of the balloon (2) magnetic fo ...
Work, Energy, and Power
... multiplying 2 numbers. A scalaron the formula. In this case it means that is a quantity with NO F and x MUST be parallel. To ensure that ...
... multiplying 2 numbers. A scalaron the formula. In this case it means that is a quantity with NO F and x MUST be parallel. To ensure that ...
Work, Energy, and Power
... multiplying 2 numbers. A scalaron the formula. In this case it means that is a quantity with NO F and x MUST be parallel. To ensure that ...
... multiplying 2 numbers. A scalaron the formula. In this case it means that is a quantity with NO F and x MUST be parallel. To ensure that ...
Slide 1
... • Rotation – all points on the wheel move with the same angular speed ω • Translation – all point on the wheel move with the ...
... • Rotation – all points on the wheel move with the same angular speed ω • Translation – all point on the wheel move with the ...
K-1 Speed©! “Feel the Physics!”
... At the starting line of a race you are at rest, therefore you tend to stay at rest. But when you get the green light, you accelerate as fast as you can go, and feel as though you are ...
... At the starting line of a race you are at rest, therefore you tend to stay at rest. But when you get the green light, you accelerate as fast as you can go, and feel as though you are ...
PPT
... string. If the string breaks at the instant shown, which path will the ball follow? Physics 101: Lecture 8, Pg 2 ...
... string. If the string breaks at the instant shown, which path will the ball follow? Physics 101: Lecture 8, Pg 2 ...
Chapter 9
... momentum when they are ejected out of the engine, the rocket receives a compensating momentum in the opposite direction Therefore, the rocket is accelerated as a result of the “push” from the exhaust gases In free space, the center of mass of the system (rocket plus expelled gases) moves uniformly, ...
... momentum when they are ejected out of the engine, the rocket receives a compensating momentum in the opposite direction Therefore, the rocket is accelerated as a result of the “push” from the exhaust gases In free space, the center of mass of the system (rocket plus expelled gases) moves uniformly, ...