Forces and Gravity (Part 1)
... Resultant forces – question 2 2. What is the resultant force on the bird? The forces acting in each direction horizontally are equal in size, so there is no resultant force in this direction. Resultant force = 5 N – 5 N = 0 N 5 N The vertical forces are not balanced, the bird will accelerate in a d ...
... Resultant forces – question 2 2. What is the resultant force on the bird? The forces acting in each direction horizontally are equal in size, so there is no resultant force in this direction. Resultant force = 5 N – 5 N = 0 N 5 N The vertical forces are not balanced, the bird will accelerate in a d ...
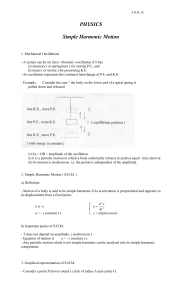
Physics - Harmonic Motion
... amplitude is the maximum displacement value. On the graph, one cycle is the segment of the curve from in phase point to the next sequential in phase point. In phase points? These are points along the displacement path where the object is doing the same thing. • No better way to understand the thing ...
... amplitude is the maximum displacement value. On the graph, one cycle is the segment of the curve from in phase point to the next sequential in phase point. In phase points? These are points along the displacement path where the object is doing the same thing. • No better way to understand the thing ...
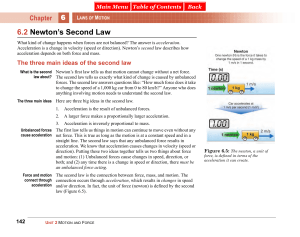
Applying Newton second law to horizontal motion
... 26. An airboat with mass 4.50 102 kg, including passengers, has an engine that produces a net horizontal force of 8.14 102 N, after accounting for forces of resistance. (a) Find the acceleration of the airboat. (b) Starting from rest, how long does it take the airboat to reach a speed of 16.0 m/s? ...
... 26. An airboat with mass 4.50 102 kg, including passengers, has an engine that produces a net horizontal force of 8.14 102 N, after accounting for forces of resistance. (a) Find the acceleration of the airboat. (b) Starting from rest, how long does it take the airboat to reach a speed of 16.0 m/s? ...
Physics v. 2016
... Physics Algebra-Based First Year Physics Course. The main goal of this course is to provide students with a clear and logical presentation of the principles of physics. They will engage in the methods used by physicists to explain and predict the fundamental functions of the physical world both desc ...
... Physics Algebra-Based First Year Physics Course. The main goal of this course is to provide students with a clear and logical presentation of the principles of physics. They will engage in the methods used by physicists to explain and predict the fundamental functions of the physical world both desc ...
Uniform Circular Motion
... identical diameter and speed but one object has twice the mass of the other. The force required to keep the more massive object on the circular path is A. the same as B. one fourth of Answer: D.The mass is directly C. half of proportional to centripetal force. D. twice ...
... identical diameter and speed but one object has twice the mass of the other. The force required to keep the more massive object on the circular path is A. the same as B. one fourth of Answer: D.The mass is directly C. half of proportional to centripetal force. D. twice ...
No Slide Title
... Example of a non-conservative force: friction f We shall calculate the work the work done by friction as it moves the cup along a closed path that starts at point A and ends at point A. During the trip we apply a force F = -f so that the net force on the cup, and thus its acceleration a is zero ...
... Example of a non-conservative force: friction f We shall calculate the work the work done by friction as it moves the cup along a closed path that starts at point A and ends at point A. During the trip we apply a force F = -f so that the net force on the cup, and thus its acceleration a is zero ...
PHYSICS
... (i) A percussive musical instrument (e.g. a drum) gives out a note whose intensity decreases with time. (slightly damped oscillations due to air resistance) (ii) The paper cone of a loud speaker vibrates, but is heavily damped so as to lose energy (as sound wave energy) to the surrounding air. d) Ot ...
... (i) A percussive musical instrument (e.g. a drum) gives out a note whose intensity decreases with time. (slightly damped oscillations due to air resistance) (ii) The paper cone of a loud speaker vibrates, but is heavily damped so as to lose energy (as sound wave energy) to the surrounding air. d) Ot ...
Document
... Consider a falling firecracker that explodes into two pieces. The momenta of the fragments combine by vector rules to equal the original momentum of the falling firecracker. ...
... Consider a falling firecracker that explodes into two pieces. The momenta of the fragments combine by vector rules to equal the original momentum of the falling firecracker. ...
A force is a push or pull on an object. In this lesson, you will be
... A force is a push or pull on an object. In this lesson, you will be learning about gravitational force. Gravity is the force of attraction between the masses of two objects. Have you ever heard the saying, What goes up must come down? On Earth, gravity helps keep our atmosphere from drifting off int ...
... A force is a push or pull on an object. In this lesson, you will be learning about gravitational force. Gravity is the force of attraction between the masses of two objects. Have you ever heard the saying, What goes up must come down? On Earth, gravity helps keep our atmosphere from drifting off int ...
ISNS4371_011107_bw - The University of Texas at Dallas
... - experienced moment of inspiration at 24 years old - saw apple fall from tree and suddenly understood gravity - published most famous book in science in 1687 - Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica - Principia for short ...
... - experienced moment of inspiration at 24 years old - saw apple fall from tree and suddenly understood gravity - published most famous book in science in 1687 - Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica - Principia for short ...
Newton`s Second Law of Motion (Chap. 4)
... Speed of falling objects increases until drag force balances weight. When forces balance, zero acceleration so constant velocity. Speed for which air resistance balances weight called terminal speed. High terminal speed (better open the chute!) ...
... Speed of falling objects increases until drag force balances weight. When forces balance, zero acceleration so constant velocity. Speed for which air resistance balances weight called terminal speed. High terminal speed (better open the chute!) ...
Chapter 2: Kinematics in One Dimension
... Even though the force of gravity between less massive objects is, it would be noticeable if it were the only force around. However, on Earth the gravity of Earth overpowers these other gravities, not to mention the fact that the gravity between you & other objects are pulling in all sorts of directi ...
... Even though the force of gravity between less massive objects is, it would be noticeable if it were the only force around. However, on Earth the gravity of Earth overpowers these other gravities, not to mention the fact that the gravity between you & other objects are pulling in all sorts of directi ...
Document
... WB by force FB , and WC by force FC . Then determine Wnet WA WB WC Method 2: Calculate first Fnet FA FB FC ; Then determine Wnet F d ...
... WB by force FB , and WC by force FC . Then determine Wnet WA WB WC Method 2: Calculate first Fnet FA FB FC ; Then determine Wnet F d ...