Motion Relative to a non-inertial frame
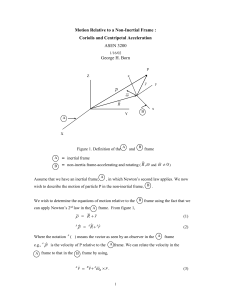
... In Eq. (19), we have moved the centripetal and Coriolis accelerations to the force side of the equation. In this situation they are referred to as the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass. Hence, the signs of the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass are opposite t ...
... In Eq. (19), we have moved the centripetal and Coriolis accelerations to the force side of the equation. In this situation they are referred to as the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass. Hence, the signs of the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass are opposite t ...
Motion - leitl
... As the vehicles are travelling at constant speed, a = 0 and thus ΣF = 0 Thus driving force = total retarding force Thus driving Force = 800 N Q: What is the value of the tension, T, in the towbar? Looking at the car alone the forces acting are the tension in the towbar and the retarding force. Since ...
... As the vehicles are travelling at constant speed, a = 0 and thus ΣF = 0 Thus driving force = total retarding force Thus driving Force = 800 N Q: What is the value of the tension, T, in the towbar? Looking at the car alone the forces acting are the tension in the towbar and the retarding force. Since ...
1999 Question 2 solution
... Newton's law of universal gravitation Gravity is a force that exists throughout the Universe. It makes things fall down when you drop them, it keeps satellites in the orbits, it leads to tides on Earth, it causes stars and black holes to form and it will ultimately determine the fate of the Universe ...
... Newton's law of universal gravitation Gravity is a force that exists throughout the Universe. It makes things fall down when you drop them, it keeps satellites in the orbits, it leads to tides on Earth, it causes stars and black holes to form and it will ultimately determine the fate of the Universe ...
Newton`s Laws and Momentum - science
... If you want to accelerate the resultant force must act in the direction you are travelling. And if you want to decelerate the resultant force must act in the opposite direction that you are travelling in. If you want to change direction there must me a resultant force at right angles to the directio ...
... If you want to accelerate the resultant force must act in the direction you are travelling. And if you want to decelerate the resultant force must act in the opposite direction that you are travelling in. If you want to change direction there must me a resultant force at right angles to the directio ...
PPTX - University of Toronto Physics
... Kinetic friction does oppose the relative motion of two surfaces. If the one of these surfaces is stationary, then it will tend to slow down the moving object. Can friction ever speed things up? ANSWER: Yes! Static friction between your feet and the floor is what allows you to walk! Walking certainl ...
... Kinetic friction does oppose the relative motion of two surfaces. If the one of these surfaces is stationary, then it will tend to slow down the moving object. Can friction ever speed things up? ANSWER: Yes! Static friction between your feet and the floor is what allows you to walk! Walking certainl ...
Momentum and Collisions
... In order to change the momentum of an object, a force must be applied (from Newton’s first law). The rate of change of momentum of an object is proportional to the resultant force acting on the object. This is an alternative way of stating Newton’s second law in terms of momentum. In a tennis match, ...
... In order to change the momentum of an object, a force must be applied (from Newton’s first law). The rate of change of momentum of an object is proportional to the resultant force acting on the object. This is an alternative way of stating Newton’s second law in terms of momentum. In a tennis match, ...
Momentum
... • Ask 3 questions & write down unknown terms • Reread passages that are unclear • Relate back to your questions & teacher questions after each passage ...
... • Ask 3 questions & write down unknown terms • Reread passages that are unclear • Relate back to your questions & teacher questions after each passage ...
F g - mrbernabo
... An object will only change its Rotational speed if a Net Torque is applied. No net Torque = keeps rotating at the same speed ...
... An object will only change its Rotational speed if a Net Torque is applied. No net Torque = keeps rotating at the same speed ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Chapter 3 Kinematics in 2d
... The question was: “What happens when you jump inside a rotating cylinder like the one on the movie 2001: A Space Odysey” Contrary to the answer given, you do not float to the other side and hit your head. The simulated gravity does not require continuous contact with the surface. From your perspecti ...
... The question was: “What happens when you jump inside a rotating cylinder like the one on the movie 2001: A Space Odysey” Contrary to the answer given, you do not float to the other side and hit your head. The simulated gravity does not require continuous contact with the surface. From your perspecti ...























