Chapter 10 Forces
... Section 2: Friction, Gravity, and Elastic Forces Standard 8.2.b Students know when an object is subject to two or more forces at once, the result is the cumulative effect of all the forces. Standard 8.2.d Students know how to identify separately the two or more forces that are acting on a single sta ...
... Section 2: Friction, Gravity, and Elastic Forces Standard 8.2.b Students know when an object is subject to two or more forces at once, the result is the cumulative effect of all the forces. Standard 8.2.d Students know how to identify separately the two or more forces that are acting on a single sta ...
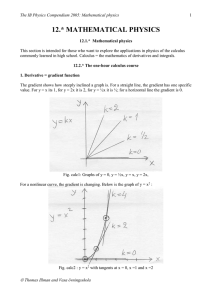
12. MATHEMATICAL PHYSICS
... true"!). In relativity we must change Newton's II law F = ma since m is not constant. We can use the momentum instead : F = ma = m(v-u) = mv - mu and then impulse = Ft = change in momentum = p = mv - mu which for an infinitely short time dt becomes: Fdt = dp and dividing with dt then: F = dp/dt (f ...
... true"!). In relativity we must change Newton's II law F = ma since m is not constant. We can use the momentum instead : F = ma = m(v-u) = mv - mu and then impulse = Ft = change in momentum = p = mv - mu which for an infinitely short time dt becomes: Fdt = dp and dividing with dt then: F = dp/dt (f ...
Work and Energy
... stop, but the plunger spring is not compressed. Measure the length of the plunger relative to the end cap of the Dynamics Cart. Record the plunger length x. (c) Completely compress the plunger spring on the cart and lock the spring in position. Launch the cart along the track and use the motion sens ...
... stop, but the plunger spring is not compressed. Measure the length of the plunger relative to the end cap of the Dynamics Cart. Record the plunger length x. (c) Completely compress the plunger spring on the cart and lock the spring in position. Launch the cart along the track and use the motion sens ...
Welcome to PHY 1151: Principles of Physics I
... each torque is determined by the type of angular acceleration it alone would produce. Dr. Jie Zou PHY 1151G Department of Physics ...
... each torque is determined by the type of angular acceleration it alone would produce. Dr. Jie Zou PHY 1151G Department of Physics ...
SCi.roller-coaster-project2
... using the mathematic expression KE = ½ m X v2 . The formula for finding PE is PE = mhg (mass x height x gravity) to see how much energy the object has so it could move if forced to. When the object rolls down a ramp, it’s PE converts to KE and KE to PE when it stops. It changes as the ball stops and ...
... using the mathematic expression KE = ½ m X v2 . The formula for finding PE is PE = mhg (mass x height x gravity) to see how much energy the object has so it could move if forced to. When the object rolls down a ramp, it’s PE converts to KE and KE to PE when it stops. It changes as the ball stops and ...
Period 3 Activity Sheet: Motion and Forces
... In activity 3.2 we found that the force of gravity causes the velocity of a cart to increase as it rolls down a ramp. We now calculate the rate of change in velocity (the acceleration) of the cart as it rolls down the ramp. 1) Use two blocks to support the wooden ramp. Hold the cart at rest at the t ...
... In activity 3.2 we found that the force of gravity causes the velocity of a cart to increase as it rolls down a ramp. We now calculate the rate of change in velocity (the acceleration) of the cart as it rolls down the ramp. 1) Use two blocks to support the wooden ramp. Hold the cart at rest at the t ...
Physics II - Magnetism - Ms. Gamm
... the maximum displacement value. On the graph, one cycle is the segment of the curve from in phase point to the next sequential in phase point. In phase points? Okay, okay already. These are points along the displacement path where the object is doing the same thing. No better way to understand the t ...
... the maximum displacement value. On the graph, one cycle is the segment of the curve from in phase point to the next sequential in phase point. In phase points? Okay, okay already. These are points along the displacement path where the object is doing the same thing. No better way to understand the t ...
Summary of the unit on force, motion, and energy
... track. Significantly, what we have done is to remove ways for the ball to interact with other things. The essential point being made is that a moving object slows down because something has interfered with it. Slowing down is not a property built into the object. We should search for the cause outsi ...
... track. Significantly, what we have done is to remove ways for the ball to interact with other things. The essential point being made is that a moving object slows down because something has interfered with it. Slowing down is not a property built into the object. We should search for the cause outsi ...
7-1 Work Done by a Constant Force The work done by a constant
... A pendulum bob is swinging back and forth in an arc in the plane of the page as seen below. The Tension force is 20 N, and the arc length is 5 m. The Work done by the Tension force in one quarter swing (up or down) is ...
... A pendulum bob is swinging back and forth in an arc in the plane of the page as seen below. The Tension force is 20 N, and the arc length is 5 m. The Work done by the Tension force in one quarter swing (up or down) is ...
Newton`s Second Law
... In this experiment a low friction air track will be used to test the validity of Newton’s Second Law. A hanging mass will be attached to a glider placed on the air track by means of a light (negligible mass) string. By varying the amount of mass that is hanging we will vary the net force acting on t ...
... In this experiment a low friction air track will be used to test the validity of Newton’s Second Law. A hanging mass will be attached to a glider placed on the air track by means of a light (negligible mass) string. By varying the amount of mass that is hanging we will vary the net force acting on t ...
Syllabus
... In terms of velocity with constant magnitude (only the direction of the velocity changes). Component of tangential acceleration in circular motion is not discussed. ...
... In terms of velocity with constant magnitude (only the direction of the velocity changes). Component of tangential acceleration in circular motion is not discussed. ...
Section 2 Forces, Energy and Power
... Assuming the frictional forces to be unchanged, calculate: (i) the new engine force (ii) the force exerted by the tow bar on the caravan. The car brakes and decelerates at 5·0 m s 2 . Calculate the force exerted by the brakes (assume the other frictional forces remain constant). ...
... Assuming the frictional forces to be unchanged, calculate: (i) the new engine force (ii) the force exerted by the tow bar on the caravan. The car brakes and decelerates at 5·0 m s 2 . Calculate the force exerted by the brakes (assume the other frictional forces remain constant). ...
Newton Stations Instructions
... • From standing still, suddenly walk quickly forward. • From standing still, suddenly walk quickly backwards. • Walk steadily forward, gently keeping the ball on the book with your other hand, then let go of the ball while walking steadily with the ball staying on the book. Then stop suddenly. ...
... • From standing still, suddenly walk quickly forward. • From standing still, suddenly walk quickly backwards. • Walk steadily forward, gently keeping the ball on the book with your other hand, then let go of the ball while walking steadily with the ball staying on the book. Then stop suddenly. ...
1999 Question 2 solution
... Newton's law of universal gravitation Gravity is a force that exists throughout the Universe. It makes things fall down when you drop them, it keeps satellites in the orbits, it leads to tides on Earth, it causes stars and black holes to form and it will ultimately determine the fate of the Universe ...
... Newton's law of universal gravitation Gravity is a force that exists throughout the Universe. It makes things fall down when you drop them, it keeps satellites in the orbits, it leads to tides on Earth, it causes stars and black holes to form and it will ultimately determine the fate of the Universe ...