the physics of car accidnets
... d = Braking Distance g = Acceleration due to gravity (9.80 m/sec2) V = Initial vehicle speed (m/sec) µ = Coefficient of friction between the tires and the roadway ...
... d = Braking Distance g = Acceleration due to gravity (9.80 m/sec2) V = Initial vehicle speed (m/sec) µ = Coefficient of friction between the tires and the roadway ...
Chapter 4 Motion and Forces Vocabulary
... Terminal velocity-The maximum velocity a falling object achieves. Law of universal gravitation -The law that states that the force of gravity acts between all objects in the universe. Momentum-The product of an object’s mass and velocity. Law of conservation of momentum-The rule that the total momen ...
... Terminal velocity-The maximum velocity a falling object achieves. Law of universal gravitation -The law that states that the force of gravity acts between all objects in the universe. Momentum-The product of an object’s mass and velocity. Law of conservation of momentum-The rule that the total momen ...
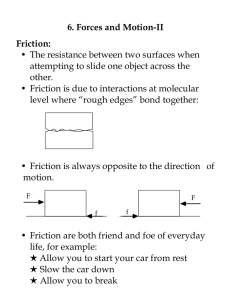
6. Forces and Motion-II Friction: • The resistance between two surfaces when
... A small coin is placed on a turntable making 3 revolutions in 3.14 s. (a) What are the speed and acceleration of the coin when it rides without slipping at 5.0 cm from the center of the turntable? (b) What is the magnitude of the friction force if the mass of the coin is 2.0 g? (c) What is the coeff ...
... A small coin is placed on a turntable making 3 revolutions in 3.14 s. (a) What are the speed and acceleration of the coin when it rides without slipping at 5.0 cm from the center of the turntable? (b) What is the magnitude of the friction force if the mass of the coin is 2.0 g? (c) What is the coeff ...
Are you a conservative or a non-conservative?
... in elevation is the top of the sledding hill than the base? (assume friction is negligible) Answer: 12.1m. ...
... in elevation is the top of the sledding hill than the base? (assume friction is negligible) Answer: 12.1m. ...
Friction Problems ACTIVITY 1: Cut out the problem and the steps
... 4. A child’s wagon of mass 20kg is rolling across the grass with initial speed of 10m/s. The force of friction slows it to a stop in 5s. What is the force of rolling friction between the wheels of the wagon and the grass? 5. Rather than taking the stairs, Martin gets from the second floor of his hou ...
... 4. A child’s wagon of mass 20kg is rolling across the grass with initial speed of 10m/s. The force of friction slows it to a stop in 5s. What is the force of rolling friction between the wheels of the wagon and the grass? 5. Rather than taking the stairs, Martin gets from the second floor of his hou ...
Friction
... are not in motion relative to each other (no slipping) Kinetic friction is the force exerted when the two objects are in motion relative to each other (slipping) Force of kinetic friction is fk = µk n. It depends on µk which depends on the materials and on the normal force n which is the force pushi ...
... are not in motion relative to each other (no slipping) Kinetic friction is the force exerted when the two objects are in motion relative to each other (slipping) Force of kinetic friction is fk = µk n. It depends on µk which depends on the materials and on the normal force n which is the force pushi ...
Lecture 2
... B.N.J. PERSSON, Sliding Friction, Springer (2000); J.KRIM, Surf. Sci. 500, 741 (2002) ...
... B.N.J. PERSSON, Sliding Friction, Springer (2000); J.KRIM, Surf. Sci. 500, 741 (2002) ...
∑ = F ma F ma ∑ = μ
... Exactly same problem as the object on a horizontal surface however the force pushing (or pulling) is at some angle and must be split into forces in the x-direction and y-direction. In these cases, we will call the retarding force, friction; assume the object is moving at a constant velocity; and con ...
... Exactly same problem as the object on a horizontal surface however the force pushing (or pulling) is at some angle and must be split into forces in the x-direction and y-direction. In these cases, we will call the retarding force, friction; assume the object is moving at a constant velocity; and con ...
What is a force that slows down motion between two surfaces that
... If gravity acts between all objects in the universe, why don’t we feel pulled to other objects the way that we are held on Earth? (Earth has a much larger mass than any objects around us) ...
... If gravity acts between all objects in the universe, why don’t we feel pulled to other objects the way that we are held on Earth? (Earth has a much larger mass than any objects around us) ...
Insert the title here
... • A 50.0 kg bucket is being lifted by a rope. The rope will not break if the tension is 525 N or less. The bucket started at rest, and after being lifted 3.0 m, it is moving at 3.0 m/s. If the acceleration is constant, if the rope in danger of breaking? ...
... • A 50.0 kg bucket is being lifted by a rope. The rope will not break if the tension is 525 N or less. The bucket started at rest, and after being lifted 3.0 m, it is moving at 3.0 m/s. If the acceleration is constant, if the rope in danger of breaking? ...
Chap. 8 Friction
... CHARACTERISTICS OF DRY FRICTION (Section 8.1) Friction is defined as a force of resistance acting on a body which prevents or retards slipping of the body relative to a second body. Experiments show that frictional forces act tangent (parallel) to the contacting surface in a direction opposing the ...
... CHARACTERISTICS OF DRY FRICTION (Section 8.1) Friction is defined as a force of resistance acting on a body which prevents or retards slipping of the body relative to a second body. Experiments show that frictional forces act tangent (parallel) to the contacting surface in a direction opposing the ...
Friction Factors - OUHSDPhysicsCollaboration
... We are constantly aware of the frictional force that opposes the motion of one surface in contact with another. When there is a sheet of ice on a sidewalk, friction is reduced, and it is difficult to walk. The lack of friction is an inconvenience. However, machines are lubricated to reduce friction ...
... We are constantly aware of the frictional force that opposes the motion of one surface in contact with another. When there is a sheet of ice on a sidewalk, friction is reduced, and it is difficult to walk. The lack of friction is an inconvenience. However, machines are lubricated to reduce friction ...
Friction and ramps notes
... even with twice the area of contact. For this to be true, it is essential that ALL other variables be rigidly controlled. ...
... even with twice the area of contact. For this to be true, it is essential that ALL other variables be rigidly controlled. ...
Forces
... size of the net force acting on the object and the mass of the object. So, the relationship between acceleration, net force, and mass can be defined as: ...
... size of the net force acting on the object and the mass of the object. So, the relationship between acceleration, net force, and mass can be defined as: ...
Lecture 8: Forces & The Laws of Motion
... a) the same direction as the truck’s acceleration b) opposite the direction of the truck’s acceleration c) the net force is zero ...
... a) the same direction as the truck’s acceleration b) opposite the direction of the truck’s acceleration c) the net force is zero ...