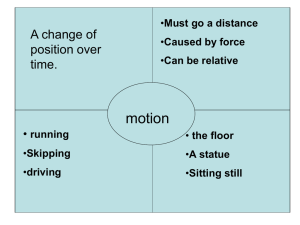
Study Guide - Chapter 5
... Friction - a force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are in contact 1. Friction can cause a moving object, such as a ball, to slow down and eventually stop 2. The amount of friction between two surfaces depends on two factors: A. The amount of force pushing the two surfaces together B. T ...
... Friction - a force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are in contact 1. Friction can cause a moving object, such as a ball, to slow down and eventually stop 2. The amount of friction between two surfaces depends on two factors: A. The amount of force pushing the two surfaces together B. T ...
Study Guide - Chapter 5
... Friction - a force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are in contact 1. Friction can cause a moving object, such as a ball, to slow down and eventually stop 2. The amount of friction between two surfaces depends on two factors: A. The amount of force pushing the two surfaces together B. T ...
... Friction - a force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are in contact 1. Friction can cause a moving object, such as a ball, to slow down and eventually stop 2. The amount of friction between two surfaces depends on two factors: A. The amount of force pushing the two surfaces together B. T ...
Friction
... • Friction is the force that opposes the motion between two surfaces that touch. • The surface of any object is rough. • Even an object that feels smooth is covered with tiny hills and valleys. • The contact between the hills of valleys of two surfaces causes them to stick, resulting in friction. ...
... • Friction is the force that opposes the motion between two surfaces that touch. • The surface of any object is rough. • Even an object that feels smooth is covered with tiny hills and valleys. • The contact between the hills of valleys of two surfaces causes them to stick, resulting in friction. ...
Friction - Prairie Science
... with each other. • Friction must be overcome before motion occurs. • Friction is caused by the uneven surfaces of the touching objects. As surfaces are pressed together, they tend to interlock and offer resistance to being moved over each other. ...
... with each other. • Friction must be overcome before motion occurs. • Friction is caused by the uneven surfaces of the touching objects. As surfaces are pressed together, they tend to interlock and offer resistance to being moved over each other. ...
static friction - University of Toronto Physics
... • A sled of mass 5.0 kg is pulled at a constant velocity by a rope which makes an angle of 20.0° above the horizontal. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the sled and the snow is 0.030. What is the tension in the rope? (Fpull in the diagram) ...
... • A sled of mass 5.0 kg is pulled at a constant velocity by a rope which makes an angle of 20.0° above the horizontal. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the sled and the snow is 0.030. What is the tension in the rope? (Fpull in the diagram) ...
A body acted on by no net force moves with constant velocity
... a) A crate of mass m is on the flat bed of a pick up truck. The coefficient of friction between the crate and the truck is m. The truck is traveling at the constant velocity of magnitude V1. Draw the free body diagram for the crate. b) The truck starts to accelerate with an acceleration ac. Draw the ...
... a) A crate of mass m is on the flat bed of a pick up truck. The coefficient of friction between the crate and the truck is m. The truck is traveling at the constant velocity of magnitude V1. Draw the free body diagram for the crate. b) The truck starts to accelerate with an acceleration ac. Draw the ...
LAB # 5 - Coefficient of static friction
... Friction is generally grouped in two classes; kinetic, in which the two surfaces are in relative motion and static, in which they are not. Empirically, it is often (but not invariably) found that the maximum static frictional force is directly proportional to the normal force of contact between the ...
... Friction is generally grouped in two classes; kinetic, in which the two surfaces are in relative motion and static, in which they are not. Empirically, it is often (but not invariably) found that the maximum static frictional force is directly proportional to the normal force of contact between the ...
Kinematics Multiples
... 3. A crate of mass 100 kg is at rest on a horizontal floor. The coefficient of static friction between the crate and the floor is 0.4, and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.3. A force F of magnitude 344 N is then applied to the crate, parallel to the floor. Which of the following is true? a. ...
... 3. A crate of mass 100 kg is at rest on a horizontal floor. The coefficient of static friction between the crate and the floor is 0.4, and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.3. A force F of magnitude 344 N is then applied to the crate, parallel to the floor. Which of the following is true? a. ...
lectureslides09
... in the string, (b) the acceleration of each object, and (c) the distance each object will move in the first second of motion if both objects start from rest. ...
... in the string, (b) the acceleration of each object, and (c) the distance each object will move in the first second of motion if both objects start from rest. ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... If an object weighs 1100 N but has a mass of 125 kg, which planet is it on? 1. Venus, g = 8.8 m/s2 2. Mars, g = 3.7 m/s2 3. Jupiter, g = 24.8 m/s2 ...
... If an object weighs 1100 N but has a mass of 125 kg, which planet is it on? 1. Venus, g = 8.8 m/s2 2. Mars, g = 3.7 m/s2 3. Jupiter, g = 24.8 m/s2 ...
Sliding Mass Problems
... Draw a force diagram and label the known information for each problem. Use your diagrams to write a valid equation for Newton’s Second Law and solve for the unknowns. You will need to use other equations (form Chapter 5) to solve. 1. A loaded snow sled is pulled by six huskies with a force of 1,250 ...
... Draw a force diagram and label the known information for each problem. Use your diagrams to write a valid equation for Newton’s Second Law and solve for the unknowns. You will need to use other equations (form Chapter 5) to solve. 1. A loaded snow sled is pulled by six huskies with a force of 1,250 ...
Speed up Slow down Change direction 2 m/s 2 Ball rolling down a
... •Obj. may or may not move •Affects acceleration •More mass need more force ...
... •Obj. may or may not move •Affects acceleration •More mass need more force ...
mr04Tsol
... Solutions to MR4T: Newton’s Laws II – Frictional Forces A. Qualitative Questions: 1. When you’re driving a car at constant speed all the petrol or gas you’re burning is being used just to overcome frictional forces, such as air resistance and friction in the drive train of the car. However friction ...
... Solutions to MR4T: Newton’s Laws II – Frictional Forces A. Qualitative Questions: 1. When you’re driving a car at constant speed all the petrol or gas you’re burning is being used just to overcome frictional forces, such as air resistance and friction in the drive train of the car. However friction ...
Lecture Notes for Assignments #1 and 2
... Fm > Fk and µs > µk. (When you try to push a stalled car off the road, it is hard to get the car push started; once the car begins to move, it is easier to continue to move the car.) Answer to Assignment #1: The friction force acting to oppose motion does not depend on the surface area of contact bu ...
... Fm > Fk and µs > µk. (When you try to push a stalled car off the road, it is hard to get the car push started; once the car begins to move, it is easier to continue to move the car.) Answer to Assignment #1: The friction force acting to oppose motion does not depend on the surface area of contact bu ...
f F = mg X
... • µs does not depend on the mass or surface area of the object • Has value: 0 < µs < 1.5 • If no applied vertical force ...
... • µs does not depend on the mass or surface area of the object • Has value: 0 < µs < 1.5 • If no applied vertical force ...
Chapter 6: Force and Motion II
... Between the sled and the plane, the coefficient of static friction is 0.25, and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.15. (a) What is the minimum magnitude of the force F, parallel to the plane that will prevent the sled from slipping down the plane? (b) What is the minimum magnitude F that will ...
... Between the sled and the plane, the coefficient of static friction is 0.25, and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.15. (a) What is the minimum magnitude of the force F, parallel to the plane that will prevent the sled from slipping down the plane? (b) What is the minimum magnitude F that will ...
Lecture 9 - West Virginia University
... If an objects is located on a surface at rest, at least two forces will act on it: (i) The gravitational force (downwards) and (ii) the normal force (upwards) exerted by the surface on the object to compensate gravitation. ...
... If an objects is located on a surface at rest, at least two forces will act on it: (i) The gravitational force (downwards) and (ii) the normal force (upwards) exerted by the surface on the object to compensate gravitation. ...