1. The velocity of an object is the
... A) speed B) acceleration C) speed and direction D) momentum and weight 2. The tendency of an object at rest to stay at rest and the tendency of an object in straight-line motion to continue moving is _____. A) motion B) friction C) inertia D) momentum ...
... A) speed B) acceleration C) speed and direction D) momentum and weight 2. The tendency of an object at rest to stay at rest and the tendency of an object in straight-line motion to continue moving is _____. A) motion B) friction C) inertia D) momentum ...
Document
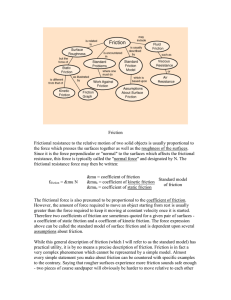
... proportional to the magnitude of the normal force between two surfaces, and does not depend on the total surface area of contact between the two surfaces. ...
... proportional to the magnitude of the normal force between two surfaces, and does not depend on the total surface area of contact between the two surfaces. ...
PHY440 - Assignment 2 - 25.9.13
... frictionless and take m1 = 2.00 kg, m2 = 6.00 kg, and = 55.0°. (a) Draw free-body diagrams of both objects. Find (b) the magnitude of the acceleration of the objects, (c) the tension in the string, and (d) the speed of each object 2.00 s after it is released from rest. ...
... frictionless and take m1 = 2.00 kg, m2 = 6.00 kg, and = 55.0°. (a) Draw free-body diagrams of both objects. Find (b) the magnitude of the acceleration of the objects, (c) the tension in the string, and (d) the speed of each object 2.00 s after it is released from rest. ...
Physics: The very basics
... G(y) = gravity, depending on height (constant if height doesn’t change dramatically) ...
... G(y) = gravity, depending on height (constant if height doesn’t change dramatically) ...
force - Cloudfront.net
... • Suppose you have filled a cardboard box with books and want to move it. • It’s too heavy to lift, so you start pushing on it, but it doesn’t ...
... • Suppose you have filled a cardboard box with books and want to move it. • It’s too heavy to lift, so you start pushing on it, but it doesn’t ...
Forces and The Laws of Motion
... • The acceleration is directly proportional to the net external force and inversely proportional to the object’s mass ...
... • The acceleration is directly proportional to the net external force and inversely proportional to the object’s mass ...
Problem Set #2a
... c. The guy in the middle has a weight, a normal force under each foot, and a friction force under each foot keeping his legs from sliding out (like Bambi on ice!). Finally he should have forces from each of the other two guys. d. The group as a whole should have 1 weight (all of their weights combi ...
... c. The guy in the middle has a weight, a normal force under each foot, and a friction force under each foot keeping his legs from sliding out (like Bambi on ice!). Finally he should have forces from each of the other two guys. d. The group as a whole should have 1 weight (all of their weights combi ...
Physics 11 Assignment #2
... 8. An Atwood machine consists of two masses (m1=3.8 kg) and (m2=4.2 kg). What is the acceleration of the masses? What is the tension in the rope? Note: you must derive the equation for tension using a free-body diagram to receive full credit. (2) ...
... 8. An Atwood machine consists of two masses (m1=3.8 kg) and (m2=4.2 kg). What is the acceleration of the masses? What is the tension in the rope? Note: you must derive the equation for tension using a free-body diagram to receive full credit. (2) ...
motion - SCHOOLinSITES
... action exerted on a body in order to change body’s state of rest or motion. has magnitude and direction. net force • combination of all forces acting on an object. balanced forces: Objects either do not move or move at constant velocity. unbalanced force any change in an object’s state of mo ...
... action exerted on a body in order to change body’s state of rest or motion. has magnitude and direction. net force • combination of all forces acting on an object. balanced forces: Objects either do not move or move at constant velocity. unbalanced force any change in an object’s state of mo ...
Chapter 4B. Friction and Equilibrium
... Heat can sometimes cause surfaces to become deformed or sticky. In such cases, temperature can be a factor. ...
... Heat can sometimes cause surfaces to become deformed or sticky. In such cases, temperature can be a factor. ...
L9.ppt - University of Iowa Physics
... Gravity pulls the block down the incline Friction acts to keep the block from sliding down • At some point as the angle if the plane is increased the block will start slipping • At this point, the friction force and gravity are equal • The block then slides down with constant velocity • For larger a ...
... Gravity pulls the block down the incline Friction acts to keep the block from sliding down • At some point as the angle if the plane is increased the block will start slipping • At this point, the friction force and gravity are equal • The block then slides down with constant velocity • For larger a ...
Newtons Laws Review Questions and Key
... ____ 1. The tendency of an object to resist change in its motion (not wanting to change its motion) is known as a. mass. b. inertia. c. force. ____2. A net force (an unbalanced force that changes motion) causes an object to a. stay at the same speed. b. not move. c. accelerate (speed up) or decelera ...
... ____ 1. The tendency of an object to resist change in its motion (not wanting to change its motion) is known as a. mass. b. inertia. c. force. ____2. A net force (an unbalanced force that changes motion) causes an object to a. stay at the same speed. b. not move. c. accelerate (speed up) or decelera ...
Document
... object at rest remains at rest, UNLESS acted upon by an EXTERNAL (unbalanced) Force. There are TWO conditions here and one constraint. Condition #1 – The object CAN move but must be at a CONSTANT SPEED Condition #2 – The object is at REST Constraint – As long as the forces are BALANCED!!!!! And if a ...
... object at rest remains at rest, UNLESS acted upon by an EXTERNAL (unbalanced) Force. There are TWO conditions here and one constraint. Condition #1 – The object CAN move but must be at a CONSTANT SPEED Condition #2 – The object is at REST Constraint – As long as the forces are BALANCED!!!!! And if a ...
Operational Manual
... wastesenergy. A motor bicyclecan run round a comer becauseof the friction betweenthe tyres andthe road surface,but its top speedis governedby the wind resistanceof the driver andvehicle. Friction is the outcomeof one surfaceslidingover another(sliding friction), or it may also be the maximumresistan ...
... wastesenergy. A motor bicyclecan run round a comer becauseof the friction betweenthe tyres andthe road surface,but its top speedis governedby the wind resistanceof the driver andvehicle. Friction is the outcomeof one surfaceslidingover another(sliding friction), or it may also be the maximumresistan ...
THINGSYOUNEEDTOKNOWFORCE
... Friction(Ff)- Force parallel to the surface of contact. Friction can be static or kinetic. (more below) ...
... Friction(Ff)- Force parallel to the surface of contact. Friction can be static or kinetic. (more below) ...
Chapter 7 Study Guide: Forces Focus on the highlighted terms and
... static friction-occurs between objects that aren’t moving. Ex:The friction between a box and the ground as you try to move it, but it does not move. Be able to recognize or give examples of the types of friction. Lesson 7.3: Newton’s Laws of Motion *Newton’s First Law of Motion: Objects at rest will ...
... static friction-occurs between objects that aren’t moving. Ex:The friction between a box and the ground as you try to move it, but it does not move. Be able to recognize or give examples of the types of friction. Lesson 7.3: Newton’s Laws of Motion *Newton’s First Law of Motion: Objects at rest will ...
Static Friction
... kinetic friction. Typical results for the woods I have used are 0.4 for the static coefficient and 0.3 for the kinetic coefficient. When carefully standardized surfaces are used to measure the friction coefficients, the difference between static and kinetic coefficients tends to disappear, indicatin ...
... kinetic friction. Typical results for the woods I have used are 0.4 for the static coefficient and 0.3 for the kinetic coefficient. When carefully standardized surfaces are used to measure the friction coefficients, the difference between static and kinetic coefficients tends to disappear, indicatin ...
Force and Motion Football Game
... • The blue car has a greater acceleration. It is changing its velocity at a more drastic rate. ...
... • The blue car has a greater acceleration. It is changing its velocity at a more drastic rate. ...