Newton`s Laws Online
... QUESTION: If both teams pull the tag with equal force, what would the net force be? Section 3: Newton’s Second Law State Newton’s Second Law and write the equation. QUESTION: How much net force is required to accelerate a 1000 kg car at 5.00 m/s2? QUESTION: If you apply a net force of 1 N on 200 g-b ...
... QUESTION: If both teams pull the tag with equal force, what would the net force be? Section 3: Newton’s Second Law State Newton’s Second Law and write the equation. QUESTION: How much net force is required to accelerate a 1000 kg car at 5.00 m/s2? QUESTION: If you apply a net force of 1 N on 200 g-b ...
Lab 4: Friction
... surface. The coefficient of friction again depends on the nature of the materials in contact, and varies from material to material. The coefficients of friction are determined experimentally, and are listed in tables by material. Also, the values of µs and µk are always less than 1. In this experim ...
... surface. The coefficient of friction again depends on the nature of the materials in contact, and varies from material to material. The coefficients of friction are determined experimentally, and are listed in tables by material. Also, the values of µs and µk are always less than 1. In this experim ...
Forces and Motion
... Static friction acts on unmoving objects. The word static describes a fixed or stationary object. Once the force is greater than static friction it is no longer applied. Secondly, sliding friction. It occurs between two objects sliding past each other, it also slows things down. This is when bumps o ...
... Static friction acts on unmoving objects. The word static describes a fixed or stationary object. Once the force is greater than static friction it is no longer applied. Secondly, sliding friction. It occurs between two objects sliding past each other, it also slows things down. This is when bumps o ...
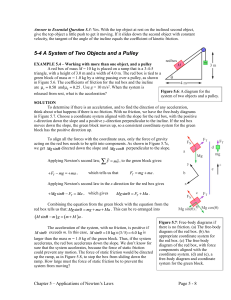
5-4 A System of Two Objects and a Pulley
... To determine if there is an acceleration, and to find the direction of any acceleration, think about what happens if there is no friction. With no friction, we have the free-body diagrams in Figure 5.7. Choose a coordinate system aligned with the slope for the red box, with the positive x-direction ...
... To determine if there is an acceleration, and to find the direction of any acceleration, think about what happens if there is no friction. With no friction, we have the free-body diagrams in Figure 5.7. Choose a coordinate system aligned with the slope for the red box, with the positive x-direction ...
Student Worksheet () - TI Education
... Friction is a force that opposes motion when two surfaces are in contact with one another. Friction depends on the texture of both surfaces. It is also dependent on the force that pushes the two surfaces together. This force is called the normal force. The friction force that exists between two surf ...
... Friction is a force that opposes motion when two surfaces are in contact with one another. Friction depends on the texture of both surfaces. It is also dependent on the force that pushes the two surfaces together. This force is called the normal force. The friction force that exists between two surf ...
Physics I - Rose
... information on textbooks, but does give the weight of a one-pound object. Place a pound weight in one hand and the textbook on the other. The sensation on your hand is the weight of the object. The sensation from the textbook is about five times the sensation from the pound weight. So we conclude th ...
... information on textbooks, but does give the weight of a one-pound object. Place a pound weight in one hand and the textbook on the other. The sensation on your hand is the weight of the object. The sensation from the textbook is about five times the sensation from the pound weight. So we conclude th ...
What are Forces?
... We rely on friction in many ways. An athlete usually wears shoes which provide him or her with a greater friction between the shoe and the surface. We rely on friction as an important aspect of our motion. In what other ways does friction play a role in our everyday lives? ...
... We rely on friction in many ways. An athlete usually wears shoes which provide him or her with a greater friction between the shoe and the surface. We rely on friction as an important aspect of our motion. In what other ways does friction play a role in our everyday lives? ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... • Because of Earth’s gravitational pull and their own inertia, projectiles follow a curved path due to horizontal and vertical velocities. When you release a ball, the ball moves downward because of gravity, but the horizontal speed remains the same. http://phet.colorado.edu/en/s imulation/projectil ...
... • Because of Earth’s gravitational pull and their own inertia, projectiles follow a curved path due to horizontal and vertical velocities. When you release a ball, the ball moves downward because of gravity, but the horizontal speed remains the same. http://phet.colorado.edu/en/s imulation/projectil ...
Name_______________ Per_____ IB/AP Physics I – Forces Group
... shows the directions of the four forces. Find the resulting motion of the boy if F1=50N, F2=100N, F3=150N, and F4=60N. (a) Make an estimate of the net force by adding the four vectors in the drawing. (b) Find the net force precisely by using the method of components, then find the acceleration of th ...
... shows the directions of the four forces. Find the resulting motion of the boy if F1=50N, F2=100N, F3=150N, and F4=60N. (a) Make an estimate of the net force by adding the four vectors in the drawing. (b) Find the net force precisely by using the method of components, then find the acceleration of th ...
Finding the coefficient of friction used in a simulation
... shown in the properties tab as 0.64 kg, the net force on the object is 0.64 Kg * 6/3.2 = 1.2 Newtons. You will also not that the properties tab lists the coefficient of kinetic friction used. We are trying to test that value with these results. Don’t use it. If you note in my simulation that the ma ...
... shown in the properties tab as 0.64 kg, the net force on the object is 0.64 Kg * 6/3.2 = 1.2 Newtons. You will also not that the properties tab lists the coefficient of kinetic friction used. We are trying to test that value with these results. Don’t use it. If you note in my simulation that the ma ...
s - Nuffield Foundation
... constant acceleration equations In the following problems you will need to combine the friction model with Newton’s Second Law and the constant acceleration equations. 6 A car of mass 1 tonne is travelling along a straight horizontal road at 15 ms–1 when it brakes sharply then skids. Friction brings ...
... constant acceleration equations In the following problems you will need to combine the friction model with Newton’s Second Law and the constant acceleration equations. 6 A car of mass 1 tonne is travelling along a straight horizontal road at 15 ms–1 when it brakes sharply then skids. Friction brings ...