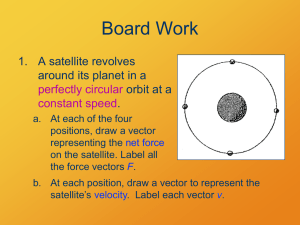
Name: Sect:______ Date
... 3. Describe the difference between a balanced and unbalance force. Balanced forces are equal but in opposite directions so there is no motion as a result, while unbalanced forces are unequal which cause an object to move. 4. When an object resists a change in it motion, this is called____inertia____ ...
... 3. Describe the difference between a balanced and unbalance force. Balanced forces are equal but in opposite directions so there is no motion as a result, while unbalanced forces are unequal which cause an object to move. 4. When an object resists a change in it motion, this is called____inertia____ ...
Circular Motion Problems
... A 515kg roller coaster is at the bottom of a loop with a radius of 10m. If the speed at the bottom of the loop is 20m/s, what is the force of the track pushing up on the vehicle at this point? 25,750 N ...
... A 515kg roller coaster is at the bottom of a loop with a radius of 10m. If the speed at the bottom of the loop is 20m/s, what is the force of the track pushing up on the vehicle at this point? 25,750 N ...
LECTURE 19: Universal Law of Gravitation
... WARM UP: What direction is the static friction pointing in if a car is going around a banked turn at the minimum speed possible? ...
... WARM UP: What direction is the static friction pointing in if a car is going around a banked turn at the minimum speed possible? ...
Chapter 13: universal gravitation
... Kepler's first law: planets are orbiting the sun in a path described as an ellipse, where the sun is at one focus of the ellipse. Kepler's second law: The radius vector sweeps equal areas in equal times for a planet in motion around the sun. ...
... Kepler's first law: planets are orbiting the sun in a path described as an ellipse, where the sun is at one focus of the ellipse. Kepler's second law: The radius vector sweeps equal areas in equal times for a planet in motion around the sun. ...
Gravity, Air Resistence, Terminal Velocity, and Projectile Motion
... Describe and explain what is meant by terminal velocity. Describe and explain how forces change on a falling object. ...
... Describe and explain what is meant by terminal velocity. Describe and explain how forces change on a falling object. ...
Projectile Motion
... any object that is launched with an initial velocity and continues to move; affected only by the force of gravity. Trajectory: the path a projectile follows. Usually parabolic Range: horizontal distance covered by a projectile Height: the maximum vertical distance reached by a projectile ...
... any object that is launched with an initial velocity and continues to move; affected only by the force of gravity. Trajectory: the path a projectile follows. Usually parabolic Range: horizontal distance covered by a projectile Height: the maximum vertical distance reached by a projectile ...
Artificial gravity

Artificial gravity is the theoretical increase or decrease of apparent gravity (g-force) by artificial means, particularly in space, but also on Earth. It can be practically achieved by the use of different forces, particularly the centripetal force and linear acceleration.The creation of artificial gravity is considered desirable for long-term space travel or habitation, for ease of mobility, for in-space fluid management, and to avoid the adverse long-term health effects of weightlessness.A number of methods for generating artificial gravity have been proposed, as well as an even larger number of science fiction approaches using both real and fictitious forces. Practical outer space applications of artificial gravity for humans have not yet been built and flown, principally due to the large size of the spacecraft required to produce centripetal acceleration.