Glossary of Terms Handout
... Specific Impulse -- A measurement of a rocket's relative performance. Expressed in seconds, the number of which a rocket can produce one pound of thrust from one pound of fuel. The higher the specific impulse, the less fuel required to produce a given amount of thrust. Spectrum -- A range of frequen ...
... Specific Impulse -- A measurement of a rocket's relative performance. Expressed in seconds, the number of which a rocket can produce one pound of thrust from one pound of fuel. The higher the specific impulse, the less fuel required to produce a given amount of thrust. Spectrum -- A range of frequen ...
Force Test 14
... Starting with newton’s second law, create a differential equation that would allow for the determination of the velocity of the object as a function of time. Arrange the previous equation for integration, substituting limits but do not integrate. ...
... Starting with newton’s second law, create a differential equation that would allow for the determination of the velocity of the object as a function of time. Arrange the previous equation for integration, substituting limits but do not integrate. ...
1 PHYSICS 231 Lecture 7: Newton`s Laws
... Isaac Newton (1642-1727) “In the beginning of 1665 I found the…rule for reducing any dignity of binomial to a series. The same year in May I found the method of tangents and in November the method of fluxions and in the next year in January had the Theory of Colours and in May following I had the e ...
... Isaac Newton (1642-1727) “In the beginning of 1665 I found the…rule for reducing any dignity of binomial to a series. The same year in May I found the method of tangents and in November the method of fluxions and in the next year in January had the Theory of Colours and in May following I had the e ...
Calculating force
... Calculating the translational force required to move a given load in a specific manner is the first step in sizing a linear actuator. In general, there are four components of force, or thrust, to overcome — that due to mass, gravity, friction, and associated counterforces such as spring, cutting, an ...
... Calculating the translational force required to move a given load in a specific manner is the first step in sizing a linear actuator. In general, there are four components of force, or thrust, to overcome — that due to mass, gravity, friction, and associated counterforces such as spring, cutting, an ...
Newton`s Laws and Forces
... Just because there is no movement doesn’t mean that there are no forces. No movement just means that all of the forces acting on one of the objects balance each other out. ...
... Just because there is no movement doesn’t mean that there are no forces. No movement just means that all of the forces acting on one of the objects balance each other out. ...
Artificial gravity

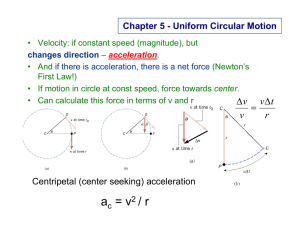
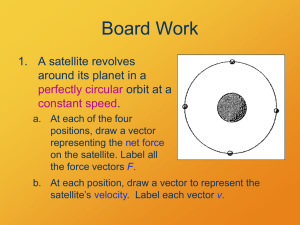
Artificial gravity is the theoretical increase or decrease of apparent gravity (g-force) by artificial means, particularly in space, but also on Earth. It can be practically achieved by the use of different forces, particularly the centripetal force and linear acceleration.The creation of artificial gravity is considered desirable for long-term space travel or habitation, for ease of mobility, for in-space fluid management, and to avoid the adverse long-term health effects of weightlessness.A number of methods for generating artificial gravity have been proposed, as well as an even larger number of science fiction approaches using both real and fictitious forces. Practical outer space applications of artificial gravity for humans have not yet been built and flown, principally due to the large size of the spacecraft required to produce centripetal acceleration.