here
... low topography of Snake River Plain eventually is removed due to sedimentary deposit (density ~2700 kg/m3), what will be the crustal thickness then? Information that might be helpful: Gravitational constant G=6.67384 × 10-11 m3 kg-1 s-2 Earth radius 6371 km Earth mass 5.972×1024 kg The gravitational ...
... low topography of Snake River Plain eventually is removed due to sedimentary deposit (density ~2700 kg/m3), what will be the crustal thickness then? Information that might be helpful: Gravitational constant G=6.67384 × 10-11 m3 kg-1 s-2 Earth radius 6371 km Earth mass 5.972×1024 kg The gravitational ...
Veritasium Videos seen in class What is Gravity? https://www
... https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zN6kCa6xi9k This video address the reason behind the Moon’s orbit around the Earth. Remember there are two forces keeping the Moon in orbit – gravity and inertia. Gravity is pulling the Moon towards the Earth, while inertia keeps the Moon wanting to go in a straight l ...
... https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zN6kCa6xi9k This video address the reason behind the Moon’s orbit around the Earth. Remember there are two forces keeping the Moon in orbit – gravity and inertia. Gravity is pulling the Moon towards the Earth, while inertia keeps the Moon wanting to go in a straight l ...
Chapter 6
... 5. Apply Newton’s 2nd law which means find the net force in the y and find the net force in the x. SFx and Sfy 6. Solve equations you got from 4 and 5 ...
... 5. Apply Newton’s 2nd law which means find the net force in the y and find the net force in the x. SFx and Sfy 6. Solve equations you got from 4 and 5 ...
Motion
... If the car stops, the person’s body remains in motion until the unbalanced force (seatbelt) stops them ...
... If the car stops, the person’s body remains in motion until the unbalanced force (seatbelt) stops them ...
pptx
... Newton’s Law of Gravity Any two objects with mass experience an attractive force from gravity that tries to pull them towards each other. The strength of this force depends on the masses of the two bodies, and the distance between their centers (squared). The attractive force is greater for larger ...
... Newton’s Law of Gravity Any two objects with mass experience an attractive force from gravity that tries to pull them towards each other. The strength of this force depends on the masses of the two bodies, and the distance between their centers (squared). The attractive force is greater for larger ...
Quiz
... 4. What is the angular acceleration caused by a frictional force of 200 N on a runner whose centre is 95.0 cm above a level runway if her moment of inertia is 12.00 kg.m2? (Ignore the vertical force.) a) –16.67 rad/s2 b) –2400 rad/s2 c) –190.0 rad/s2 d) –15.83 rad/s2 ...
... 4. What is the angular acceleration caused by a frictional force of 200 N on a runner whose centre is 95.0 cm above a level runway if her moment of inertia is 12.00 kg.m2? (Ignore the vertical force.) a) –16.67 rad/s2 b) –2400 rad/s2 c) –190.0 rad/s2 d) –15.83 rad/s2 ...
Newton’s law of Universal Gravitation
... If all of gravity is “used up” keeping the orbiting object in a circular orbit, then there is nothing left to push against a scale: apparent weightlessness. ...
... If all of gravity is “used up” keeping the orbiting object in a circular orbit, then there is nothing left to push against a scale: apparent weightlessness. ...
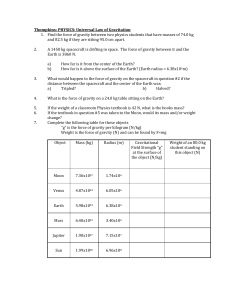
[ ]kg - thecubscientist.com
... (note how small this number is…it gives you an idea why the force of gravity is so weak!!!) m1 = the mass of object 1 [kg] m2 = the mass of object 2 [kg] r = the distance between the centers of the objects [m] ...
... (note how small this number is…it gives you an idea why the force of gravity is so weak!!!) m1 = the mass of object 1 [kg] m2 = the mass of object 2 [kg] r = the distance between the centers of the objects [m] ...
Newton`s Second Law Questions
... Newton’s Second Law Questions Name: 1. What is Newton’s Second Law of Motion? ...
... Newton’s Second Law Questions Name: 1. What is Newton’s Second Law of Motion? ...
grade 9 RWS 3 - Buds Public School
... kept it there and just before and just before return journey from moon to earth he weighed the soil there on the surface of moon and found that it was only 10N.Why did its weight decrease and how much was the loss in mass of soil?(g earth=10m/s2,gmoon=g earth/6) 4. Which accident will be more damagi ...
... kept it there and just before and just before return journey from moon to earth he weighed the soil there on the surface of moon and found that it was only 10N.Why did its weight decrease and how much was the loss in mass of soil?(g earth=10m/s2,gmoon=g earth/6) 4. Which accident will be more damagi ...
Artificial gravity

Artificial gravity is the theoretical increase or decrease of apparent gravity (g-force) by artificial means, particularly in space, but also on Earth. It can be practically achieved by the use of different forces, particularly the centripetal force and linear acceleration.The creation of artificial gravity is considered desirable for long-term space travel or habitation, for ease of mobility, for in-space fluid management, and to avoid the adverse long-term health effects of weightlessness.A number of methods for generating artificial gravity have been proposed, as well as an even larger number of science fiction approaches using both real and fictitious forces. Practical outer space applications of artificial gravity for humans have not yet been built and flown, principally due to the large size of the spacecraft required to produce centripetal acceleration.
















![[ ]kg - thecubscientist.com](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/016331706_1-976c776aa4d8193e3d462b588961a530-300x300.png)