Chap5-Conceptual Modules
... the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students exc ...
... the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students exc ...
the File
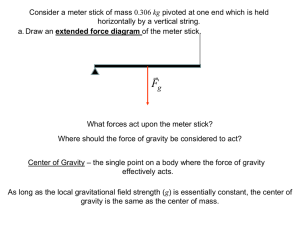
... A. Acceleration is any change in the speed or direction or an object. B. Second Law of Motion states that objects acceleration depends on the size and direction of the forces acting on it and on the mass of the object. 1. Example friends helping you (size) push a wagon full of bricks (mass) compared ...
... A. Acceleration is any change in the speed or direction or an object. B. Second Law of Motion states that objects acceleration depends on the size and direction of the forces acting on it and on the mass of the object. 1. Example friends helping you (size) push a wagon full of bricks (mass) compared ...
Document
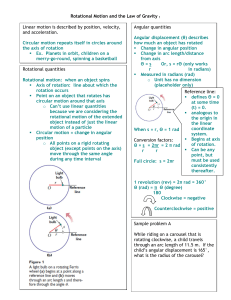
... Remember on the first day of class where we made a general rule of thumb...about 2 mph is about 1 m/s ...
... Remember on the first day of class where we made a general rule of thumb...about 2 mph is about 1 m/s ...
Possible Multiple-choice Questions about Gravity
... c. The speed at which we launch rockets from the Earth d. The number of sunspots on the Sun. e. The number of meteors that hit an object. 27. A person on Pluto’s surface would experience a(n) _____ gravitational force compared to on Earth. a. Weaker, because Pluto is further from the Sun. b. Weaker, ...
... c. The speed at which we launch rockets from the Earth d. The number of sunspots on the Sun. e. The number of meteors that hit an object. 27. A person on Pluto’s surface would experience a(n) _____ gravitational force compared to on Earth. a. Weaker, because Pluto is further from the Sun. b. Weaker, ...
PDF (View)
... must have at the top of its circular motion if the water is not to spill out of the upside-down pail? For faster speeds, find the tension in the string and the magnitude of the contact force between the water and the bucket. ...
... must have at the top of its circular motion if the water is not to spill out of the upside-down pail? For faster speeds, find the tension in the string and the magnitude of the contact force between the water and the bucket. ...
Artificial gravity

Artificial gravity is the theoretical increase or decrease of apparent gravity (g-force) by artificial means, particularly in space, but also on Earth. It can be practically achieved by the use of different forces, particularly the centripetal force and linear acceleration.The creation of artificial gravity is considered desirable for long-term space travel or habitation, for ease of mobility, for in-space fluid management, and to avoid the adverse long-term health effects of weightlessness.A number of methods for generating artificial gravity have been proposed, as well as an even larger number of science fiction approaches using both real and fictitious forces. Practical outer space applications of artificial gravity for humans have not yet been built and flown, principally due to the large size of the spacecraft required to produce centripetal acceleration.