P1elec1
... simply adding together the many individual Electric fields due to the point charges! (See Computer Homework, Vol 3 #1 & #2 for examples. These programs are NOT required for this course, but you may want to look at the Introductions and see how to work these types of problems. If you simply type in g ...
... simply adding together the many individual Electric fields due to the point charges! (See Computer Homework, Vol 3 #1 & #2 for examples. These programs are NOT required for this course, but you may want to look at the Introductions and see how to work these types of problems. If you simply type in g ...
Physics Web Search: Torque
... 5. What eventually happens to the lady bug? _______________________________ 6. From Newton’s second law, a force will cause an __________________________ 7. When considering angular motion, a torque will cause an ___________________ ____________________ (consider both torque equations) 8. What must ...
... 5. What eventually happens to the lady bug? _______________________________ 6. From Newton’s second law, a force will cause an __________________________ 7. When considering angular motion, a torque will cause an ___________________ ____________________ (consider both torque equations) 8. What must ...
p1210ch5
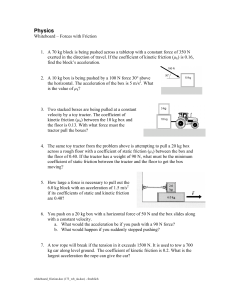
... • We’ll start with equilibrium, in which a body is at rest or moving with constant velocity. • Next, we’ll study objects that are not in equilibrium and deal with the relationship between forces and motion. • We’ll analyze the friction force that acts when a body slides over a surface. ...
... • We’ll start with equilibrium, in which a body is at rest or moving with constant velocity. • Next, we’ll study objects that are not in equilibrium and deal with the relationship between forces and motion. • We’ll analyze the friction force that acts when a body slides over a surface. ...
The Symmetries of the DFSD Space
... because of the vibratory nature of the photon. The objectivity factor W = TB/T, is “responsible” for the particle-like nature of the photon [1]. The energy of the photon is a consequence of the “switching-on” (appearance in our regular 3D space) of the basicenergy. Its zero-charge is a consequence o ...
... because of the vibratory nature of the photon. The objectivity factor W = TB/T, is “responsible” for the particle-like nature of the photon [1]. The energy of the photon is a consequence of the “switching-on” (appearance in our regular 3D space) of the basicenergy. Its zero-charge is a consequence o ...
Weightlessness

Weightlessness, or an absence of 'weight', is an absence of stress and strain resulting from externally applied mechanical contact-forces, typically normal forces from floors, seats, beds, scales, and the like. Counterintuitively, a uniform gravitational field does not by itself cause stress or strain, and a body in free fall in such an environment experiences no g-force acceleration and feels weightless. This is also termed ""zero-g"" where the term is more correctly understood as meaning ""zero g-force.""When bodies are acted upon by non-gravitational forces, as in a centrifuge, a rotating space station, or within a space ship with rockets firing, a sensation of weight is produced, as the contact forces from the moving structure act to overcome the body's inertia. In such cases, a sensation of weight, in the sense of a state of stress can occur, even if the gravitational field was zero. In such cases, g-forces are felt, and bodies are not weightless.When the gravitational field is non-uniform, a body in free fall suffers tidal effects and is not stress-free. Near a black hole, such tidal effects can be very strong. In the case of the Earth, the effects are minor, especially on objects of relatively small dimension (such as the human body or a spacecraft) and the overall sensation of weightlessness in these cases is preserved. This condition is known as microgravity and it prevails in orbiting spacecraft.