AP Physics C: Mechanics 2016 Free
... 2016 AP® PHYSICS C: MECHANICS FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS PHYSICS C: MECHANICS SECTION II Time—45 minutes 3 Questions Directions: Answer all three questions. The suggested time is about 15 minutes for answering each of the questions, which are worth 15 points each. The parts within a question may not h ...
... 2016 AP® PHYSICS C: MECHANICS FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS PHYSICS C: MECHANICS SECTION II Time—45 minutes 3 Questions Directions: Answer all three questions. The suggested time is about 15 minutes for answering each of the questions, which are worth 15 points each. The parts within a question may not h ...
The Multipole Moments
... We have expressed all quantities of interest with respect to the metric components. On the other hand the metric can be expressed in terms of the multipole moments. ...
... We have expressed all quantities of interest with respect to the metric components. On the other hand the metric can be expressed in terms of the multipole moments. ...
VPython - pen
... The design and operation of a cyclotron is discussed in Section 20.1.4. (a) Show that the "period" of the motion, the time between one kick to the right and the next kick in the same direction, does not depend on the current speed of the proton (at speeds small compared to the speed of light). As a ...
... The design and operation of a cyclotron is discussed in Section 20.1.4. (a) Show that the "period" of the motion, the time between one kick to the right and the next kick in the same direction, does not depend on the current speed of the proton (at speeds small compared to the speed of light). As a ...
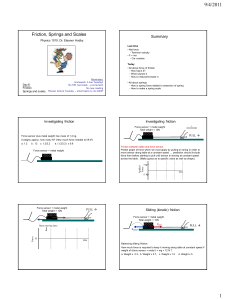
01 Newtons 2nd
... The top block begins to move as soon as F reaches a certain minimum value; the bottom block would never move even as F increases further. Both blocks begin to move simultaneously as F reaches a certain minimum value; as F increases further, the acceleration of the top block exceeds the acceleration ...
... The top block begins to move as soon as F reaches a certain minimum value; the bottom block would never move even as F increases further. Both blocks begin to move simultaneously as F reaches a certain minimum value; as F increases further, the acceleration of the top block exceeds the acceleration ...
chapter15-3
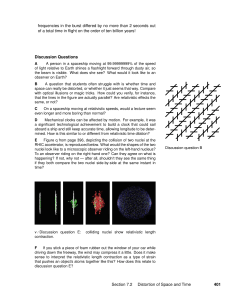
... A Question Two identical conducting spheres A and B carry equal charge. They are separated by a distance much larger than their diameters. A third identical conducting sphere C is uncharged. Sphere C is first touched to A, then to B, and finally removed. As a result, the electrostatic force between ...
... A Question Two identical conducting spheres A and B carry equal charge. They are separated by a distance much larger than their diameters. A third identical conducting sphere C is uncharged. Sphere C is first touched to A, then to B, and finally removed. As a result, the electrostatic force between ...
Weightlessness

Weightlessness, or an absence of 'weight', is an absence of stress and strain resulting from externally applied mechanical contact-forces, typically normal forces from floors, seats, beds, scales, and the like. Counterintuitively, a uniform gravitational field does not by itself cause stress or strain, and a body in free fall in such an environment experiences no g-force acceleration and feels weightless. This is also termed ""zero-g"" where the term is more correctly understood as meaning ""zero g-force.""When bodies are acted upon by non-gravitational forces, as in a centrifuge, a rotating space station, or within a space ship with rockets firing, a sensation of weight is produced, as the contact forces from the moving structure act to overcome the body's inertia. In such cases, a sensation of weight, in the sense of a state of stress can occur, even if the gravitational field was zero. In such cases, g-forces are felt, and bodies are not weightless.When the gravitational field is non-uniform, a body in free fall suffers tidal effects and is not stress-free. Near a black hole, such tidal effects can be very strong. In the case of the Earth, the effects are minor, especially on objects of relatively small dimension (such as the human body or a spacecraft) and the overall sensation of weightlessness in these cases is preserved. This condition is known as microgravity and it prevails in orbiting spacecraft.