Electricity and Gravity Review 1) The gravity between two electrons
... 1) The gravity between two electrons differs from the electrical force because the gravity is a) weaker and attractive b) stronger and attractive c) weaker and repulsive d) stronger and repulsive 2) An electron is heading directly toward a positive plate of charge. Therefore it is a) slowing down b) ...
... 1) The gravity between two electrons differs from the electrical force because the gravity is a) weaker and attractive b) stronger and attractive c) weaker and repulsive d) stronger and repulsive 2) An electron is heading directly toward a positive plate of charge. Therefore it is a) slowing down b) ...
Electric Fields
... - charge distributes itself evenly over the surface of a conductor making the net field inside zero Electric field is always perpendicular to the surface of a conductor Excess charge tends to accumulate on sharp points or areas of greatest ...
... - charge distributes itself evenly over the surface of a conductor making the net field inside zero Electric field is always perpendicular to the surface of a conductor Excess charge tends to accumulate on sharp points or areas of greatest ...
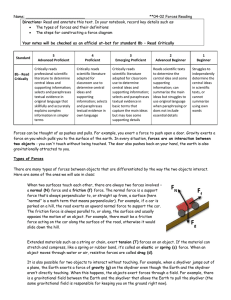
Laws of Motion
... Newton’s 1st Law: The natural state of an object is to keep its motion A change of motion occurs only if there is net force Inertia = the tendency of an object not to change its motion Mass is quantitative measure of an object’s inertia Newton’s 1st Law is also known as the law of inertia. It w ...
... Newton’s 1st Law: The natural state of an object is to keep its motion A change of motion occurs only if there is net force Inertia = the tendency of an object not to change its motion Mass is quantitative measure of an object’s inertia Newton’s 1st Law is also known as the law of inertia. It w ...
Title of PAPER - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... tolerance to g acceleration. The value calculated will not have any major impact on the health of the jumper as it is below the threshold stated. With the freefall lasting approximately 5 seconds [1] the whole jump can be estimated to last around 20 seconds which is a relatively low time for the for ...
... tolerance to g acceleration. The value calculated will not have any major impact on the health of the jumper as it is below the threshold stated. With the freefall lasting approximately 5 seconds [1] the whole jump can be estimated to last around 20 seconds which is a relatively low time for the for ...
Supplementary Exercise for Newton`s laws of motion
... A. They fall together, taking a longer time than the coin would in falling from the same height on Earth. B. They fall together, taking a shorter time than the coin would in falling from the same height on Earth. C. The coin falls faster than the feather, but both take a longer time than if they wer ...
... A. They fall together, taking a longer time than the coin would in falling from the same height on Earth. B. They fall together, taking a shorter time than the coin would in falling from the same height on Earth. C. The coin falls faster than the feather, but both take a longer time than if they wer ...
Weightlessness

Weightlessness, or an absence of 'weight', is an absence of stress and strain resulting from externally applied mechanical contact-forces, typically normal forces from floors, seats, beds, scales, and the like. Counterintuitively, a uniform gravitational field does not by itself cause stress or strain, and a body in free fall in such an environment experiences no g-force acceleration and feels weightless. This is also termed ""zero-g"" where the term is more correctly understood as meaning ""zero g-force.""When bodies are acted upon by non-gravitational forces, as in a centrifuge, a rotating space station, or within a space ship with rockets firing, a sensation of weight is produced, as the contact forces from the moving structure act to overcome the body's inertia. In such cases, a sensation of weight, in the sense of a state of stress can occur, even if the gravitational field was zero. In such cases, g-forces are felt, and bodies are not weightless.When the gravitational field is non-uniform, a body in free fall suffers tidal effects and is not stress-free. Near a black hole, such tidal effects can be very strong. In the case of the Earth, the effects are minor, especially on objects of relatively small dimension (such as the human body or a spacecraft) and the overall sensation of weightlessness in these cases is preserved. This condition is known as microgravity and it prevails in orbiting spacecraft.























