Force
... An object is in free fall if it only has the force of gravity acting on it. In a vacuum, where there is no air at all, objects fall at the same rate of acceleration. But on Earth falling objects encounter air resistance, a type of fluid friction. ...
... An object is in free fall if it only has the force of gravity acting on it. In a vacuum, where there is no air at all, objects fall at the same rate of acceleration. But on Earth falling objects encounter air resistance, a type of fluid friction. ...
PHSX 114, Wednesday, September 18, 2002
... •Historical context will be discussed Friday •The first great “unification” in physics – motion of a falling apple and motion of the moon about the Earth explained by the same theory ...
... •Historical context will be discussed Friday •The first great “unification” in physics – motion of a falling apple and motion of the moon about the Earth explained by the same theory ...
Slide 1 - USD 306
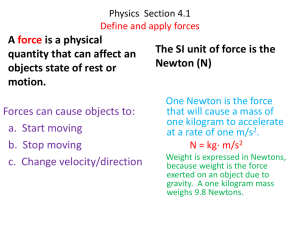
... objects state of rest or motion. Forces can cause objects to: a. Start moving b. Stop moving c. Change velocity/direction ...
... objects state of rest or motion. Forces can cause objects to: a. Start moving b. Stop moving c. Change velocity/direction ...
Section 1
... G is equal to 6.67 x 10-11 N·m2/kg2, which means that it's a very small number. This is indicative of the fact that as fundamental forces go, gravity is very weak. Note also that r doesn't represent the distance from the surface of either body but from the centers. Thus, at sea level on Earth, r is ...
... G is equal to 6.67 x 10-11 N·m2/kg2, which means that it's a very small number. This is indicative of the fact that as fundamental forces go, gravity is very weak. Note also that r doesn't represent the distance from the surface of either body but from the centers. Thus, at sea level on Earth, r is ...
File
... The purpose of this activity is to use a gravity and orbit simulation to calculate the value of G. Part 1: Finding G with the Gravity Force Lab Change the mass and distance values for a broad mixture of situations, completing the first 4 columns of the chart below. Then use the formula to calculate ...
... The purpose of this activity is to use a gravity and orbit simulation to calculate the value of G. Part 1: Finding G with the Gravity Force Lab Change the mass and distance values for a broad mixture of situations, completing the first 4 columns of the chart below. Then use the formula to calculate ...
Newton`s Second Law
... Newton’s First Law: An object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion remains in motion with the same speed and direction (maintains its velocity) unless it experiences an unbalanced force. Example: A soccer ball resting on the grass remains motionless until a force is applied (a kick). Th ...
... Newton’s First Law: An object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion remains in motion with the same speed and direction (maintains its velocity) unless it experiences an unbalanced force. Example: A soccer ball resting on the grass remains motionless until a force is applied (a kick). Th ...
Forces
... Newton’s Law of Gravity • Gravity is the natural force that pulls one object toward another. The strength of this pull depends on the mass of the objects involved. • The pull is directly proportional to the masses of the objects and inversely proportional to the distance between the objects. ...
... Newton’s Law of Gravity • Gravity is the natural force that pulls one object toward another. The strength of this pull depends on the mass of the objects involved. • The pull is directly proportional to the masses of the objects and inversely proportional to the distance between the objects. ...
L23_gravity
... The planet Saturn is about 100 times more massive than Earth, and about 10 times farther from the Sun. How does the gravitational attraction between Saturn and the Sun compare to that between Earth and the Sun? ...
... The planet Saturn is about 100 times more massive than Earth, and about 10 times farther from the Sun. How does the gravitational attraction between Saturn and the Sun compare to that between Earth and the Sun? ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance
... • Mass is the amount of matter in your body • Weight is the amount of force acting on your body • So on the Moon, you would have the same mass as on Earth but weigh less on the Moon since the Moon is less massive than Earth ...
... • Mass is the amount of matter in your body • Weight is the amount of force acting on your body • So on the Moon, you would have the same mass as on Earth but weigh less on the Moon since the Moon is less massive than Earth ...