Gravitation and Rotational Motion
... product of the universal gravitational constant and the mass of the sun. Speed of a Satellite Orbiting Earth- this is equal to the square root of the universal gravitational constant times the mass of Earth, divided by the radius of the orbit. Period of a Satellite Orbiting Earth- this is equal to 2 ...
... product of the universal gravitational constant and the mass of the sun. Speed of a Satellite Orbiting Earth- this is equal to the square root of the universal gravitational constant times the mass of Earth, divided by the radius of the orbit. Period of a Satellite Orbiting Earth- this is equal to 2 ...
Newton`s 2nd Law
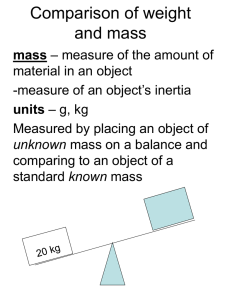
... Inertial mass Relates to how a mass responds to an external force (also called a contact force). If you push a stalled car into motion you are testing its inertial mass. Gravitational mass Relates to how a mass responds to the force of gravity (also called a field force). If you lift up a stalled ca ...
... Inertial mass Relates to how a mass responds to an external force (also called a contact force). If you push a stalled car into motion you are testing its inertial mass. Gravitational mass Relates to how a mass responds to the force of gravity (also called a field force). If you lift up a stalled ca ...
Slide 1
... it is sitting on a table, the force of gravity is still there; what other force is there? The force exerted perpendicular to a surface is called the normal force. It is exactly as large as needed to balance the force from the object ...
... it is sitting on a table, the force of gravity is still there; what other force is there? The force exerted perpendicular to a surface is called the normal force. It is exactly as large as needed to balance the force from the object ...
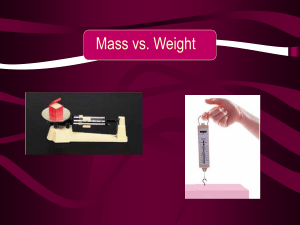
Weight - The University of Iowa
... • Galileo showed that all objects (regardless of mass) fall to earth with the same acceleration g = 10 m/s2 • This is only true if we remove the effects of air resistance. demos • We can show this by dropping two very different objects inside a chamber that has the air removed. ...
... • Galileo showed that all objects (regardless of mass) fall to earth with the same acceleration g = 10 m/s2 • This is only true if we remove the effects of air resistance. demos • We can show this by dropping two very different objects inside a chamber that has the air removed. ...
Document
... • What pushes a flying ball in an upwards direction • Do objects fall sideways • Is the moon falling ...
... • What pushes a flying ball in an upwards direction • Do objects fall sideways • Is the moon falling ...
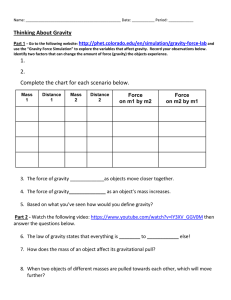
Name: Notes - 4.2 Newton`s First Law of Motion: Inertia 1. State
... 3. Why does an object given a push across a surface slow down? Why is this in agreement with Newton’s 1st Law? ...
... 3. Why does an object given a push across a surface slow down? Why is this in agreement with Newton’s 1st Law? ...
L3 - Department of Physics & Astronomy
... • Galileo showed that all objects (regardless of mass) fall to earth with the same acceleration g = 10 m/s2 • This is only true if we remove the effects of air resistance. demos • We can show this by dropping two very different objects inside a chamber that has the air removed. ...
... • Galileo showed that all objects (regardless of mass) fall to earth with the same acceleration g = 10 m/s2 • This is only true if we remove the effects of air resistance. demos • We can show this by dropping two very different objects inside a chamber that has the air removed. ...