Document
... If I double m1, what happens to the force of gravity? If I triple m2, what happens to the force of gravity? If I double the distance between the masses, what happens to the force of gravity? If I halve the distance between the masses, what happens to the force of gravity? If I triple the distance, w ...
... If I double m1, what happens to the force of gravity? If I triple m2, what happens to the force of gravity? If I double the distance between the masses, what happens to the force of gravity? If I halve the distance between the masses, what happens to the force of gravity? If I triple the distance, w ...
Newton Review
... 4. What is the force in Newton’s of an object whose mass is 100 kg and accelerates at 5 m/s2? F = ma; 500 N = 100 kg x 5 m/s2. 5. What is the acceleration of an object of 100 N that has a mass of 5 kg? 100N/5kg = 20 m/s2 6. What is matter? What is mass? What is volume? What is the volume of a box of ...
... 4. What is the force in Newton’s of an object whose mass is 100 kg and accelerates at 5 m/s2? F = ma; 500 N = 100 kg x 5 m/s2. 5. What is the acceleration of an object of 100 N that has a mass of 5 kg? 100N/5kg = 20 m/s2 6. What is matter? What is mass? What is volume? What is the volume of a box of ...
Document
... Newton could not finish his theory mathematically so he put his papers in a drawer until he had developed __________________. This took him 20 years!! ...
... Newton could not finish his theory mathematically so he put his papers in a drawer until he had developed __________________. This took him 20 years!! ...
30 Physics
... Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object (measured in kilograms) and weight is the force of gravity pulling down on an object (measured in Newtons). So why do so many people confuse the two and/or not differentiate the two? It just so happens that the more mass an object has the more i ...
... Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object (measured in kilograms) and weight is the force of gravity pulling down on an object (measured in Newtons). So why do so many people confuse the two and/or not differentiate the two? It just so happens that the more mass an object has the more i ...
Document
... If you were to stand on the beach for 24 hours, how many times would you see the ocean rise and fall? Rise 2 times, fall 2 times ...
... If you were to stand on the beach for 24 hours, how many times would you see the ocean rise and fall? Rise 2 times, fall 2 times ...
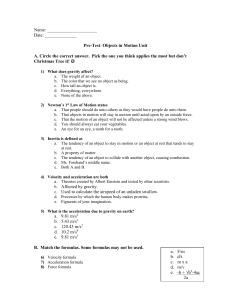
Name - forehandspace
... A. Circle the correct answer. Pick the one you think applies the most but don’t Christmas Tree it! 1) What does gravity affect? a. The weight of an object. b. The color that we see an object as being. c. How tall an object is. d. Everything, everywhere. e. None of the above. 2) Newton’s 1st Law of ...
... A. Circle the correct answer. Pick the one you think applies the most but don’t Christmas Tree it! 1) What does gravity affect? a. The weight of an object. b. The color that we see an object as being. c. How tall an object is. d. Everything, everywhere. e. None of the above. 2) Newton’s 1st Law of ...
Document
... • What is your weight and mass ? • Weight W is the force of gravity acting on a mass m causing acceleration g • Using F = m a, and the Law of Gravitation W = m g = G (m MEarth) /R2 (R – Radius of the Earth) The mass m of the falling object cancels out and does not matter; therefore all objects fall ...
... • What is your weight and mass ? • Weight W is the force of gravity acting on a mass m causing acceleration g • Using F = m a, and the Law of Gravitation W = m g = G (m MEarth) /R2 (R – Radius of the Earth) The mass m of the falling object cancels out and does not matter; therefore all objects fall ...
Final Exam Study Guide
... You are authorized to have a 3x5 card for the Final Exam. You may only use a handwritten 3x5 card. You will turn it in after the Exam. The Final Exam is 60 questions and you will have 90 minutes. There are no retakes for the Final Exam. Speed = Distance divided by time. If distance = zero, then spee ...
... You are authorized to have a 3x5 card for the Final Exam. You may only use a handwritten 3x5 card. You will turn it in after the Exam. The Final Exam is 60 questions and you will have 90 minutes. There are no retakes for the Final Exam. Speed = Distance divided by time. If distance = zero, then spee ...
Variation of g (acceleration due to gravity) - cal
... To find the acceleration due to gravity at sea level you can plug in values of G and the mass (in kilograms) and radius (in meters) of the Earth to obtain the calculated value of g: g = GM/r2 This agrees approximately with the measured value of g. The difference may be attributed to several factors: ...
... To find the acceleration due to gravity at sea level you can plug in values of G and the mass (in kilograms) and radius (in meters) of the Earth to obtain the calculated value of g: g = GM/r2 This agrees approximately with the measured value of g. The difference may be attributed to several factors: ...
PHYSICS FORCES TEST REVIEW WORKSHEET
... 2. A man has a weight of 2470 newtons on Earth and a weight of 243 newtons on planet Z. What is the acceleration due to gravity on planet Z? 0.96m/s2 Use this graph to answer questions 3-5. This is a 1204g wood mass being pulled by the force meter at a constant velocity. -1.2-Force (N) -0.8--0.4--ti ...
... 2. A man has a weight of 2470 newtons on Earth and a weight of 243 newtons on planet Z. What is the acceleration due to gravity on planet Z? 0.96m/s2 Use this graph to answer questions 3-5. This is a 1204g wood mass being pulled by the force meter at a constant velocity. -1.2-Force (N) -0.8--0.4--ti ...
Gravity - ClassZone
... Earth’s gravitational pull is about 91 percent of what it is at Earth’s surface. The extra distance makes a difference in the force of only about 9 percent. If a spacecraft is launched with a speed of 11,000 meters per second or more, it is moving too fast to go into an orbit. Instead, the spacecraf ...
... Earth’s gravitational pull is about 91 percent of what it is at Earth’s surface. The extra distance makes a difference in the force of only about 9 percent. If a spacecraft is launched with a speed of 11,000 meters per second or more, it is moving too fast to go into an orbit. Instead, the spacecraf ...