1 PHYSICS 231 Lecture 7: Newton`s Laws
... “In the beginning of 1665 I found the…rule for reducing any dignity of binomial to a series. The same year in May I found the method of tangents and in November the method of fluxions and in the next year in January had the Theory of Colours and in May following I had the entrance into the inverse m ...
... “In the beginning of 1665 I found the…rule for reducing any dignity of binomial to a series. The same year in May I found the method of tangents and in November the method of fluxions and in the next year in January had the Theory of Colours and in May following I had the entrance into the inverse m ...
Circular Motion
... 2. A child rides on a carousel at constant speed. In which direction does each of the following vectors point? a. velocity ...
... 2. A child rides on a carousel at constant speed. In which direction does each of the following vectors point? a. velocity ...
con review circ gravity soln
... 9) Using complete sentences, explain why an astronaut on the orbiting space shuttle experiences apparent ...
... 9) Using complete sentences, explain why an astronaut on the orbiting space shuttle experiences apparent ...
Document
... • Force and mass are directly related • Force and acc are directly related • Mass and acc are indirectly related • And finally, the label for force is the Newton. • Newtons = (kg)(m/s2) ...
... • Force and mass are directly related • Force and acc are directly related • Mass and acc are indirectly related • And finally, the label for force is the Newton. • Newtons = (kg)(m/s2) ...
Newton`s laws of motion
... Newton's Second Law of Motion When a net external force F acts on an object of mass m, the acceleration a that results is directly proportional to the net force and has a magnitude that is inversely proportional to the mass. The direction of the acceleration is the same as the direction of the net ...
... Newton's Second Law of Motion When a net external force F acts on an object of mass m, the acceleration a that results is directly proportional to the net force and has a magnitude that is inversely proportional to the mass. The direction of the acceleration is the same as the direction of the net ...
Force and Motion Before Newton
... Orbital Energy and Speed • Another way to look at the changing speed of an orbiting body is through the energy of the body • Energy of an orbiting body has two components: kinetic and gravitational potential energy – Kinetic energy = energy of motion – Gravitational potential energy = energy of pos ...
... Orbital Energy and Speed • Another way to look at the changing speed of an orbiting body is through the energy of the body • Energy of an orbiting body has two components: kinetic and gravitational potential energy – Kinetic energy = energy of motion – Gravitational potential energy = energy of pos ...
Conceptual Physics
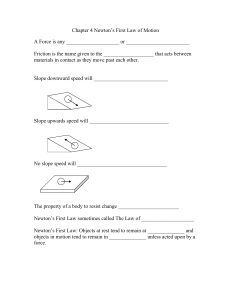
... Newton’s First Law sometimes called The Law of ____________________ Newton’s First Law: Objects at rest tend to remain at ______________ and objects in motion tend to remain in ______________ unless acted upon by a force. ...
... Newton’s First Law sometimes called The Law of ____________________ Newton’s First Law: Objects at rest tend to remain at ______________ and objects in motion tend to remain in ______________ unless acted upon by a force. ...
Chapter 6 Forces and Motion
... Terminal Velocity- The constant velocity of a falling object when the force of air resistance is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the force of gravity. Free fall - the motion of a body when only the force of gravity is acting on the body. Projectile motion- the curved path that an obj ...
... Terminal Velocity- The constant velocity of a falling object when the force of air resistance is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the force of gravity. Free fall - the motion of a body when only the force of gravity is acting on the body. Projectile motion- the curved path that an obj ...
vocabulary
... A vector quantity that expresses the relation of the velocity of a body, wave, field, or other physical system, to its energy. The direction of the momentum of a single object indicates the direction of its motion. Momentum is a conserved quantity (it remains constant unless acted upon by an outside ...
... A vector quantity that expresses the relation of the velocity of a body, wave, field, or other physical system, to its energy. The direction of the momentum of a single object indicates the direction of its motion. Momentum is a conserved quantity (it remains constant unless acted upon by an outside ...
File - Lanier Bureau of Investigation
... b. A distance/time graph measures speed. c. The formula for speed is distance divided by time. d. A distance/time graph of constant speed and velocity is a straight line. e. Velocity changes when speed changes f. You can combine velocities by adding if they are going the same direction. g. Accelerat ...
... b. A distance/time graph measures speed. c. The formula for speed is distance divided by time. d. A distance/time graph of constant speed and velocity is a straight line. e. Velocity changes when speed changes f. You can combine velocities by adding if they are going the same direction. g. Accelerat ...
Document
... Whiteboard and Interpret In 6.42 minutes…or less to prepare, then we will present the whiteboards. 1. Graph the shape of your assigned independent variables to the gravitational forces experienced by the objects. 2. Write 2 statements that describe the relationship of the variables graphed 3. Prese ...
... Whiteboard and Interpret In 6.42 minutes…or less to prepare, then we will present the whiteboards. 1. Graph the shape of your assigned independent variables to the gravitational forces experienced by the objects. 2. Write 2 statements that describe the relationship of the variables graphed 3. Prese ...
Physical Science: Test Force
... A. Elastic B. Kinetic C. Sliding D. Inelastic E. Static 2. What is the unbalanced force that slows down a ball rolling across the floor? A. the force of gravity C. the force of inertia B. the force of momentum D. the force of friction 3. Which of the four main types of forces is the weakest? A. Elec ...
... A. Elastic B. Kinetic C. Sliding D. Inelastic E. Static 2. What is the unbalanced force that slows down a ball rolling across the floor? A. the force of gravity C. the force of inertia B. the force of momentum D. the force of friction 3. Which of the four main types of forces is the weakest? A. Elec ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion POWERPOINT
... FREE FALL- when an object is being pulled down by gravity, but no other forces are acting on it. Does free fall occur with air resistance? ...
... FREE FALL- when an object is being pulled down by gravity, but no other forces are acting on it. Does free fall occur with air resistance? ...