Aristotle`s Laws of Motion
... Force of man on ground As the man pushes on the ground, the ground responds by pushing on the man. It is this force that pushes both the man and the boulder up the hill! ...
... Force of man on ground As the man pushes on the ground, the ground responds by pushing on the man. It is this force that pushes both the man and the boulder up the hill! ...
5th set - Nathan Dawson
... on a table. Which path will the ball follow when it gets to the end of the ...
... on a table. Which path will the ball follow when it gets to the end of the ...
Physics 50 Workshop
... 4. An electron travels in a straight line from the cathode of a vacuum tube to its anode (negative and positive ends, respectively) due to the electric field between the two ends of the tube. It travels a distance of 1.0 cm. The electron starts at rest and reaches the anode at a speed of 6.0 x 106 m ...
... 4. An electron travels in a straight line from the cathode of a vacuum tube to its anode (negative and positive ends, respectively) due to the electric field between the two ends of the tube. It travels a distance of 1.0 cm. The electron starts at rest and reaches the anode at a speed of 6.0 x 106 m ...
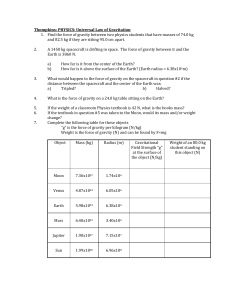
(Honors Physics) Universal Law of Gravitation
... Determine each of the following for the spacecraft when it is at point A . a. The total mechanical energy of the spacecraft, assuming that the gravitational potential energy is zero at an infinite distance from the Earth. b. The magnitude of the angular momentum of the spacecraft about the center of ...
... Determine each of the following for the spacecraft when it is at point A . a. The total mechanical energy of the spacecraft, assuming that the gravitational potential energy is zero at an infinite distance from the Earth. b. The magnitude of the angular momentum of the spacecraft about the center of ...
Force and Motion Vocabulary: Force: A push or pull on an object
... Force and Motion Vocabulary: Force: A push or pull on an object Motion: Process of moving or being moved Gravity: The force that pulls things toward Earth Height: the measurement from base to top Distance: an amount of space between two things or people Surface: the outside part or uppermost layer o ...
... Force and Motion Vocabulary: Force: A push or pull on an object Motion: Process of moving or being moved Gravity: The force that pulls things toward Earth Height: the measurement from base to top Distance: an amount of space between two things or people Surface: the outside part or uppermost layer o ...
Quiz
... force’s line of action passes through the centre of gravity of a body? a) object will continue moving at constant velocity b) object will accelerate in the direction of the force with no change in spin c) object will accelerate linearly and angularly ...
... force’s line of action passes through the centre of gravity of a body? a) object will continue moving at constant velocity b) object will accelerate in the direction of the force with no change in spin c) object will accelerate linearly and angularly ...
Forces Review
... gravitational constant, and g the magnitude of the acceleration due to gravity is true? (a) The values of g and G do not depend on location. (b) The values of g and G depend on location. (c) The value of G is the same everywhere in the universe, but the value of g is not. (d) The value of g is the s ...
... gravitational constant, and g the magnitude of the acceleration due to gravity is true? (a) The values of g and G do not depend on location. (b) The values of g and G depend on location. (c) The value of G is the same everywhere in the universe, but the value of g is not. (d) The value of g is the s ...
7-Universal Gravitation
... evidenced by objects carried up a flight of stairs feeling heavier. Gravity decreases with altitude because the distance from the center of the Earth is increased ...
... evidenced by objects carried up a flight of stairs feeling heavier. Gravity decreases with altitude because the distance from the center of the Earth is increased ...
forces and motion study guide
... 13. The least number of photographs needed to tell if a horse is moving is __________________. 14. Henri wants to explain what is meant by mass. He should describe the mass of his body as being ________________________________________________________________________. 15. ____________________________ ...
... 13. The least number of photographs needed to tell if a horse is moving is __________________. 14. Henri wants to explain what is meant by mass. He should describe the mass of his body as being ________________________________________________________________________. 15. ____________________________ ...
Gravity Review Sheet Answers:
... Whenever we tell how fast or slow something is going, we tell how far the object will move in a given time, such as miles per hour or meters per second. This is called the object’s speed. When we also tell in which the direction the object is traveling, we now refer to its movement as its velocity. ...
... Whenever we tell how fast or slow something is going, we tell how far the object will move in a given time, such as miles per hour or meters per second. This is called the object’s speed. When we also tell in which the direction the object is traveling, we now refer to its movement as its velocity. ...