5-6,7,8,9
... 3. It has the same value along the rope (for example, between points A and B). The following assumptions are made: a. The rope has negligible mass compared to the mass of the object it pulls. b. The rope does not stretch. If a pulley is used as in fig.(b) and fig.(c), we assume that the pulley is ma ...
... 3. It has the same value along the rope (for example, between points A and B). The following assumptions are made: a. The rope has negligible mass compared to the mass of the object it pulls. b. The rope does not stretch. If a pulley is used as in fig.(b) and fig.(c), we assume that the pulley is ma ...
File
... • Find the mass of an object that accelerates 5 m/s2 when pushed with a force of 25 N • Find the acceleration of an object with a mass of 2 kg that is pushed with a force of 6 N • Find the acceleration of an object with a mass of 2 kg that is pushed with a force of 6 N ...
... • Find the mass of an object that accelerates 5 m/s2 when pushed with a force of 25 N • Find the acceleration of an object with a mass of 2 kg that is pushed with a force of 6 N • Find the acceleration of an object with a mass of 2 kg that is pushed with a force of 6 N ...
Investigating g On Other Planets Virtual Lab
... Discussion: A __________is any push or pull on an object and is measured in Newtons. ______________ forces are forces that are equal and opposite. ________________forces can cause a change in motion. According to Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion, if a net force is applied to an object, the object will ___ ...
... Discussion: A __________is any push or pull on an object and is measured in Newtons. ______________ forces are forces that are equal and opposite. ________________forces can cause a change in motion. According to Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion, if a net force is applied to an object, the object will ___ ...
Physics - bsparrow
... BUT, the elephant also has a bigger mass proportional to that BIGGER F. BIGGER “m”. That means that the BIGGER “F” cancels the BIGGER “m” and the objects fall at the same acceleration. ...
... BUT, the elephant also has a bigger mass proportional to that BIGGER F. BIGGER “m”. That means that the BIGGER “F” cancels the BIGGER “m” and the objects fall at the same acceleration. ...
Newton`s Laws Summative Assessment
... 2. When an unbalanced force acts on an object, the force ______________________. a. changes the motion of the object b. is canceled by another force c. does not change the motion of the object d. dis equal to the weight of the object ...
... 2. When an unbalanced force acts on an object, the force ______________________. a. changes the motion of the object b. is canceled by another force c. does not change the motion of the object d. dis equal to the weight of the object ...
Document
... be able to find acceleration for simple systems free body diagrams look over projectile motion don’t worry about any long derivations we did in ...
... be able to find acceleration for simple systems free body diagrams look over projectile motion don’t worry about any long derivations we did in ...
Problem: Suppose I pull a package with a force of
... Problem : A snail massing .23 kg slides down an incline of 25° at a constant velocity. The snail slides 1.5 m. What is the work done by the normal force, by gravity, and by friction? What is the total work done on the snail? ...
... Problem : A snail massing .23 kg slides down an incline of 25° at a constant velocity. The snail slides 1.5 m. What is the work done by the normal force, by gravity, and by friction? What is the total work done on the snail? ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... realized that there must be a force acting between Earth and the moon that kept the moon in orbit. What is a force? [A force is a push or a pull]. When one object pushes or pulls on another, you say that the first object exerts a force on the second object. In science, we represent forces by arrows. ...
... realized that there must be a force acting between Earth and the moon that kept the moon in orbit. What is a force? [A force is a push or a pull]. When one object pushes or pulls on another, you say that the first object exerts a force on the second object. In science, we represent forces by arrows. ...
distance d speed = or: s = time t final velocity
... ⇒ Weight is different from mass Mass is the amount of matter an object has and can only be changed when matter is added or taken away from the object. Weight is the attractive force between objects, and varies with mass and distance. Newton’s Third Law: For every action force, there is an equal an ...
... ⇒ Weight is different from mass Mass is the amount of matter an object has and can only be changed when matter is added or taken away from the object. Weight is the attractive force between objects, and varies with mass and distance. Newton’s Third Law: For every action force, there is an equal an ...
Multiple Choice: Motion and Forces Name: Core: ___ Date: ___1
... slowly slow down, and then stop move with constant speed ...
... slowly slow down, and then stop move with constant speed ...
Forces in One Dimension
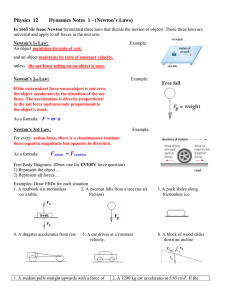
... “The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force on it and inversely proportional to its mass.” This sentence is a statement of ____ . ...
... “The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force on it and inversely proportional to its mass.” This sentence is a statement of ____ . ...