Connecting Motion with Force
... Inertia- the tendency of an object to resist any changes in its motion. - velocity remains the same unless a force changes it. - The more mass an object has, the greater its inertia. Ex: bowling ball vs. tennis ball ...
... Inertia- the tendency of an object to resist any changes in its motion. - velocity remains the same unless a force changes it. - The more mass an object has, the greater its inertia. Ex: bowling ball vs. tennis ball ...
circular motion ppt pdf
... Newton and Satellite Motion Newton’s Law of Gravitation predicts artificial satellites can orbit the earth with centripetal acceleration. Satellites have acceleration towards the center of Earth, but they also have tangential speed to keep them in orbit! Astronauts in orbit are often described as “ ...
... Newton and Satellite Motion Newton’s Law of Gravitation predicts artificial satellites can orbit the earth with centripetal acceleration. Satellites have acceleration towards the center of Earth, but they also have tangential speed to keep them in orbit! Astronauts in orbit are often described as “ ...
Forces
... • A force that pulls two objects towards each other. • Two factors that affect gravity 1. Mass- the more mass the greater the gravitational pull. 2. Distance- the farther apart two objects are the less gravitational pull. ...
... • A force that pulls two objects towards each other. • Two factors that affect gravity 1. Mass- the more mass the greater the gravitational pull. 2. Distance- the farther apart two objects are the less gravitational pull. ...
Newton*s Laws Webquest
... _____10____________ is a push or pull on an object. __________11__________________ is the difference between two opposing forces. Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion states that if a net force acts on an object, the object will ________12____________ in the direction of the force. Acceleration is a change in ...
... _____10____________ is a push or pull on an object. __________11__________________ is the difference between two opposing forces. Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion states that if a net force acts on an object, the object will ________12____________ in the direction of the force. Acceleration is a change in ...
Newtonian Revolution
... It is said that Newton’s thoughts about motion and gravity were set into action after an apple fell on his head. ...
... It is said that Newton’s thoughts about motion and gravity were set into action after an apple fell on his head. ...
Name: ___________ Date: ______ Hour: ______ What do Newton
... 21. How are the forces in each force pair related? _____________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ 22. What action and reaction forces are present when you are sitting on a chair? _______________ ________________________________________ ...
... 21. How are the forces in each force pair related? _____________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ 22. What action and reaction forces are present when you are sitting on a chair? _______________ ________________________________________ ...
Gravity and Motion
... friction), free fall can occur only where there is no air - in a vacuum (a place in which there is no matter) or in space. • Astronauts “float” in orbiting spaceships because of free fall. ...
... friction), free fall can occur only where there is no air - in a vacuum (a place in which there is no matter) or in space. • Astronauts “float” in orbiting spaceships because of free fall. ...
Review for Intro. Physics Part A Final Exam
... bicycle goes from rest to 5km/h which has a a) car greater b) bike acceleration? c) same same d) I don’t know ...
... bicycle goes from rest to 5km/h which has a a) car greater b) bike acceleration? c) same same d) I don’t know ...
HW#5b Page 1 of 4 1 * 0.111111 3 F F F = = 1 * 0.0657 3.9 F F F = =
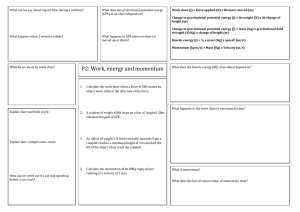
... The object is lowered down by distance x, the gravitational potential decreases by mgx. The higher it is, the larger the gravitational potential. Problem 7. You and a friend both solve a problem involving a skier going down a slope. When comparing solutions, you notice that your choice for the y = 0 ...
... The object is lowered down by distance x, the gravitational potential decreases by mgx. The higher it is, the larger the gravitational potential. Problem 7. You and a friend both solve a problem involving a skier going down a slope. When comparing solutions, you notice that your choice for the y = 0 ...