SEISMIC SLEUTHS
... ______ is directly related to _____. • The greater the mass the greater the tendency to ___________change of an object’s motion. • objects will continue to do as they are doing __________ __________. ...
... ______ is directly related to _____. • The greater the mass the greater the tendency to ___________change of an object’s motion. • objects will continue to do as they are doing __________ __________. ...
Newton`s First and Second Laws
... An object at rest will remain at rest, and an object moving at a constant velocity will continue moving at a constant velocity, unless acted upon by an unbalanced force Clothes on the floor will stay there unless someone uses a force to pick them up A tennis ball that was hit will continue until a f ...
... An object at rest will remain at rest, and an object moving at a constant velocity will continue moving at a constant velocity, unless acted upon by an unbalanced force Clothes on the floor will stay there unless someone uses a force to pick them up A tennis ball that was hit will continue until a f ...
Guide_Test1
... 6. Free-Fall; Roger tosses a ball straight upward at speed 32 m/s. Calculate the maximum height of the ball. Calculate the time in seconds that it takes for the ball to reach its maximum height. (Note: at the highest point velocity = 0 m/s, accl. = 9.8 m/s2 acting downward) 7. Also, the hints at end ...
... 6. Free-Fall; Roger tosses a ball straight upward at speed 32 m/s. Calculate the maximum height of the ball. Calculate the time in seconds that it takes for the ball to reach its maximum height. (Note: at the highest point velocity = 0 m/s, accl. = 9.8 m/s2 acting downward) 7. Also, the hints at end ...
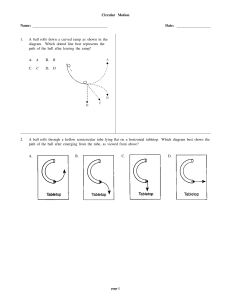
Circular Motion Name: Date: 1. A ball rolls down a curved ramp as
... The diagram shows an object with a mass of 1.0 kilogram attached to a string 0.50 meter long. The object is moving at a constant speed of 5.0 meters per second in a horizontal circular path with center at point O. ...
... The diagram shows an object with a mass of 1.0 kilogram attached to a string 0.50 meter long. The object is moving at a constant speed of 5.0 meters per second in a horizontal circular path with center at point O. ...
If you put your cursor over a text box, it will be an arrow and WILL
... Which of the following is an example of acceleration? a) A runner moving at a constant speed of 2 m/s in a straight line. b) A car going at a constant speed around a circular track. c) An airplane taxiing at a constant speed in a straight line. d) All of the above. ...
... Which of the following is an example of acceleration? a) A runner moving at a constant speed of 2 m/s in a straight line. b) A car going at a constant speed around a circular track. c) An airplane taxiing at a constant speed in a straight line. d) All of the above. ...
Class14
... a , F and v are constantly changing •However, the magnitudes a, F, v and r are constants of the motion. •The frame in which the mass is moving is not inertial, i.e. it is accelerating. ...
... a , F and v are constantly changing •However, the magnitudes a, F, v and r are constants of the motion. •The frame in which the mass is moving is not inertial, i.e. it is accelerating. ...
Lecture 8: Forces & The Laws of Motion
... Questions of Yesterday 1) You are going through a vertical loop on roller coaster at a constant speed. At what point is the force exerted by the tracks on you (and the cart you are in) the greatest? a) at the highest point b) at the lowest point c) halfway between the highest and lowest point d) th ...
... Questions of Yesterday 1) You are going through a vertical loop on roller coaster at a constant speed. At what point is the force exerted by the tracks on you (and the cart you are in) the greatest? a) at the highest point b) at the lowest point c) halfway between the highest and lowest point d) th ...
Newton`s First Law- Every object remains at rest or moves at a
... Net Force- sum of all forces acting on an object ...
... Net Force- sum of all forces acting on an object ...
Complete the following on a separate sheet of paper
... 7. If a car is able to accelerate at 6.0 m/s2, what acceleration can it attain if it is towing another car of equal mass? Explain your answer. 8. A constant unchanging force of 30.25 N is applied to a 12.02 kg object for exactly 15.00 seconds. What is the final velocity of the object after the 15.00 ...
... 7. If a car is able to accelerate at 6.0 m/s2, what acceleration can it attain if it is towing another car of equal mass? Explain your answer. 8. A constant unchanging force of 30.25 N is applied to a 12.02 kg object for exactly 15.00 seconds. What is the final velocity of the object after the 15.00 ...