CH02-2 Constant Net Force in 2D or 3D Summary of Analytic
... The component of velocity that is perpendicular to the net force remains constant. The component of velocity that is parallel to the net force changes at a constant rate, increasing in magnitude if in the direction of the net force and decreasing in magnitude if opposite the direction of the net for ...
... The component of velocity that is perpendicular to the net force remains constant. The component of velocity that is parallel to the net force changes at a constant rate, increasing in magnitude if in the direction of the net force and decreasing in magnitude if opposite the direction of the net for ...
Midterm Review - MrStapleton.com
... a. Bob wants to lift Pam a vertical distance of 0.5m. How much work must Bob do to accomplish this? b. If Bob grabs the end of the board, he has to lift the board 1m in order to lift Pam 0.5m. How much force will Bob need to apply? c. How much torque is Pam generating? d. The torque created by Pam s ...
... a. Bob wants to lift Pam a vertical distance of 0.5m. How much work must Bob do to accomplish this? b. If Bob grabs the end of the board, he has to lift the board 1m in order to lift Pam 0.5m. How much force will Bob need to apply? c. How much torque is Pam generating? d. The torque created by Pam s ...
Name - cloudfront.net
... direction the amount of matter in an object object’s speed in a particular direction the unit used for force A change in motion caused by unbalanced forces or a change in velocity the forces acting on an object that are equal in size and opposite in direction, canceling each other out A measure of h ...
... direction the amount of matter in an object object’s speed in a particular direction the unit used for force A change in motion caused by unbalanced forces or a change in velocity the forces acting on an object that are equal in size and opposite in direction, canceling each other out A measure of h ...
Introduction to Forces- Reading 3: Balanced
... Once we understand the notation we will use for describing forces, we are ready to deal with a much more important idea than forces alone. Where motion is concerned, any single force acting on an object typically tells you very little, unless there is only one force acting on the object. Most of the ...
... Once we understand the notation we will use for describing forces, we are ready to deal with a much more important idea than forces alone. Where motion is concerned, any single force acting on an object typically tells you very little, unless there is only one force acting on the object. Most of the ...
Work, Power, and Energy - Atlanta International School Moodle
... 1. The work it does on a moving object is independent of the path of the motion between the object's initial and final position. 2. The work it does moving an object around a closed path is zero 3. The work it does is stored in the form of energy that can be released at a later time. 4. Work done by ...
... 1. The work it does on a moving object is independent of the path of the motion between the object's initial and final position. 2. The work it does moving an object around a closed path is zero 3. The work it does is stored in the form of energy that can be released at a later time. 4. Work done by ...
Chapter 7 - Legacy High School
... • Cavendish applied Newton’s law of universal gravitation to find the value of G and Earth’s mass. • When two masses, the distance between them, and the gravitational force are known, Newton’s law of universal gravitation can be used to find G. • Once the value of G is known, the law can be used aga ...
... • Cavendish applied Newton’s law of universal gravitation to find the value of G and Earth’s mass. • When two masses, the distance between them, and the gravitational force are known, Newton’s law of universal gravitation can be used to find G. • Once the value of G is known, the law can be used aga ...
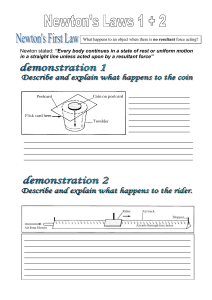
3_Newton_s_Laws_1_2
... _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ...
... _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ...
PRACExam-00
... d. is created in a vacuum only O 58. A falling ball thrown from the top of a building would be said to have accelerated motion because it would: a. follow a straight path b. fall with a constant speed N c. strike the ground with a certain force d. increase its speed during each second it is falling ...
... d. is created in a vacuum only O 58. A falling ball thrown from the top of a building would be said to have accelerated motion because it would: a. follow a straight path b. fall with a constant speed N c. strike the ground with a certain force d. increase its speed during each second it is falling ...
Performance Benchmark E
... a force. And lastly, his Third Law describes what happens when objects interacting. Newton’s Third Law states that for every action force, there is an equal and opposite reaction force. This law is also known as the Law of Action-Reaction Pair. A force is a push or pull upon an object, which results ...
... a force. And lastly, his Third Law describes what happens when objects interacting. Newton’s Third Law states that for every action force, there is an equal and opposite reaction force. This law is also known as the Law of Action-Reaction Pair. A force is a push or pull upon an object, which results ...