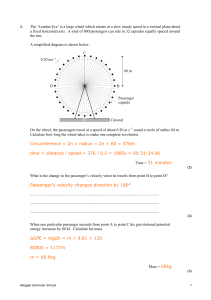
EXAM 3 - University of Utah Physics
... Place a circle or box around each answer. Specify units for each answer. Report all numbers to two significant figures. ...
... Place a circle or box around each answer. Specify units for each answer. Report all numbers to two significant figures. ...
Newton`s Law of Motion
... Balanced Forces • The net force on the box is zero because the two forces cancel each other. • Forces on an object that are equal in size and opposite in direction are called balanced forces. ...
... Balanced Forces • The net force on the box is zero because the two forces cancel each other. • Forces on an object that are equal in size and opposite in direction are called balanced forces. ...
Solutions7
... proton is shown to the right. We know that, because the proton enters the field perpendicularly to the field, its trajectory while in the field will be circular. We can use symmetry considerations to determine . The application of Newton’s 2nd law to the proton while it is in the magnetic field and ...
... proton is shown to the right. We know that, because the proton enters the field perpendicularly to the field, its trajectory while in the field will be circular. We can use symmetry considerations to determine . The application of Newton’s 2nd law to the proton while it is in the magnetic field and ...
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
... Identical masses m are attached to identical springs of spring constant k suspended from the ceiling. With both masses hanging in their equilibrium positions, mass A is pulled down 10 cm and released, while mass B is pushed up 10 cm and released. Which is correct? a) Mass A will travel a smaller dis ...
... Identical masses m are attached to identical springs of spring constant k suspended from the ceiling. With both masses hanging in their equilibrium positions, mass A is pulled down 10 cm and released, while mass B is pushed up 10 cm and released. Which is correct? a) Mass A will travel a smaller dis ...
SCIENCE (PHYSICS, CHEMISTRY) Additional materials: Answer
... If we put an unknown object on the right end, there must be a 2N force exerting on the left end to make the rod balanced in horizontal position. Then we put the same unknown object on the left end of the rod, there must be an 8N force exerting on the right end to balance the rod in horizontal positi ...
... If we put an unknown object on the right end, there must be a 2N force exerting on the left end to make the rod balanced in horizontal position. Then we put the same unknown object on the left end of the rod, there must be an 8N force exerting on the right end to balance the rod in horizontal positi ...
Big Idea
... Big Idea: All forces arise from the interactions between different objects. Concept: When two surfaces of objects are in contact with each other, the force of friction between them depends on the nature of the materials in contact and the normal force. Competency: Construct a free body diagram indic ...
... Big Idea: All forces arise from the interactions between different objects. Concept: When two surfaces of objects are in contact with each other, the force of friction between them depends on the nature of the materials in contact and the normal force. Competency: Construct a free body diagram indic ...