Jeopardy Force
... Answer A 9.00-kg object is moving in a circle with a constant speed of 45.0 m/s. If the circular path has a radius of 20.0 m, what is the net force on the object? F = mv²/r = (9.00kg)*(45 m/s)²/(20.0m) = 911 N ...
... Answer A 9.00-kg object is moving in a circle with a constant speed of 45.0 m/s. If the circular path has a radius of 20.0 m, what is the net force on the object? F = mv²/r = (9.00kg)*(45 m/s)²/(20.0m) = 911 N ...
Newton`s Third Law
... Force and Changing Momentum By ___________________ these two relationships, Newton’s second law can be written in this way: _____________________________________________ In this equation __________ is the final momentum and ___________is the initial momentum • Law of Conservation of Momentum The mom ...
... Force and Changing Momentum By ___________________ these two relationships, Newton’s second law can be written in this way: _____________________________________________ In this equation __________ is the final momentum and ___________is the initial momentum • Law of Conservation of Momentum The mom ...
The Age of Einstein
... Fitzgerald, Larmor, and other physicists at that time considered length contraction and time dilation to be “real” effects, associated with minute physical changes in the structure of rods and clocks when in motion. It was left to the young Einstein, working as a junior Patent Officer in Bern, and t ...
... Fitzgerald, Larmor, and other physicists at that time considered length contraction and time dilation to be “real” effects, associated with minute physical changes in the structure of rods and clocks when in motion. It was left to the young Einstein, working as a junior Patent Officer in Bern, and t ...
Problem Set III Solutions
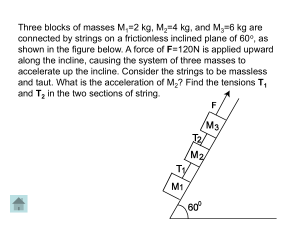
... In this case, you can always make m big enough to have the total force be large enough to pull M up the hill. (Please note that in solving this problem I assumed that either the system was stationary or just beginning to move. This means that mg = T by the equation of motion for m. However, once the ...
... In this case, you can always make m big enough to have the total force be large enough to pull M up the hill. (Please note that in solving this problem I assumed that either the system was stationary or just beginning to move. This means that mg = T by the equation of motion for m. However, once the ...
Conceptual Physics
... Read all key terms. Underline all words you are unfamiliar with. Then go back and create a flash card for each term. Use the term in a sentence, define it, or draw a picture for the term. Vocabulary 1. accuracy 2. precision 3. dependent variable 4. independent variable 5. experiment 6. hypothesis 7. ...
... Read all key terms. Underline all words you are unfamiliar with. Then go back and create a flash card for each term. Use the term in a sentence, define it, or draw a picture for the term. Vocabulary 1. accuracy 2. precision 3. dependent variable 4. independent variable 5. experiment 6. hypothesis 7. ...
unit - 4: dynamics
... parachute falling under gravity. If a heavy stone and a parachute are dropped where there is no air, both will fall together at the same rate. Experiments showed that the velocity of a freely falling body under gravity increases at a constant rate. i.e., with a constant acceleration. The acceleratio ...
... parachute falling under gravity. If a heavy stone and a parachute are dropped where there is no air, both will fall together at the same rate. Experiments showed that the velocity of a freely falling body under gravity increases at a constant rate. i.e., with a constant acceleration. The acceleratio ...
Document
... conversion of energy from one form into another • work must first be done in lifting the cars to the top of the first hill. • the work is stored as gravitational potential energy • you are then on your way! ...
... conversion of energy from one form into another • work must first be done in lifting the cars to the top of the first hill. • the work is stored as gravitational potential energy • you are then on your way! ...
Secondary Robot
... law of motion, the acceleration of an object is a quantifiable concept. We are able to use this Law of Motion to make predictions about the acceleration of an object given the net force and mass. The implications here are four fold: 1) if the net force increases and the mass stays the same the accel ...
... law of motion, the acceleration of an object is a quantifiable concept. We are able to use this Law of Motion to make predictions about the acceleration of an object given the net force and mass. The implications here are four fold: 1) if the net force increases and the mass stays the same the accel ...