Physics 2A Chapter 5 HW Solutions
... Thus Fnet = 0. It is tempting to think that the belt exerts a friction force on the crate. But if it did, there would be a net force because there are no other possible horizontal forces to balance a friction force. Because there is no net force, there cannot be a friction force. The only forces are ...
... Thus Fnet = 0. It is tempting to think that the belt exerts a friction force on the crate. But if it did, there would be a net force because there are no other possible horizontal forces to balance a friction force. Because there is no net force, there cannot be a friction force. The only forces are ...
Conservation of Momentum
... Two ice skaters, with masses of 45 kg and 65 kg, are at rest and facing each other over a surface of ice. They push off from each other and the 45 kg skater moves away with a velocity of 6 m/s. Find the final velocity of the 65 kg skater. ...
... Two ice skaters, with masses of 45 kg and 65 kg, are at rest and facing each other over a surface of ice. They push off from each other and the 45 kg skater moves away with a velocity of 6 m/s. Find the final velocity of the 65 kg skater. ...
Rotational Equilibrium and Dynamics1 Net torque: Add up individual
... a. Remember to resolve into components for forces acting at an angle 2. Add up all forces acting on the object Second condition of equilibrium 1. Choose an axis for the object to rotate around (torque). a. The axis chosen doesn’t matter, so choose an axis that will help you! An unknown force that ac ...
... a. Remember to resolve into components for forces acting at an angle 2. Add up all forces acting on the object Second condition of equilibrium 1. Choose an axis for the object to rotate around (torque). a. The axis chosen doesn’t matter, so choose an axis that will help you! An unknown force that ac ...
File - Mrs. Hart`s Science Place
... A. The soccer ball is moving and the basketball is not moving. If the soccer ball is moving to the right and hits the basketball, in which direction will the basketball move? The basketball will move to the right B. The basketball has a mass of 10 kg. If it is accelerating at a rate of 3 m/s/s, what ...
... A. The soccer ball is moving and the basketball is not moving. If the soccer ball is moving to the right and hits the basketball, in which direction will the basketball move? The basketball will move to the right B. The basketball has a mass of 10 kg. If it is accelerating at a rate of 3 m/s/s, what ...
Physical Quantities: Dimensions and Units
... object’s velocity with respect to time) force (“push” or “pull” that can change an object’s motion) (Note that weight is just a special case of a force— the force of gravity) ...
... object’s velocity with respect to time) force (“push” or “pull” that can change an object’s motion) (Note that weight is just a special case of a force— the force of gravity) ...
Name of Model
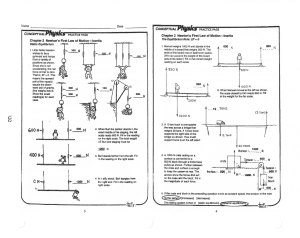
... 1. For each of the drawings below, draw a system schema labeling all the objects and forces present. Then draw a free body diagram. If necessary, draw another diagram showing the components of any forces. Be sure to include any equality marks if there are forces (or ...
... 1. For each of the drawings below, draw a system schema labeling all the objects and forces present. Then draw a free body diagram. If necessary, draw another diagram showing the components of any forces. Be sure to include any equality marks if there are forces (or ...
Psc CH-06
... • Its direction is the same direction as the acceleration of the object barring any resistive forces ...
... • Its direction is the same direction as the acceleration of the object barring any resistive forces ...
Stacey Carpenter
... Isaac Newton is one of the most famous scientists. His formula, F = ma, is the most important formula in early physics and, along with Einstein's E = mc2, is one of the two best-known formulas in all of physics. Newton looked at the movement of objects, just as Galileo did. He started with inertia ...
... Isaac Newton is one of the most famous scientists. His formula, F = ma, is the most important formula in early physics and, along with Einstein's E = mc2, is one of the two best-known formulas in all of physics. Newton looked at the movement of objects, just as Galileo did. He started with inertia ...
Document
... Newton’s first law is valid. This excludes rotating and accelerating frames. How can we tell if we are in an inertial reference frame? By checking to see if Newton’s first law holds! Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... Newton’s first law is valid. This excludes rotating and accelerating frames. How can we tell if we are in an inertial reference frame? By checking to see if Newton’s first law holds! Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Dynamics Multiple Choice Homework
... A. less than zero B. between zero and Mg C. equal to Mg D. greater than Mg E. zero 33. An elevator of mass M is pulled upwards by a cable; the elevator has a positive, but decreasing, velocity. What is the tension in the cable (neglecting the mass of the cable)? A. less than zero B. between zero and ...
... A. less than zero B. between zero and Mg C. equal to Mg D. greater than Mg E. zero 33. An elevator of mass M is pulled upwards by a cable; the elevator has a positive, but decreasing, velocity. What is the tension in the cable (neglecting the mass of the cable)? A. less than zero B. between zero and ...





![1.[12 pts] A figure skater is spinning with an angular velocity of +15](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017172838_1-3a9cad339920c851c005a2a4ec9a91cf-300x300.png)