1 enzyme catalysis lab protocol
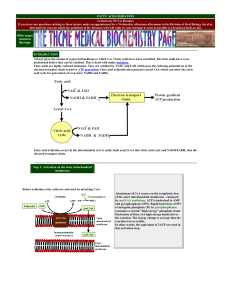
... to the active site of the enzyme. One result of this temporary bond is a reduction in the energy required to activate the reaction of the substrate molecule so that the products of the reaction are formed more easily. Note that the enzyme are not changed in thee reactions and can be recycled to brea ...
... to the active site of the enzyme. One result of this temporary bond is a reduction in the energy required to activate the reaction of the substrate molecule so that the products of the reaction are formed more easily. Note that the enzyme are not changed in thee reactions and can be recycled to brea ...
Lecture 15 (Parker) - Department of Chemistry ::: CALTECH
... Citric acid cycle=Krebs cycle=tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle Acetyl CoA ...
... Citric acid cycle=Krebs cycle=tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle Acetyl CoA ...
Two-electron effects pervading the formation of highly excited
... PACS numbers: 33.80.Rv, 34.80.Gs, 42.50.Hz ...
... PACS numbers: 33.80.Rv, 34.80.Gs, 42.50.Hz ...
2.8 Respiration
... • Cell respiration is the controlled release of energy from organic compounds in cells to form ATP. • ATP or Adenosine triphosphates is the molecule which directly fuels the majority of biological reactions. – Everyday each person will hydrolyse (reduce) 1025 ATP molecules to ADP. – The ADP is reduc ...
... • Cell respiration is the controlled release of energy from organic compounds in cells to form ATP. • ATP or Adenosine triphosphates is the molecule which directly fuels the majority of biological reactions. – Everyday each person will hydrolyse (reduce) 1025 ATP molecules to ADP. – The ADP is reduc ...
Micro Chapter 5 ppt. 11th edition
... (c) Substrate concentration. With increasing concentration of substrate molecules, the rate of reaction increases until the active sites on all the enzyme molecules are filled, at which point the maximum rate of reaction is reached. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... (c) Substrate concentration. With increasing concentration of substrate molecules, the rate of reaction increases until the active sites on all the enzyme molecules are filled, at which point the maximum rate of reaction is reached. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Diffusion
... concentration to an area of low concentration. They are said to move down a concentration gradient. Diffusion is a passive process which means that no energy is needed. ...
... concentration to an area of low concentration. They are said to move down a concentration gradient. Diffusion is a passive process which means that no energy is needed. ...
- Te Kura
... carries out all its life processes. This includes its interactions with its biotic and abiotic environment, such as: •• its relationships with other organisms •• its reproductive strategies to ensure the species survives •• the resources and opportunities provided by the habitat •• and the adaptatio ...
... carries out all its life processes. This includes its interactions with its biotic and abiotic environment, such as: •• its relationships with other organisms •• its reproductive strategies to ensure the species survives •• the resources and opportunities provided by the habitat •• and the adaptatio ...
C - 鄭智美的Homepage
... – Consumes oxygen and organic molecules such as glucose – Yields ATP Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... – Consumes oxygen and organic molecules such as glucose – Yields ATP Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Connecting Proline and γ-Aminobutyric Acid in Stressed
... distances of these groups become shorter, resembling to the CO2 molecule. When the abstraction occurred from 5-endo Pro no minima was found on the product side until a complete dissociation of the carboxyl group occurs (the final C1-C2 distance is 2.711 Å, and the value of the O1-C1-O2 angle is 173. ...
... distances of these groups become shorter, resembling to the CO2 molecule. When the abstraction occurred from 5-endo Pro no minima was found on the product side until a complete dissociation of the carboxyl group occurs (the final C1-C2 distance is 2.711 Å, and the value of the O1-C1-O2 angle is 173. ...
Living Things - Somerset Area School District
... Seed Plants - Plant Responses and Growth Relating Cause and Effect A cause makes something happen. An effect is what happens. As you read through the paragraphs under the heading “Hormones and Tropisms," identify four effects of plant hormones. Write the information in a graphic organizer like the ...
... Seed Plants - Plant Responses and Growth Relating Cause and Effect A cause makes something happen. An effect is what happens. As you read through the paragraphs under the heading “Hormones and Tropisms," identify four effects of plant hormones. Write the information in a graphic organizer like the ...
Grandma Johnson Diagnostic Question Cluster
... Carbon transformations are occurring everywhere in a forest. Plants are photosynthesizing, generating organic carbon from carbon dioxide. Organic carbon is being transformed into other organic sources within plants, and between organisms through processes such as biosynthesis and digestion. All orga ...
... Carbon transformations are occurring everywhere in a forest. Plants are photosynthesizing, generating organic carbon from carbon dioxide. Organic carbon is being transformed into other organic sources within plants, and between organisms through processes such as biosynthesis and digestion. All orga ...
Lab 5 Sugar Fermentation in Yeast
... transport chain (a chain of proteins found on the inner membrane of the mitochondria). Both alcoholic and lactic acid fermentation involve only glycolysis. Since both the Kreb’s cycle and the electron transport chain require oxygen to function, neither process can occur under anaerobic conditions. F ...
... transport chain (a chain of proteins found on the inner membrane of the mitochondria). Both alcoholic and lactic acid fermentation involve only glycolysis. Since both the Kreb’s cycle and the electron transport chain require oxygen to function, neither process can occur under anaerobic conditions. F ...
1 Carbon and Energy in Ecosystems Diagnostic Question
... Carbon transformations are occurring everywhere in a forest. Plants are photosynthesizing, generating organic carbon from carbon dioxide. Organic carbon is being transformed into other organic sources within plants, and between organisms through processes such as biosynthesis and digestion. All orga ...
... Carbon transformations are occurring everywhere in a forest. Plants are photosynthesizing, generating organic carbon from carbon dioxide. Organic carbon is being transformed into other organic sources within plants, and between organisms through processes such as biosynthesis and digestion. All orga ...
PDF - MD Body and Med spa
... Alternatively you can email any problems to Dr. Brookes who will reply to your message as soon as possible ([email protected]). Other pages related to this topic ...
... Alternatively you can email any problems to Dr. Brookes who will reply to your message as soon as possible ([email protected]). Other pages related to this topic ...
2.8 Respiration - biology4friends
... used as a fuel in vehicles, sometimes in a pure state and sometimes mixed with gasoline (petrol). Describe how bioethanol can be produced from plant material with reference to the function of yeast in the process. ...
... used as a fuel in vehicles, sometimes in a pure state and sometimes mixed with gasoline (petrol). Describe how bioethanol can be produced from plant material with reference to the function of yeast in the process. ...
Energy for Cells
... CO2 and H2O. Per glucose molecule, there is a net gain of 2 ATP from glycolysis, which takes place in the cytoplasm. The citric acid cycle, which occurs in the matrix of mitochondria, accounts for 2 ATP per glucose molecule. This means that a total of 4 ATP form due to substrate-level ATP synthesis ...
... CO2 and H2O. Per glucose molecule, there is a net gain of 2 ATP from glycolysis, which takes place in the cytoplasm. The citric acid cycle, which occurs in the matrix of mitochondria, accounts for 2 ATP per glucose molecule. This means that a total of 4 ATP form due to substrate-level ATP synthesis ...
Stoichiometry - ChemistryatBiotech
... Sulfuric acid, an important chemical in industry, is manufactured and sold by XYZ company. • Sulfur dioxide gas is combined with water and oxygen to make H₂SO₄. • The company is expecting a shipment of 500 kg of SO₂ and wants to know how much H₂SO₄ can be made from this shipment. ...
... Sulfuric acid, an important chemical in industry, is manufactured and sold by XYZ company. • Sulfur dioxide gas is combined with water and oxygen to make H₂SO₄. • The company is expecting a shipment of 500 kg of SO₂ and wants to know how much H₂SO₄ can be made from this shipment. ...
Fisheries Fact Sheet - Mangrove
... either broken down by fungi and bacteria, eaten by crabs that live on the forest floor or are carried into marine and estuarine habitats where they are eaten by a variety of fish, crabs and other invertebrates. Decaying organic material breaks down into small particles (detritus) which are quickly c ...
... either broken down by fungi and bacteria, eaten by crabs that live on the forest floor or are carried into marine and estuarine habitats where they are eaten by a variety of fish, crabs and other invertebrates. Decaying organic material breaks down into small particles (detritus) which are quickly c ...
LESSON 5 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION The
... hemoglobin molecule. Hemoglobin then carries the oxygen to the cells where internal respiration removes the oxygen into the cell and allows the waste carbon dioxide to attach to the hemoglobin and then be removed from the body. Inside the cell membrane, oxygen is used in a process called cellular re ...
... hemoglobin molecule. Hemoglobin then carries the oxygen to the cells where internal respiration removes the oxygen into the cell and allows the waste carbon dioxide to attach to the hemoglobin and then be removed from the body. Inside the cell membrane, oxygen is used in a process called cellular re ...
Human Biology The Chemistry of Living Things 2.1 Multiple Choice
... A) slow down the speed at which chemical reactions occur, but do not alter the final products formed B) facilitate chemical reactions by altering the final products formed C) maintain primary structure D) can participate only in reactions that synthesize new products E) are referred to as enzymes An ...
... A) slow down the speed at which chemical reactions occur, but do not alter the final products formed B) facilitate chemical reactions by altering the final products formed C) maintain primary structure D) can participate only in reactions that synthesize new products E) are referred to as enzymes An ...
Respiration Notes
... the amount of cartilage in their walls decreases and the amount of smooth muscle ...
... the amount of cartilage in their walls decreases and the amount of smooth muscle ...
lopez 09_Lecture_Presentation
... CALLED THE REDUCING AGENT (THIS IS THE OIL PART) THE ELECTRON RECEPTOR IS CALLED THE OXIDIZING AGENT (THIS IS THE RIG PART) SOME REDOX REACTIONS DO NOT TRANSFER ELECTRONS BUT CHANGE THE ELECTRON SHARING IN COVALENT BONDS AN EXAMPLE IS THE REACTION BETWEEN Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., ...
... CALLED THE REDUCING AGENT (THIS IS THE OIL PART) THE ELECTRON RECEPTOR IS CALLED THE OXIDIZING AGENT (THIS IS THE RIG PART) SOME REDOX REACTIONS DO NOT TRANSFER ELECTRONS BUT CHANGE THE ELECTRON SHARING IN COVALENT BONDS AN EXAMPLE IS THE REACTION BETWEEN Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., ...
Topic 1 Patterns in Nature
... Living things use raw materials in different ways to construct new living tissues and repair existing tissues. All living organisms carry out similar processes to form the structures that make up their bodies. To carry out these processes, raw materials need to be obtained. The types of raw material ...
... Living things use raw materials in different ways to construct new living tissues and repair existing tissues. All living organisms carry out similar processes to form the structures that make up their bodies. To carry out these processes, raw materials need to be obtained. The types of raw material ...
Respiratory System
... relate to cellular respiration? How does the circulatory system relate to the respiratory system and to cellular respiration? ...
... relate to cellular respiration? How does the circulatory system relate to the respiratory system and to cellular respiration? ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.