Introduction to Cellular Respiration •ATP is needed in order for cells
... •Each protein in the chain oscillates between reduced and oxidized states as the energetic electrons from NADH and FADH2 pass through their region. ...
... •Each protein in the chain oscillates between reduced and oxidized states as the energetic electrons from NADH and FADH2 pass through their region. ...
2013 Ecology Review
... MULTIPLE CHOICE Circle ALL that are true. There may be more than one correct answer. During which process do plants use carbon dioxide? A. cellular respiration B. photosynthesis C. denitrification D. transpiration In the nitrogen cycle, bacteria that live in soil and on plant roots in a symbiotic r ...
... MULTIPLE CHOICE Circle ALL that are true. There may be more than one correct answer. During which process do plants use carbon dioxide? A. cellular respiration B. photosynthesis C. denitrification D. transpiration In the nitrogen cycle, bacteria that live in soil and on plant roots in a symbiotic r ...
Document
... - As a result of hydration synthesis monomers gain or store energy. - Also referred to as a hydrolysis reaction, because water is added and then broken apart during the reaction ...
... - As a result of hydration synthesis monomers gain or store energy. - Also referred to as a hydrolysis reaction, because water is added and then broken apart during the reaction ...
29 Cellular Respiration Biology “B”
... _____ 3.) The definition of glycolysis is: a.) the breakage of lipids b.) the breakage of protein c.) glyco- referring to glucose and -lysis, meaning to break d.) the creation starch _____ 4.) Glucose breaks into: a.) 3 pyruvate b.)oxygen and water c.) 2 pyruvate d.) none of these _____ 5.) Pyruvate ...
... _____ 3.) The definition of glycolysis is: a.) the breakage of lipids b.) the breakage of protein c.) glyco- referring to glucose and -lysis, meaning to break d.) the creation starch _____ 4.) Glucose breaks into: a.) 3 pyruvate b.)oxygen and water c.) 2 pyruvate d.) none of these _____ 5.) Pyruvate ...
Plant and Animal Structure Unit
... place in chloroplasts of leaf cells. Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll. “chloro” is a Greek word for “green”. Chlorophyll makes plants green in color. Chlorophyll captures energy from sunlight. ...
... place in chloroplasts of leaf cells. Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll. “chloro” is a Greek word for “green”. Chlorophyll makes plants green in color. Chlorophyll captures energy from sunlight. ...
Document
... a layer of cells called the epidermis (B). The vascular tissue, xylem and phloem are found within the veins of the leaf. Veins are actually extensions that run from to tips of the roots all the way up to the edges of the leaves. The outer layer of the vein is made of cells called bundle sheath cells ...
... a layer of cells called the epidermis (B). The vascular tissue, xylem and phloem are found within the veins of the leaf. Veins are actually extensions that run from to tips of the roots all the way up to the edges of the leaves. The outer layer of the vein is made of cells called bundle sheath cells ...
biochem notes
... Peptide Bond • Covalent bond linking two amino acids • A condensation reaction (water is formed and released) • Long chains of amino acids has positive and negative regions which fold to give protein molecules unique shapes • The shapes can be denatured when heated ...
... Peptide Bond • Covalent bond linking two amino acids • A condensation reaction (water is formed and released) • Long chains of amino acids has positive and negative regions which fold to give protein molecules unique shapes • The shapes can be denatured when heated ...
Ecology Chapter 3-1
... ecosystems. • These cycles are the water cycle, Nutrient Cycle, Carbon Cycle, nitrogen cycle and ...
... ecosystems. • These cycles are the water cycle, Nutrient Cycle, Carbon Cycle, nitrogen cycle and ...
lecture 02b
... – Cofactors have an effect on nutrition • Bacteria have certain mineral requirements. • Vitamins are cofactors that are needed in the “diet”. ...
... – Cofactors have an effect on nutrition • Bacteria have certain mineral requirements. • Vitamins are cofactors that are needed in the “diet”. ...
BY 123 Mock Exam #2 Answer Key Chapters 8,9,10,12,13 Catabolic
... 15) Which of the following statements correctly describes the role of oxygen in cellular respiration? a. It is reduced in glycolysis as glucose is oxidized b. It combines with H+ diffusing through ATP sythase to produce H2O c. It provides the activation energy needed for oxidation to occur d. It is ...
... 15) Which of the following statements correctly describes the role of oxygen in cellular respiration? a. It is reduced in glycolysis as glucose is oxidized b. It combines with H+ diffusing through ATP sythase to produce H2O c. It provides the activation energy needed for oxidation to occur d. It is ...
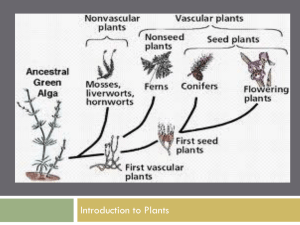
Chapter 9: Fungi and Aquatic Plants
... • Most biologists believe that true land pants probably evolved from green algae. • It is also believed that the early invasion of land plants was facilitated by symbiotic relationships between fungi and plants via mycorrhizal. That is, the fungi helped supply nutrients to the roots of the land plan ...
... • Most biologists believe that true land pants probably evolved from green algae. • It is also believed that the early invasion of land plants was facilitated by symbiotic relationships between fungi and plants via mycorrhizal. That is, the fungi helped supply nutrients to the roots of the land plan ...
Ch 3-4 Reading Guide
... 47. Which of the following describes how ALL consumers get their energy? a. Directly from the sun b. From eating primary producers c. From inorganic chemicals like hydrogen sulfide d. From eating organisms that are living or were once living 48. Nutrients move through an ecosystem in a. Biogeochemi ...
... 47. Which of the following describes how ALL consumers get their energy? a. Directly from the sun b. From eating primary producers c. From inorganic chemicals like hydrogen sulfide d. From eating organisms that are living or were once living 48. Nutrients move through an ecosystem in a. Biogeochemi ...
Chapter 8
... • Phosphorylation of some intermediates (Uses 2 ATPs) • 1) Where does it take place? • Splits a 6 carbon sugar into two 3 carbon molecules (pyruvic acid) • Coenzyme NAD is reduced to NADH • Substrate-level-phosphorylation (4 ATPs are synthesized but 2 are used!!!) • NET YIELD = 2 ATP + 2 NADH + 2 py ...
... • Phosphorylation of some intermediates (Uses 2 ATPs) • 1) Where does it take place? • Splits a 6 carbon sugar into two 3 carbon molecules (pyruvic acid) • Coenzyme NAD is reduced to NADH • Substrate-level-phosphorylation (4 ATPs are synthesized but 2 are used!!!) • NET YIELD = 2 ATP + 2 NADH + 2 py ...
If you did a 10 minute wall sit, what would your muscles start to feel
... If you did a 10 minute wall sit, what would your muscles start to feel like? Why do they begin to feel like that? ...
... If you did a 10 minute wall sit, what would your muscles start to feel like? Why do they begin to feel like that? ...
life processes
... Transport of water and minerals in the plant. ii. Transport of food and other substances in the plant. B. Transportation in human beings The main transport system in human beings is the blood circulatory system. In the human circulatory system, the blood caries oxygen, digested food and other ch ...
... Transport of water and minerals in the plant. ii. Transport of food and other substances in the plant. B. Transportation in human beings The main transport system in human beings is the blood circulatory system. In the human circulatory system, the blood caries oxygen, digested food and other ch ...
Document
... Name: _______________________________ Period: ___________ Date: _____________ 5. Compare and contrast hydrolysis reactions with condensation reaction. A condensation reaction chemically bonds monomers to create polymers by the release of a water molecules. A hydrolysis reaction breaks polymers apar ...
... Name: _______________________________ Period: ___________ Date: _____________ 5. Compare and contrast hydrolysis reactions with condensation reaction. A condensation reaction chemically bonds monomers to create polymers by the release of a water molecules. A hydrolysis reaction breaks polymers apar ...
Biology Objective 3
... When testing an hypothesis, there should be only one variable changed at a time. If this is not possible, then all possible reasons for an outcome need to be considered. In this case, carbon dioxide can be produced by chemical reactions other than cellular respiration, which is a biotic process. Tha ...
... When testing an hypothesis, there should be only one variable changed at a time. If this is not possible, then all possible reasons for an outcome need to be considered. In this case, carbon dioxide can be produced by chemical reactions other than cellular respiration, which is a biotic process. Tha ...
EXCHANGE IN MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS
... • NOSE/MOUTHTRACHEABRON CHI • ALVEOLI (CAVITIES CONTAINING CAPILLARIES) • THESE ALVEOLI PROVIDE A LARGE SURFACE AREA TO EXCHANGE OXYGEN AND CARBON DIOXIDE • (de-oxygenated blood is pumped through the pulmonary arteries to the lungs and then the pulmonary veins return oxygenated blood from the lun ...
... • NOSE/MOUTHTRACHEABRON CHI • ALVEOLI (CAVITIES CONTAINING CAPILLARIES) • THESE ALVEOLI PROVIDE A LARGE SURFACE AREA TO EXCHANGE OXYGEN AND CARBON DIOXIDE • (de-oxygenated blood is pumped through the pulmonary arteries to the lungs and then the pulmonary veins return oxygenated blood from the lun ...
Ecology EOG Review - wendyadornato
... Every organism needs to obtain _____________________ in order to live. For example, plants get energy from the sun, some animals eat plants, and some animals eat other animals. A __________________________________ is the sequence of who eats whom in a biological community (an ecosystem) to obtain nu ...
... Every organism needs to obtain _____________________ in order to live. For example, plants get energy from the sun, some animals eat plants, and some animals eat other animals. A __________________________________ is the sequence of who eats whom in a biological community (an ecosystem) to obtain nu ...
Ecology - Part 2
... Carbon Cycle Worksheet • 1. What is the process by which plants convert carbon dioxide into energy-rich carbon compounds? • 2. Explain what can happen over millions of years to the carbon compounds in organisms that die and decompose. • 3. What processes in the transparency release carbon dioxide i ...
... Carbon Cycle Worksheet • 1. What is the process by which plants convert carbon dioxide into energy-rich carbon compounds? • 2. Explain what can happen over millions of years to the carbon compounds in organisms that die and decompose. • 3. What processes in the transparency release carbon dioxide i ...
Plant behaviour
... Auxin moves away from light If the plant is bathed in even light, there is an even amount of auxin throughout the entire tip. If the light is concentrated on one side, the auxin moves to the “dark side”, and produces greater growth on that side, elongating one side of the tip, creating a bend. ...
... Auxin moves away from light If the plant is bathed in even light, there is an even amount of auxin throughout the entire tip. If the light is concentrated on one side, the auxin moves to the “dark side”, and produces greater growth on that side, elongating one side of the tip, creating a bend. ...
macromolecule packet
... 25. __________ bonds form when water is removed to hold _________ acids together. Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings (cuticle) on plants, pigments (chlorophyll), and steroids. Lipids have more carb ...
... 25. __________ bonds form when water is removed to hold _________ acids together. Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings (cuticle) on plants, pigments (chlorophyll), and steroids. Lipids have more carb ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.