cycles of matter worksheets
... 6. Plants remove CO2 from the atmosphere is a process called: photosynthesis 7. Plants and animals release CO2 into the atmosphere in a process called: respiration 8. How is carbon returned to the atmosphere? Organisms return carbon dioxide to the atmosphere by respiration. It is not just animals th ...
... 6. Plants remove CO2 from the atmosphere is a process called: photosynthesis 7. Plants and animals release CO2 into the atmosphere in a process called: respiration 8. How is carbon returned to the atmosphere? Organisms return carbon dioxide to the atmosphere by respiration. It is not just animals th ...
as an RTF file
... Because of this inability to run away, have a different way of responding to stress and injury than animals do - have their own way of dealing with environmental change. Plants exhibit indeterminate growth: indeterminate growth means that they do not have a pre-programmed size, shape and often, even ...
... Because of this inability to run away, have a different way of responding to stress and injury than animals do - have their own way of dealing with environmental change. Plants exhibit indeterminate growth: indeterminate growth means that they do not have a pre-programmed size, shape and often, even ...
Ecosystem Processes
... • Unlike other nutrients, phosphorous does not exist as an atmospheric gas. • Rock phosphates dissolve in rain as rock weathers, carrying phosphates into streams and soil. • Phosphates settle out on the bottoms of ponds, and may consolidate back into ...
... • Unlike other nutrients, phosphorous does not exist as an atmospheric gas. • Rock phosphates dissolve in rain as rock weathers, carrying phosphates into streams and soil. • Phosphates settle out on the bottoms of ponds, and may consolidate back into ...
macromolecules
... Structure – Made mostly of carbon, hydrogen, a small amount of oxygen and fatty acids. Also are attached with single bonds and double bonds depending on the lipid Lipids usually have 2 hydrophilic heads and 2 hydrophobic tails ...
... Structure – Made mostly of carbon, hydrogen, a small amount of oxygen and fatty acids. Also are attached with single bonds and double bonds depending on the lipid Lipids usually have 2 hydrophilic heads and 2 hydrophobic tails ...
Diversity if Life Jeopardy Questions
... 5 The diversity of life increases as these two factors increase. HUMIDITY AND TEMPERATURE. 1 Plants are not found in deep ocean areas because of a lack of this. LIGHT 2 85% of all plants on Earth are found here. OCEAN 3 More than 20% of all known mammalian species are this animal. BAT 3 Homeostasis ...
... 5 The diversity of life increases as these two factors increase. HUMIDITY AND TEMPERATURE. 1 Plants are not found in deep ocean areas because of a lack of this. LIGHT 2 85% of all plants on Earth are found here. OCEAN 3 More than 20% of all known mammalian species are this animal. BAT 3 Homeostasis ...
Lecture Resource ()
... In each of these transformations, one of the bonds to the a-carbon of the amino acid substrate is broken in the first step of the reaction ...
... In each of these transformations, one of the bonds to the a-carbon of the amino acid substrate is broken in the first step of the reaction ...
Substance Element Molecule Compound Organic
... 13. Explain how the digestive system, muscular system, and the circulatory system work together to supply all cells with the nutrients they need to function properly, INCLUDE the role the villi play in this process. The digestive system mechanically and chemically breaksdown food into small molecule ...
... 13. Explain how the digestive system, muscular system, and the circulatory system work together to supply all cells with the nutrients they need to function properly, INCLUDE the role the villi play in this process. The digestive system mechanically and chemically breaksdown food into small molecule ...
A. glycolysis
... delivered to the electron transport chain 2. the electron transport chain is responsible for the majority of ATPs made during cellular respiration 3. series of oxidation-reduction reactions ...
... delivered to the electron transport chain 2. the electron transport chain is responsible for the majority of ATPs made during cellular respiration 3. series of oxidation-reduction reactions ...
Ecology Powerpoint
... • Organisms make up population – Group of organisms of the same species – Interbreed and live in the same area – Can compete for food, water, mates ...
... • Organisms make up population – Group of organisms of the same species – Interbreed and live in the same area – Can compete for food, water, mates ...
Previously… - JohnTanScienceEportfolio
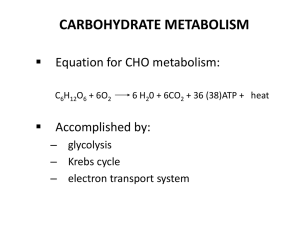
... • Aerobic respiration is the process whereby food substances are broken down in the presence of oxygen with the release of energy in living cells. Carbon dioxide and water are released as waste products. • Word equation for aerobic respiration: ...
... • Aerobic respiration is the process whereby food substances are broken down in the presence of oxygen with the release of energy in living cells. Carbon dioxide and water are released as waste products. • Word equation for aerobic respiration: ...
Jeopardy Biology 3 PowerPoint
... It’s the process where enzymes read the DNA sequence and create a mRNA strand. A – Transcription B – Translation C – Protein Synthesis D – Splicing ...
... It’s the process where enzymes read the DNA sequence and create a mRNA strand. A – Transcription B – Translation C – Protein Synthesis D – Splicing ...
Document
... Open water phytoplankton and bacteria Ice-edge phytoplankton and bacteria Under-ice phytoplankton and bacteria Melt pond algae and bacteria Marine aggregates at the sea surface (e.g. the centric diatom Melosira sp.) ...
... Open water phytoplankton and bacteria Ice-edge phytoplankton and bacteria Under-ice phytoplankton and bacteria Melt pond algae and bacteria Marine aggregates at the sea surface (e.g. the centric diatom Melosira sp.) ...
Cellular Respiration
... • Before cells can use the energy in complex carbohydrates (a major source of energy for organisms), the large polymers are broken down into simple sugars such as glucose (C6H12O6). Then, glucose is split even further to release energy. ...
... • Before cells can use the energy in complex carbohydrates (a major source of energy for organisms), the large polymers are broken down into simple sugars such as glucose (C6H12O6). Then, glucose is split even further to release energy. ...
SBI3C Exam Review
... relaxation phase in which blood enters the atria and flows in the ventricle = LUBB sound with the opening of the valve between the atria and ventricles. This is when the blood pressure is low. The systole is the contraction phase where the ventricles are filled with blood and pushed out with great ...
... relaxation phase in which blood enters the atria and flows in the ventricle = LUBB sound with the opening of the valve between the atria and ventricles. This is when the blood pressure is low. The systole is the contraction phase where the ventricles are filled with blood and pushed out with great ...
AP Biology Transition of Life from Aquatic to Terrestrial Biomes
... a byproduct of using amino acids in Cellular respiration by Deamination. It is removed from the body by the excretory system. a. Fish release the ammonia directly into the water. b. Other animals must use water to convert the ammonia to either urea or uric acid. This allows it to be stored and remov ...
... a byproduct of using amino acids in Cellular respiration by Deamination. It is removed from the body by the excretory system. a. Fish release the ammonia directly into the water. b. Other animals must use water to convert the ammonia to either urea or uric acid. This allows it to be stored and remov ...
Document
... – they are strong and flexible. – celery strings are strands of collenchyma. – they have unevenly thick cell walls. ...
... – they are strong and flexible. – celery strings are strands of collenchyma. – they have unevenly thick cell walls. ...
SI Worksheet #10 (Chapter 9) BY 123 Meeting 10/8/2015 Chapter 9
... During the first four steps of glycolysis, two phosphate groups are transferred to glucose via phosphorylation, where ATP is converted to ADP. The end product is fructose 1, 6-bisphosphate. 2. Sugar Splitting Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate gets split into two fragments, dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) ...
... During the first four steps of glycolysis, two phosphate groups are transferred to glucose via phosphorylation, where ATP is converted to ADP. The end product is fructose 1, 6-bisphosphate. 2. Sugar Splitting Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate gets split into two fragments, dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) ...
2421_Ch5.ppt
... Ejects two more pairs of H+ at the next two steps in the chain A total of 3 pairs of H+ have been ejected when an NADH completes it’s passage along the chain Each pair of H+ ions passes through an ATP Synthase molecule making one ATP as they pass through ...
... Ejects two more pairs of H+ at the next two steps in the chain A total of 3 pairs of H+ have been ejected when an NADH completes it’s passage along the chain Each pair of H+ ions passes through an ATP Synthase molecule making one ATP as they pass through ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.