corrected version for study guide
... 3phosphates that are like a tightly wound spring and when that last phosphate is released energy is released to do cell work, ATP must be produced from the breakdown of food. 14. Define calories and kilocalories as units of energy and how they are calculated. unit of measurement – the amount of ener ...
... 3phosphates that are like a tightly wound spring and when that last phosphate is released energy is released to do cell work, ATP must be produced from the breakdown of food. 14. Define calories and kilocalories as units of energy and how they are calculated. unit of measurement – the amount of ener ...
Cellular Respiration - Seattle Central College
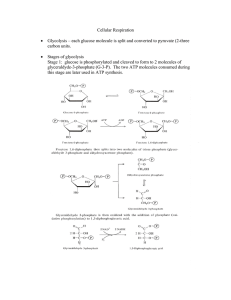
... glucose and the conversion of Fructose-6-phosphate to Fructose-1,6-diphosphate. The net production of ATP per glucose is 2. ...
... glucose and the conversion of Fructose-6-phosphate to Fructose-1,6-diphosphate. The net production of ATP per glucose is 2. ...
Physiology of Respiratory System
... • CO binds to the binding site that oxygen binds to on hemoglobin preventing gas transport of oxygen ...
... • CO binds to the binding site that oxygen binds to on hemoglobin preventing gas transport of oxygen ...
ecosystem - Wando High School
... • Conversion of biochemical compounds: organisms store carbon in organic molecules such as carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. For example, when consumers eat plants and/or animals, some of the compounds are used for energy; others are converted to compounds that are incorporated int ...
... • Conversion of biochemical compounds: organisms store carbon in organic molecules such as carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. For example, when consumers eat plants and/or animals, some of the compounds are used for energy; others are converted to compounds that are incorporated int ...
3.-electron-transport-chain-ATP-synthesis
... High energy electrons pass from one protein molecule in the chain to another • MOVEMENT OF HYDROGEN IONS The energy received allows the proteins to pump hydrogen across the membrane, so that they can be pumped back across by ATP synthase. This movement of H+ ions drives the enzyme to synthesis ...
... High energy electrons pass from one protein molecule in the chain to another • MOVEMENT OF HYDROGEN IONS The energy received allows the proteins to pump hydrogen across the membrane, so that they can be pumped back across by ATP synthase. This movement of H+ ions drives the enzyme to synthesis ...
gynura - Super Floral Retailing
... PESTS Aphids may cause Gynuras’ leaves to pucker or curl. For small infestations, affected leaves can be picked off and put in the trash while the rest of the plant is rinsed thoroughly with warm water. After three days, recheck the plant, and use a cotton swab dipped in soapy water to treat ...
... PESTS Aphids may cause Gynuras’ leaves to pucker or curl. For small infestations, affected leaves can be picked off and put in the trash while the rest of the plant is rinsed thoroughly with warm water. After three days, recheck the plant, and use a cotton swab dipped in soapy water to treat ...
The Ferns - Science 10 With Mr. Francis
... able to fix nitrogen in the air to be used by other plants • Landscaping, horticulture and the florist industry • Useful in removing heavy metals like arsenic from the soil • Decomposed ferns are a component of coal formation ...
... able to fix nitrogen in the air to be used by other plants • Landscaping, horticulture and the florist industry • Useful in removing heavy metals like arsenic from the soil • Decomposed ferns are a component of coal formation ...
iii. plant classification
... B. All plant cells have _cell walls___ composed of _cellulose_____. C. Plants are _autotrophic____, which means they can use energy from the _sun___ to make _glucose__ in _photosynthesis___. Photosynthesis takes place in the _chloroplasts_____ of plant cells. The equation for photosynthesis is _6CO2 ...
... B. All plant cells have _cell walls___ composed of _cellulose_____. C. Plants are _autotrophic____, which means they can use energy from the _sun___ to make _glucose__ in _photosynthesis___. Photosynthesis takes place in the _chloroplasts_____ of plant cells. The equation for photosynthesis is _6CO2 ...
CATALYSIS OF BIOCHEMICAL REACTIONS
... It also places a partial charge on the substrate, making it react more easily with water (hydrolysis). ...
... It also places a partial charge on the substrate, making it react more easily with water (hydrolysis). ...
plantsystems
... a plant turns light energy from the sun into chemical energy in the form of sugar. ...
... a plant turns light energy from the sun into chemical energy in the form of sugar. ...
Document
... This contains enzymes that initiate the conversion of fatty acids to sugar, which a seedling can use as a source of energy and carbon until it begins photosynthesis. ...
... This contains enzymes that initiate the conversion of fatty acids to sugar, which a seedling can use as a source of energy and carbon until it begins photosynthesis. ...
Here
... 2.) This forms the enzyme-substrate complex where the enzyme goes to work (can put together or take apart a substrate.) 3.) The enzyme and products separate: the enzyme is ready to work on another substrate. ...
... 2.) This forms the enzyme-substrate complex where the enzyme goes to work (can put together or take apart a substrate.) 3.) The enzyme and products separate: the enzyme is ready to work on another substrate. ...
Cell Function Review..
... Which of the following is most accurate (true): Osmosis and diffusion are examples of active transport. Active transport requires energy, passive transport does not. Both active and passive transport require energy. Passive transport requires energy, active transport does not. ...
... Which of the following is most accurate (true): Osmosis and diffusion are examples of active transport. Active transport requires energy, passive transport does not. Both active and passive transport require energy. Passive transport requires energy, active transport does not. ...
UNIT 2 : BIOCHEMISTRY
... • Water is considered to be a polar molecule due to an ____________________________________. • The ________________________ in a water molecule are ____________________________ between hydrogen and oxygen. • Solubility of Water • The polarity of water makes it effective at __________________________ ...
... • Water is considered to be a polar molecule due to an ____________________________________. • The ________________________ in a water molecule are ____________________________ between hydrogen and oxygen. • Solubility of Water • The polarity of water makes it effective at __________________________ ...
Biology 1A Mid-Term Exam Study Guide Chapter 1 Main Concepts
... Energy flows in one direction through an ecosystem. How much energy is lost from one trophic level to the next? About 90% is lost, mostly in the form of heat. The _Sun_ is ultimately the source of all life on Earth. Producers absorb this in the chloroplasts of their cells and make food in the form o ...
... Energy flows in one direction through an ecosystem. How much energy is lost from one trophic level to the next? About 90% is lost, mostly in the form of heat. The _Sun_ is ultimately the source of all life on Earth. Producers absorb this in the chloroplasts of their cells and make food in the form o ...
(key)
... 12. Which photosynthetic reaction center (PSI or PSII) is responsible for ATP synthesis_ ___:_f...:....s'lC.;:;;____ _ _ __ NADPH synthesis_P;....;s;;...;+,___ _ _ __ ...
... 12. Which photosynthetic reaction center (PSI or PSII) is responsible for ATP synthesis_ ___:_f...:....s'lC.;:;;____ _ _ __ NADPH synthesis_P;....;s;;...;+,___ _ _ __ ...
Document
... specific role in keeping the plant alive through photosynthesis. Write the equation for photosynthesis: 6 CO2 + 6 H2O -------sunlight---------- C6H12O6 + 6 O2 ...
... specific role in keeping the plant alive through photosynthesis. Write the equation for photosynthesis: 6 CO2 + 6 H2O -------sunlight---------- C6H12O6 + 6 O2 ...
Task - Science - Grade 6 - Chemical Reactions
... Additionally, sugar found in homes is typically stored in containers, further reducing the chance of an explosive reaction. The surface area of sugar in people’s homes is minimal when compared to the surface area of the sugar dust found at the sugar plant in Georgia. ...
... Additionally, sugar found in homes is typically stored in containers, further reducing the chance of an explosive reaction. The surface area of sugar in people’s homes is minimal when compared to the surface area of the sugar dust found at the sugar plant in Georgia. ...
The Grass Between My Toes: Wait! Is That Fescue?
... Performance Objectives On a demonstration evaluation, students will be able to identify and describe the various parts of the turfgrass plants and their use in the identification of major turfgrass species with 80% accuracy Identify and describe the major parts of the turfgrass plant Describe t ...
... Performance Objectives On a demonstration evaluation, students will be able to identify and describe the various parts of the turfgrass plants and their use in the identification of major turfgrass species with 80% accuracy Identify and describe the major parts of the turfgrass plant Describe t ...
23 Plant Structure and Function teacher ppt
... Gas Exchange: The plant must open stomatal pore during photosynthesis to allow CO2 inside the plant and O2 out. ...
... Gas Exchange: The plant must open stomatal pore during photosynthesis to allow CO2 inside the plant and O2 out. ...
Document
... 11. The light-dependent reactions require light / do not require light, and they absorb and transfer sugars / energy. 12. The light-independent reactions require light / do not require light, and they build sugars / energy. 13. Use the space below to sketch a chloroplast. Label the grana, thylakoids ...
... 11. The light-dependent reactions require light / do not require light, and they absorb and transfer sugars / energy. 12. The light-independent reactions require light / do not require light, and they build sugars / energy. 13. Use the space below to sketch a chloroplast. Label the grana, thylakoids ...
Lec 01 - History of Microbiology True or False 1. Robert Koch is the
... 3. Which of these types of organisms gets its organic nutrients and energy from another organism? a. chemoheterotroph b. chemoautotroph c. photoheterotroph d. photoautotroph ...
... 3. Which of these types of organisms gets its organic nutrients and energy from another organism? a. chemoheterotroph b. chemoautotroph c. photoheterotroph d. photoautotroph ...
Chapter 36
... ii. consumers may eat more than one type of produce iii. several species may feed on same primary consumer iv. some secondary consumers are also primary consumers v. Even this figure is way over simplified vi. Even consumers of the highest level eventually become food for? 1. decomposers 11. Food ch ...
... ii. consumers may eat more than one type of produce iii. several species may feed on same primary consumer iv. some secondary consumers are also primary consumers v. Even this figure is way over simplified vi. Even consumers of the highest level eventually become food for? 1. decomposers 11. Food ch ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.