Ch. 6 Multicellular Primary Producers
... a. There are more species of red algae than green and brown combined b. The red pigment, phycobilins, masks chlorophyll c. Mostly marine d. Inhabit most shallow-water environments e. Some are parasites of other algae f. Coralline algae deposit calcium carbonate in its cell walls D. Life History 1. A ...
... a. There are more species of red algae than green and brown combined b. The red pigment, phycobilins, masks chlorophyll c. Mostly marine d. Inhabit most shallow-water environments e. Some are parasites of other algae f. Coralline algae deposit calcium carbonate in its cell walls D. Life History 1. A ...
1.1 Plant organs 1.1 Photosynthesis - Beck-Shop
... Nitrate is needed so that the plant can make proteins. You’ll remember that proteins are nutrients that living organisms need for making new cells. A plant that has not got enough nitrate can’t make enough proteins, so it cannot make enough new cells to grow well. Nitrate is also needed to make chlo ...
... Nitrate is needed so that the plant can make proteins. You’ll remember that proteins are nutrients that living organisms need for making new cells. A plant that has not got enough nitrate can’t make enough proteins, so it cannot make enough new cells to grow well. Nitrate is also needed to make chlo ...
Review Facts for the Biology SOL
... During DNA replication, enzymes unwind and unzip the double helix and each strand serves as a template for building a new DNA molecule. Free nucleotides bond to the template (A-T and C-G) forming a complementary strand. The final product of replication is two identical DNA molecules. Forensic identi ...
... During DNA replication, enzymes unwind and unzip the double helix and each strand serves as a template for building a new DNA molecule. Free nucleotides bond to the template (A-T and C-G) forming a complementary strand. The final product of replication is two identical DNA molecules. Forensic identi ...
1.5 respiration 2014
... energy by releasing energy from food (stored chemical energy). The word equation for respiration is: ...
... energy by releasing energy from food (stored chemical energy). The word equation for respiration is: ...
Let`s Classify Organisms
... Kingdom Plantae Plants are organisms that don’t need to look for nutrients. They are able to photosynthesize, or make their own food, with a little help from the Sun. When scientists break plants into smaller groups, they look at how the plants use water. Vascular plants can conduct water. Non-va ...
... Kingdom Plantae Plants are organisms that don’t need to look for nutrients. They are able to photosynthesize, or make their own food, with a little help from the Sun. When scientists break plants into smaller groups, they look at how the plants use water. Vascular plants can conduct water. Non-va ...
cell respiration
... energy found in NADH and FADH2 to make more ATP. This involves the cristae. There are electron transport chains that are used. The electrons from the NADH and FADH2 are used to move on the electron transport chain. As the electrons move down the electron transport chain, H+ ions are pumped across th ...
... energy found in NADH and FADH2 to make more ATP. This involves the cristae. There are electron transport chains that are used. The electrons from the NADH and FADH2 are used to move on the electron transport chain. As the electrons move down the electron transport chain, H+ ions are pumped across th ...
Exam #3 Review Exam #3 will cover from glycolysis to complex
... organic carbon source. An electron source, often water, is necessary. 1. The light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis are the reactions in which the energy of sunlight is converted into chemical energy in the form of ATP (this is the process happening in photosystems, see below). In oxygenic phot ...
... organic carbon source. An electron source, often water, is necessary. 1. The light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis are the reactions in which the energy of sunlight is converted into chemical energy in the form of ATP (this is the process happening in photosystems, see below). In oxygenic phot ...
ASPB – BSA Working Group on Core Concepts in Plant Biology
... reproduce, and die. Plants and their parts are made up of cells, which contain DNA and other molecules that support plant functions. Plants are rooted and do not move from place to place to acquire resources for survival. Plants grow toward resources and have specific structures, called chloroplasts ...
... reproduce, and die. Plants and their parts are made up of cells, which contain DNA and other molecules that support plant functions. Plants are rooted and do not move from place to place to acquire resources for survival. Plants grow toward resources and have specific structures, called chloroplasts ...
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
... exchange surfaces have flattened, tubular, or thin shaped body plans, which are the most efficient for gas exchange. However, these simple animals are rather small in size. Respiratory Surfaces | Large animals cannot maintain gas exchange by diffusion across their outer surface. They developed a var ...
... exchange surfaces have flattened, tubular, or thin shaped body plans, which are the most efficient for gas exchange. However, these simple animals are rather small in size. Respiratory Surfaces | Large animals cannot maintain gas exchange by diffusion across their outer surface. They developed a var ...
acetyl-CoA - Winona State University
... The Trick: the nicotinamide functional group either has a charge (NAD+; oxidized;low energy) or has an extra electron and proton (reduced; high energy; NADH). The Nic-ring structure stabilizes the extra electron so the energy in the electron can be transferred between molecules. NADH electrons most ...
... The Trick: the nicotinamide functional group either has a charge (NAD+; oxidized;low energy) or has an extra electron and proton (reduced; high energy; NADH). The Nic-ring structure stabilizes the extra electron so the energy in the electron can be transferred between molecules. NADH electrons most ...
Respiratory System Overview
... which the gases in the air that has already been drawn into the lungs by external respiration are exchanged with gases in the blood/tissues so that carbon dioxide (CO2) is removed from the blood and replaced with oxygen (O2). ...
... which the gases in the air that has already been drawn into the lungs by external respiration are exchanged with gases in the blood/tissues so that carbon dioxide (CO2) is removed from the blood and replaced with oxygen (O2). ...
Unit 4. Monera, Protoctists, Fungi and Plants.
... 8. They .................. little plants without .......... and they don’t ................ seeds. They are 9. When we ........... a tree with our ..........., the bark was .................. by 10. ............... need three .................... for photosynthesis: ............, carbon dioxide and ...
... 8. They .................. little plants without .......... and they don’t ................ seeds. They are 9. When we ........... a tree with our ..........., the bark was .................. by 10. ............... need three .................... for photosynthesis: ............, carbon dioxide and ...
Brief Answer Key (up to 2/9)
... 8.) Why are endergonic reactions linked to exergonic reactions in cells? –> So why is ATP hydrolysis an important reaction in cellular energetics? a. Endergonic reactions require an input of energy—Exergonic reactions release energy. Therefore, the energy released by the exergonic reaction can be us ...
... 8.) Why are endergonic reactions linked to exergonic reactions in cells? –> So why is ATP hydrolysis an important reaction in cellular energetics? a. Endergonic reactions require an input of energy—Exergonic reactions release energy. Therefore, the energy released by the exergonic reaction can be us ...
BIOC*4520 - University of Guelph
... The course grade will be based on performance on two midterms (in class, 16% each), assignments (10%), a term paper on a current research paper (24%) and a cumulative final examination (34%). ...
... The course grade will be based on performance on two midterms (in class, 16% each), assignments (10%), a term paper on a current research paper (24%) and a cumulative final examination (34%). ...
Respiratory system
... • Since oxygen and hemoglobin molecules are unstable, oxyhemoglobin releases oxygen into nearby cells. • More oxygen is released when: • Po2 decreases ...
... • Since oxygen and hemoglobin molecules are unstable, oxyhemoglobin releases oxygen into nearby cells. • More oxygen is released when: • Po2 decreases ...
The process of beta oxidation is named after the carbon atom in the
... acid cycle which yields an additional 96 mols of ATP for all 8 acetyl-CoA units oxidized in the process. The total energy yield of palmitic acid oxidation results in some 130 mols of ATP, 34 units from the beta-oxidation cycle and 96 form the citric acid cycle. Beta oxidation of odd numbered fatty a ...
... acid cycle which yields an additional 96 mols of ATP for all 8 acetyl-CoA units oxidized in the process. The total energy yield of palmitic acid oxidation results in some 130 mols of ATP, 34 units from the beta-oxidation cycle and 96 form the citric acid cycle. Beta oxidation of odd numbered fatty a ...
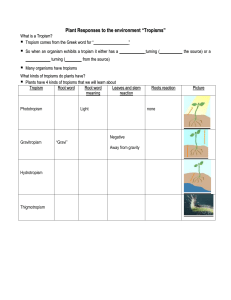
Tropism - My Teacher Site
... They use their touch sensitive fibers to know when and ___________ lands on their traps and then they close, ____________ the insect and suck up all the delicious _______________ from the insect Qu e s t i o n 1 Which of the following is false about tropisms? A. they can be positive or negative B. ...
... They use their touch sensitive fibers to know when and ___________ lands on their traps and then they close, ____________ the insect and suck up all the delicious _______________ from the insect Qu e s t i o n 1 Which of the following is false about tropisms? A. they can be positive or negative B. ...
answer_1 - Homework Market
... 6. Name the structure that contains the vestibular and vocal folds. What protective function do these folds have? ...
... 6. Name the structure that contains the vestibular and vocal folds. What protective function do these folds have? ...
Chapter 9. Cellular Respiration STAGE 1: Glycolysis
... 2. Some organisms that are exposed to oxygen, but switch to fermentation when oxygen is scarce. AP Biology ...
... 2. Some organisms that are exposed to oxygen, but switch to fermentation when oxygen is scarce. AP Biology ...
2016 For Ecology txt
... In the Caucasus region more than 2/3 of terrestrial evapotranspiration is likely to come from plant transpiration and not more than 15% from open soil and water surfaces, a similar amount is from immediate evaporation of rainfall or air moisture intercepted by plant & other surfaces. Some ‘poikilohy ...
... In the Caucasus region more than 2/3 of terrestrial evapotranspiration is likely to come from plant transpiration and not more than 15% from open soil and water surfaces, a similar amount is from immediate evaporation of rainfall or air moisture intercepted by plant & other surfaces. Some ‘poikilohy ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.