Block III - Madhya Pradesh Bhoj Open University
... The assimilation of sulfate ions begins with its activation. First, a sulphate ion reacts with ATP to yield adenosine -5’-phosphosulphate (APS) the reaction is catalyzed by enzyme ATP- sulfurylase. Now, APS reacts with another molecule of ATP to form 3’-phosphoaenosine-5’-phosphosulfate (PAPS) the r ...
... The assimilation of sulfate ions begins with its activation. First, a sulphate ion reacts with ATP to yield adenosine -5’-phosphosulphate (APS) the reaction is catalyzed by enzyme ATP- sulfurylase. Now, APS reacts with another molecule of ATP to form 3’-phosphoaenosine-5’-phosphosulfate (PAPS) the r ...
april break review packet
... through ATP synthase into the mitochondria matrix. Rush of ions “spins” ATP synthase protein, causing ADP and Pi to join forming ATP by oxidative phosphorylation 3. Photosynthesis 6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 a. Photosynthetic organisms capture free energy present in sunlight and use water and carbon ...
... through ATP synthase into the mitochondria matrix. Rush of ions “spins” ATP synthase protein, causing ADP and Pi to join forming ATP by oxidative phosphorylation 3. Photosynthesis 6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 a. Photosynthetic organisms capture free energy present in sunlight and use water and carbon ...
Feb 6 Primary Productivity: Controls, Patterns, Consequences
... organic molecules. Net primary production (NPP)- the rate at which all the plants in an ecosystem produce net useful chemical energy. NPP = GPP - respiration Cellular respiration – “burning of organic molecules to produce ATP to fuel growth and maintenance. Chapin et al. Fig 6.1 ...
... organic molecules. Net primary production (NPP)- the rate at which all the plants in an ecosystem produce net useful chemical energy. NPP = GPP - respiration Cellular respiration – “burning of organic molecules to produce ATP to fuel growth and maintenance. Chapin et al. Fig 6.1 ...
Section 6.1 Summary – pages 141-151
... Living organisms must have water for life processes, because critical molecules and ions must be free to move and collide, which only happens when they are dissolved in water. Water also transports materials in living organisms, such as in blood or sap. ...
... Living organisms must have water for life processes, because critical molecules and ions must be free to move and collide, which only happens when they are dissolved in water. Water also transports materials in living organisms, such as in blood or sap. ...
Corals
... • Polyp lays down extensive lipid reserves to be drawn on in times of starvation • High light and high food availability – ejection of pellets containing viable algal cells • Control of algal cell number ? ...
... • Polyp lays down extensive lipid reserves to be drawn on in times of starvation • High light and high food availability – ejection of pellets containing viable algal cells • Control of algal cell number ? ...
Respiratory System Part B
... Modify the structure of hemoglobin and alter its affinity for oxygen Increases of these factors: ...
... Modify the structure of hemoglobin and alter its affinity for oxygen Increases of these factors: ...
File
... 1. A protein containing more than one polypeptide chain exhibits the ________ level of protein structure a. primary. c. tertiary b. secondary d. quaternary ...
... 1. A protein containing more than one polypeptide chain exhibits the ________ level of protein structure a. primary. c. tertiary b. secondary d. quaternary ...
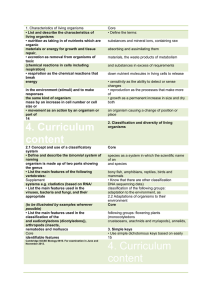
1. Characteristics of living organisms Core • List and describe the
... • mineral salts (calcium and iron only) • water • vitamins (C and D only) • Describe the use of microorganisms in the single cell protein hazards associated with food additives, 6.2 Plant nutrition Core process by which plants manufacture from light simple sugars and oxygen and carbon dioxide for ph ...
... • mineral salts (calcium and iron only) • water • vitamins (C and D only) • Describe the use of microorganisms in the single cell protein hazards associated with food additives, 6.2 Plant nutrition Core process by which plants manufacture from light simple sugars and oxygen and carbon dioxide for ph ...
Original
... 1) Electrons in H atoms from NADH + FADH2 are given up to ETC a. NADH donates electrons @ beginning b. FADH2 donates later c. Also give up protons (H+) 2) Electrons are passed down chain, losing energy ...
... 1) Electrons in H atoms from NADH + FADH2 are given up to ETC a. NADH donates electrons @ beginning b. FADH2 donates later c. Also give up protons (H+) 2) Electrons are passed down chain, losing energy ...
The Respiratory System
... and smaller tubes called bronchioles. At the end of each of these tubes are small air sacs called alveoli. Capillaries, which are small blood vessels with thin walls, are wrapped around these alveoli. ...
... and smaller tubes called bronchioles. At the end of each of these tubes are small air sacs called alveoli. Capillaries, which are small blood vessels with thin walls, are wrapped around these alveoli. ...
Version o1 o2
... The step in the water cycle in which water vapor becomes liquid water is A. condensation. B. nitrogen fixation. C. precipitation. ...
... The step in the water cycle in which water vapor becomes liquid water is A. condensation. B. nitrogen fixation. C. precipitation. ...
Bioenergetics and High Energy Compounds
... with a resulting large negative free energy change (like ATP) are used as shuttles of free energy in the cell •(the bonds are said to contain potential transfer energy) ...
... with a resulting large negative free energy change (like ATP) are used as shuttles of free energy in the cell •(the bonds are said to contain potential transfer energy) ...
Glycolysis & Fermentation
... 5 Steps in Krebs cycle Step 1 – produces citric acid Step 2 – releases CO2 Step 3 – releases CO2 Step 4 – conversion of 4-carbon compound Step 5 – 4-carbon compound converted back to oxaloacetic acid ...
... 5 Steps in Krebs cycle Step 1 – produces citric acid Step 2 – releases CO2 Step 3 – releases CO2 Step 4 – conversion of 4-carbon compound Step 5 – 4-carbon compound converted back to oxaloacetic acid ...
interactions in plants
... Think about the many interactions that occur inside the human body every moment of every day. Even a simple drink of water involves complex interactions of systems that help transport the water throughout the body and into cells. Our bodies have specialized structures that allow us to meet our basic ...
... Think about the many interactions that occur inside the human body every moment of every day. Even a simple drink of water involves complex interactions of systems that help transport the water throughout the body and into cells. Our bodies have specialized structures that allow us to meet our basic ...
Final Exam 2012 - Med Study Group
... • Both types of plants make most of their sugar in the dark. • Neither C4 plants nor CAM plants have thylakoids. 55. Which of the following processes is most directly driven by light energy? • creation of a pH gradient by pumping protons across the thylakoid membrane • carbon fixation in the stroma ...
... • Both types of plants make most of their sugar in the dark. • Neither C4 plants nor CAM plants have thylakoids. 55. Which of the following processes is most directly driven by light energy? • creation of a pH gradient by pumping protons across the thylakoid membrane • carbon fixation in the stroma ...
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle
... and fatty acids converge, their carbon skeletons being converted to CO2 ...
... and fatty acids converge, their carbon skeletons being converted to CO2 ...
Aerobic respiration
... : at ETC ( Electron Transport Chain ) *The more reduced = the more energy it holds. ...
... : at ETC ( Electron Transport Chain ) *The more reduced = the more energy it holds. ...
Ecosystem Interactions
... be neatly classified as either plants or animals. Animals and plants have a great variety of body parts and internal structures that contribute to their being able to make or find food and reproduce. Similarities among organisms are found in internal anatomical features, which can be used to infer t ...
... be neatly classified as either plants or animals. Animals and plants have a great variety of body parts and internal structures that contribute to their being able to make or find food and reproduce. Similarities among organisms are found in internal anatomical features, which can be used to infer t ...
ASC2006-Biology - UBC Let`s Talk Science
... The process by which air moves in and out of the lungs is called ventilation. The main muscle responsible for ventilation is the diaphragm (has your music teacher ever told you to breath from your diaphragm??). Other muscles that assist with ventilation are called the intercostal muscles and they a ...
... The process by which air moves in and out of the lungs is called ventilation. The main muscle responsible for ventilation is the diaphragm (has your music teacher ever told you to breath from your diaphragm??). Other muscles that assist with ventilation are called the intercostal muscles and they a ...
Bioener Notes - MacsScienceSpace
... In one minute a working muscle cell uses 10,000,000 ATP molecules. That is the cell's entire supply, so ADP must be recycled into ATP. Produce 125lbs of ATP per day. Blue Whale makes 5 tons/day. Even resting in bed, you use 20 kg of ATP every 24 hours! ...
... In one minute a working muscle cell uses 10,000,000 ATP molecules. That is the cell's entire supply, so ADP must be recycled into ATP. Produce 125lbs of ATP per day. Blue Whale makes 5 tons/day. Even resting in bed, you use 20 kg of ATP every 24 hours! ...
Respiration chapt07
... • A proton gradient is established • This proton gradient is potential energy that can be utilized to make more ATP’s – Recall diffusion: The protons want to equalize their number on both sides of the membrane ...
... • A proton gradient is established • This proton gradient is potential energy that can be utilized to make more ATP’s – Recall diffusion: The protons want to equalize their number on both sides of the membrane ...
Cellular Respiration
... 10. The second stage of cellular respiration, _______________, involves the creation of important electron-carriers needed to help synthesize ATP. a. the Krebs cycle b. glycolysis c. fermentation d. the electron transport chain 11. Which part of aerobic respiration produces the most ATP? a. the Kreb ...
... 10. The second stage of cellular respiration, _______________, involves the creation of important electron-carriers needed to help synthesize ATP. a. the Krebs cycle b. glycolysis c. fermentation d. the electron transport chain 11. Which part of aerobic respiration produces the most ATP? a. the Kreb ...
Photosynthesis

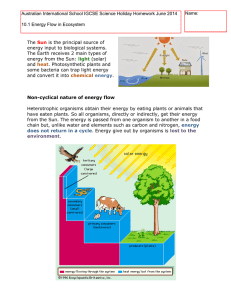
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.