Vinca minor
... commercial development of a plant used in their traditional medicine • The ethnobotanist must meet and establish rapport with the village healers - securing and maintaining the healer’s trust is the single most important skill the ethnobotanist can have • Ethnobotanists must develop their own person ...
... commercial development of a plant used in their traditional medicine • The ethnobotanist must meet and establish rapport with the village healers - securing and maintaining the healer’s trust is the single most important skill the ethnobotanist can have • Ethnobotanists must develop their own person ...
Anatomy of the Respiratory System in Children
... The lungs take in oxygen, which the body's cells need to live and carry out their normal functions. The lungs also get rid of carbon dioxide, a waste product of the cells. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped organs made up of spongy, pinkish-gray tissue. They take up most of the space in the chest, ...
... The lungs take in oxygen, which the body's cells need to live and carry out their normal functions. The lungs also get rid of carbon dioxide, a waste product of the cells. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped organs made up of spongy, pinkish-gray tissue. They take up most of the space in the chest, ...
Ch.5-Cellular Respiration
... Used immediately Stored for a medium – term Used to synthesize molecules that can store E for long term • Plants: glucose starch • Animal and fungal cells: glucose glycogen ...
... Used immediately Stored for a medium – term Used to synthesize molecules that can store E for long term • Plants: glucose starch • Animal and fungal cells: glucose glycogen ...
plant diversity i: the colonization of land outline
... 11. Compare environmental conditions faced by algae in an aquatic environment and plants in a terrestrial environment. 12. Provide evidence that suggests the division Bryophyta is a phylogenetic branch separate from vascular plants. 13. Describe adaptations of vascular plants, including modification ...
... 11. Compare environmental conditions faced by algae in an aquatic environment and plants in a terrestrial environment. 12. Provide evidence that suggests the division Bryophyta is a phylogenetic branch separate from vascular plants. 13. Describe adaptations of vascular plants, including modification ...
Bio 6 – Fermentation & Cellular Respiration Lab INTRODUCTION
... and inorganic phosphate (Pi) is exergonic and thus releases energy which cells can use to do any number of things. Once hydrolyzed, ATP can be regenerated from ADP and Pi, though this is endergonic and thus requires energy. The energy needed to regenerate ATP is obtained from “food”, whatever that m ...
... and inorganic phosphate (Pi) is exergonic and thus releases energy which cells can use to do any number of things. Once hydrolyzed, ATP can be regenerated from ADP and Pi, though this is endergonic and thus requires energy. The energy needed to regenerate ATP is obtained from “food”, whatever that m ...
CHM 326 LECTURE NOTE
... etc. Some are acyclic while others are cyclic in their structures. Some secondary metabolites are synthesised via biosynthesis and or biogenesis. Higher plants synthesised chemical compounds in vivo and degrade them by means of series of chemical reactions, each aided by enzymes, by a process known ...
... etc. Some are acyclic while others are cyclic in their structures. Some secondary metabolites are synthesised via biosynthesis and or biogenesis. Higher plants synthesised chemical compounds in vivo and degrade them by means of series of chemical reactions, each aided by enzymes, by a process known ...
Chapter 10: Chemistry of Living Systems
... The Carbon Cycle The carbon cycle, shown in Figure 2, shows how carbon and oxygen cycle through an ecosystem. Plants obtain carbon in the form of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to make carbonbased sugar molecules. Plants use sugars to store energy and to provide energy for growth and other cellu ...
... The Carbon Cycle The carbon cycle, shown in Figure 2, shows how carbon and oxygen cycle through an ecosystem. Plants obtain carbon in the form of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to make carbonbased sugar molecules. Plants use sugars to store energy and to provide energy for growth and other cellu ...
ATP ENERGY PRODUCTION - SHMD 339: Exercise Physiology 3
... • The H2 atoms removed in stage 2 are transported by coenzymes to the inner membrane of the mitochondria. • Uses coenzymes NAD+ and FAD+ to accept e- from glucose ...
... • The H2 atoms removed in stage 2 are transported by coenzymes to the inner membrane of the mitochondria. • Uses coenzymes NAD+ and FAD+ to accept e- from glucose ...
CITY PLANTS AND SEEDS
... Two examples of fresh fruit with seeds, suggestions: apple, grape (with seeds), orange (with seeds) Live potted plant (optional) BACKGROUND INFORMATION: Plants are an important part of life on earth. One of the most important thing that plants contribute to all life on earth is oxygen. Oxygen that m ...
... Two examples of fresh fruit with seeds, suggestions: apple, grape (with seeds), orange (with seeds) Live potted plant (optional) BACKGROUND INFORMATION: Plants are an important part of life on earth. One of the most important thing that plants contribute to all life on earth is oxygen. Oxygen that m ...
Ch 9 Cellular respiration
... Fermentation generates ATP by substrate level phosphorylation as long as there is enough NAD+ (get enough because in anaerobic conditions,electrons are transferred from NADH to pyruvate) pyruvate is electron acceptor for oxidizing NADH back to NAD+ and can then be reused in glycolysis ...
... Fermentation generates ATP by substrate level phosphorylation as long as there is enough NAD+ (get enough because in anaerobic conditions,electrons are transferred from NADH to pyruvate) pyruvate is electron acceptor for oxidizing NADH back to NAD+ and can then be reused in glycolysis ...
Chapter 25: Metabolism
... – Peptide bonds broken amino acids (AAs) – Free AAs used in new proteins ...
... – Peptide bonds broken amino acids (AAs) – Free AAs used in new proteins ...
Plant Science notes
... Stomata closed during the light, open at night CAM metabolism: CO2 is fixed during the night, water loss in the day is minimized. CAM plants, American aloe, pineapple, Kalanchoe, Yucca When the weather is hot and dry, keeps its stomata closed most of the time, conserving water. At the same ti ...
... Stomata closed during the light, open at night CAM metabolism: CO2 is fixed during the night, water loss in the day is minimized. CAM plants, American aloe, pineapple, Kalanchoe, Yucca When the weather is hot and dry, keeps its stomata closed most of the time, conserving water. At the same ti ...
Osmotic Stress Induces Inactivation of Photosynthesis in Guard Cell
... MCPs, in both types of protoplasts non-photochemical quenching was stimulated by hyperosmotic stress. The observed effect is indicative for partial suppression of CO2-fixation, as the transthylakoidal proton gradient, which can be sustained by non-assimilatory types of electron transport (Schreiber ...
... MCPs, in both types of protoplasts non-photochemical quenching was stimulated by hyperosmotic stress. The observed effect is indicative for partial suppression of CO2-fixation, as the transthylakoidal proton gradient, which can be sustained by non-assimilatory types of electron transport (Schreiber ...
8-28-01
... Leaf blade: (upper portion of leaf) relatively flat, extends outward at an angle from the sheath Older leaves are more visible while younger leaves are enclosed within other leaf sheaths Components of the leaf used for identification: Ligule: located at junction of blade and sheath on inner side ...
... Leaf blade: (upper portion of leaf) relatively flat, extends outward at an angle from the sheath Older leaves are more visible while younger leaves are enclosed within other leaf sheaths Components of the leaf used for identification: Ligule: located at junction of blade and sheath on inner side ...
Reaction rate
... 1) Stoichiometric: balance of the equation 2) Thermodynamic: Spontaneity and equilibrium 3) Kinetic: Rate and mechanism The factor concerned by thermodynamics is the inherent tendency or the possibility and the advancement of the reaction but not the reality and the rate. ...
... 1) Stoichiometric: balance of the equation 2) Thermodynamic: Spontaneity and equilibrium 3) Kinetic: Rate and mechanism The factor concerned by thermodynamics is the inherent tendency or the possibility and the advancement of the reaction but not the reality and the rate. ...
the plant kingdom - 1st ESO Bilingual Science
... 1. Can you give three names of gymnosperms?.......................................................................................................... 2. Are gymnosperms lonely trees or do they form big forests?..................................................................................... 3. W ...
... 1. Can you give three names of gymnosperms?.......................................................................................................... 2. Are gymnosperms lonely trees or do they form big forests?..................................................................................... 3. W ...
File - HABITAT (Home)
... single sugars that have six carbon atoms; glucose The substance that does the dissolving in a solution. For example, salt dissolved in water. Water is the solvent because it dissolves the salt. a carbohydrate made up of many glucose molecules; used for energy storage in plants. the process in which ...
... single sugars that have six carbon atoms; glucose The substance that does the dissolving in a solution. For example, salt dissolved in water. Water is the solvent because it dissolves the salt. a carbohydrate made up of many glucose molecules; used for energy storage in plants. the process in which ...
Perspectives in Nutrition, 8th Edition
... metabolic pathways, such as glycolysis, beta-oxidation, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport system. 4. Describe the role that acetyl-CoA plays in cell metabolism. 5. Identify the conditions that lead to ketogenesis and its importance in survival during fasting. 6. Describe the process ...
... metabolic pathways, such as glycolysis, beta-oxidation, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport system. 4. Describe the role that acetyl-CoA plays in cell metabolism. 5. Identify the conditions that lead to ketogenesis and its importance in survival during fasting. 6. Describe the process ...
Chapter 15 Plant Evolution and Classification Worksheets
... (Pollen image copyright MichaelTaylor, 2010, and bee image copyright Joseph Calev, 2010. Both images used under licenses from Shutterstock.com.) Seed Plants Emerge For reproduction, early vascular plants still needed moisture. Sperm had to swim from male to female reproductive organs for fertilizati ...
... (Pollen image copyright MichaelTaylor, 2010, and bee image copyright Joseph Calev, 2010. Both images used under licenses from Shutterstock.com.) Seed Plants Emerge For reproduction, early vascular plants still needed moisture. Sperm had to swim from male to female reproductive organs for fertilizati ...
Chapter 3: The Chemical Basis for Life Lesson 2: Organic Compounds
... A chemical compound is a new substance that forms when atoms of two or more elements react with each other. A chemical reaction is a process that changes some chemical substances into other chemical substances. A compound that results from a chemical reaction always has a unique and fixed chemical c ...
... A chemical compound is a new substance that forms when atoms of two or more elements react with each other. A chemical reaction is a process that changes some chemical substances into other chemical substances. A compound that results from a chemical reaction always has a unique and fixed chemical c ...
Coenzymes and cofactors Vitamins and minerals
... Some enzymes need assistance so that the catalytic process goes smoothly. Molecules, which can provide this assistance, are either cofactors or coenzymes. Function of coenzymes Coenzymes are organic carrier molecules. They are non-protein components of an enzyme that are required for the catalytic p ...
... Some enzymes need assistance so that the catalytic process goes smoothly. Molecules, which can provide this assistance, are either cofactors or coenzymes. Function of coenzymes Coenzymes are organic carrier molecules. They are non-protein components of an enzyme that are required for the catalytic p ...
PowerPoint lecture
... pathway takes place inside mitochondria • Like chloroplasts, mitochondria have an internal folded membrane system that allows them to make ATP efficiently • Electron transfer chains in this membrane set up hydrogen ion gradients that power ATP synthesis ...
... pathway takes place inside mitochondria • Like chloroplasts, mitochondria have an internal folded membrane system that allows them to make ATP efficiently • Electron transfer chains in this membrane set up hydrogen ion gradients that power ATP synthesis ...
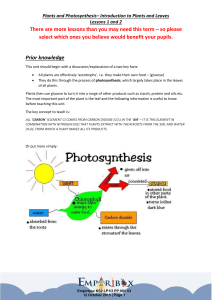
There are more lessons than you may need this term
... 1. Photosynthesis uses sunlight, carbon dioxide and water to build carbohydrates producing oxygen as a waste product 2. Gases and water vapour enter and leave the leaf through holes or stomata (sing. Stoma) normally on the underside. Expandable cells called guard cells regulate the size of the holes ...
... 1. Photosynthesis uses sunlight, carbon dioxide and water to build carbohydrates producing oxygen as a waste product 2. Gases and water vapour enter and leave the leaf through holes or stomata (sing. Stoma) normally on the underside. Expandable cells called guard cells regulate the size of the holes ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.