A Phase-Based Approach to ECM across CP in Korean
... It is here that I show that ECM is mediated by movement of VP/vP to Spec-CP. It has been suggested by many linguists that in languages like Korean and Japanese the subject can stay in the VP-internal position without moving to Spec-TP (J.-M. Yoon 1991, Fukui 1995, among many others; also see Rizzi 1 ...
... It is here that I show that ECM is mediated by movement of VP/vP to Spec-CP. It has been suggested by many linguists that in languages like Korean and Japanese the subject can stay in the VP-internal position without moving to Spec-TP (J.-M. Yoon 1991, Fukui 1995, among many others; also see Rizzi 1 ...
here
... function subsuming comitative proper and depictive comitative. The depictive function can further be split into several semantic subtypes like (in)alienable possession, container etc. Several other syntactic functions suggest themselves, such as predicative, argument or sentential. The majority of t ...
... function subsuming comitative proper and depictive comitative. The depictive function can further be split into several semantic subtypes like (in)alienable possession, container etc. Several other syntactic functions suggest themselves, such as predicative, argument or sentential. The majority of t ...
Amanda Pounder
... illustrate some common patterns. For one thing, we observe that there is morphological material that is present in the final conjunct in a coordinate construction only, while earlier conjuncts contain incomplete or “broken” forms whose completion is based on the structure of the final conjunct. In t ...
... illustrate some common patterns. For one thing, we observe that there is morphological material that is present in the final conjunct in a coordinate construction only, while earlier conjuncts contain incomplete or “broken” forms whose completion is based on the structure of the final conjunct. In t ...
BROKEN FORMS IN MORPHOLOGY
... phenomenon morphological ellipsis or brachylogy; the latter term is less familiar, but is preferable due to the wide range of phenomena to which “ellipsis” is applied in modern linguistics and to their original meanings in Greek rhetoric, whereby “ellipsis” is used where the missing material is reco ...
... phenomenon morphological ellipsis or brachylogy; the latter term is less familiar, but is preferable due to the wide range of phenomena to which “ellipsis” is applied in modern linguistics and to their original meanings in Greek rhetoric, whereby “ellipsis” is used where the missing material is reco ...
Constraints on the formal structure of Russian verb clusters
... • дутьi ‘blow’ + подутьp ‘blow a while’ > дунутьp ‘blow once’ • скрипетьi ‘squeak’ + поскрипетьp ‘squeak a while’ > скрипнутьp ‘squeak once’ • работатьi ‘work’ + поработатьp ‘work a while’ > *работнутьp ‘work once’ [NB: Some are formed ad-hoc] Laura A. Janda ...
... • дутьi ‘blow’ + подутьp ‘blow a while’ > дунутьp ‘blow once’ • скрипетьi ‘squeak’ + поскрипетьp ‘squeak a while’ > скрипнутьp ‘squeak once’ • работатьi ‘work’ + поработатьp ‘work a while’ > *работнутьp ‘work once’ [NB: Some are formed ad-hoc] Laura A. Janda ...
Te Quest for Cognates: A Reconstruction of Oblique Subject
... refer to constructions where the so-called logical subject is in an oblique case, for instance the dative. Our notion of oblique subject constructions also covers predicates where there is a nominative argument, like the nominative logical object of Dat-Nom predicates. Traditional grammar either reg ...
... refer to constructions where the so-called logical subject is in an oblique case, for instance the dative. Our notion of oblique subject constructions also covers predicates where there is a nominative argument, like the nominative logical object of Dat-Nom predicates. Traditional grammar either reg ...
Online Syntactic Storage Costs in Sentence
... two vs. three incomplete subject-verb dependencies, within the same set of items. Experiment 1 tests this prediction. Second, all of the experiments that show evidence of on-line syntactic storage cost compare conditions in which the high-storage conditions involve more incomplete subject-verb depen ...
... two vs. three incomplete subject-verb dependencies, within the same set of items. Experiment 1 tests this prediction. Second, all of the experiments that show evidence of on-line syntactic storage cost compare conditions in which the high-storage conditions involve more incomplete subject-verb depen ...
Identity of Roots - LingBuzz
... Morphology model are reviewed, and its original concept of an un-‐individuated acategorial root node is introduced. In section 2.1 arguments are presented which point to the conclusion that roots are in f ...
... Morphology model are reviewed, and its original concept of an un-‐individuated acategorial root node is introduced. In section 2.1 arguments are presented which point to the conclusion that roots are in f ...
Compromising transitivity: the problem of reciprocals
... (see Mohanan & Mohanan (1998) for detailed discussion of this question), and in fact some languages treat reciprocal constructions as straightforwardly transitive while others treat them as straightforwardly intransitive. In this article we show, however, that there are also many languages where the ...
... (see Mohanan & Mohanan (1998) for detailed discussion of this question), and in fact some languages treat reciprocal constructions as straightforwardly transitive while others treat them as straightforwardly intransitive. In this article we show, however, that there are also many languages where the ...
2244 KB
... transfer implication cannot be attributed to the semantics o f the base form, which in this case is not a verb, let alone a transfer verb. In all o f the examples (1)—(3), the appropriate inputs are simply lacking. These examples therefore suggest that the lexical-rule based model o f the applicativ ...
... transfer implication cannot be attributed to the semantics o f the base form, which in this case is not a verb, let alone a transfer verb. In all o f the examples (1)—(3), the appropriate inputs are simply lacking. These examples therefore suggest that the lexical-rule based model o f the applicativ ...
The Position of Direct and Indirect Objects of Ditransitive Verbs
... A specific feature of the English verb is that it has a potential for occurring in various clause structures and for combining with other clause elements. This feature is called valency (Allerton, 1982, p. 2). Regarding the valency of the English verb, Allerton (1982, pp. 5, 36) states that subject ...
... A specific feature of the English verb is that it has a potential for occurring in various clause structures and for combining with other clause elements. This feature is called valency (Allerton, 1982, p. 2). Regarding the valency of the English verb, Allerton (1982, pp. 5, 36) states that subject ...
A multi-modular approach to gradual change in
... semantics in the analysis of their interaction. In Autolexical Grammar (Sadock 1991, Yuasa 2005) and similar multimodular theories such as Parallel Architecture (Jackendoff 2002, Culicover & Jackendoff 2005), grammatical phenomena are systematically sorted out into syntactic and semantic modules. Some ...
... semantics in the analysis of their interaction. In Autolexical Grammar (Sadock 1991, Yuasa 2005) and similar multimodular theories such as Parallel Architecture (Jackendoff 2002, Culicover & Jackendoff 2005), grammatical phenomena are systematically sorted out into syntactic and semantic modules. Some ...
Effects of indefinite pronouns and traces on verb stress
... Notice that this suggests that adjacency of the verb to the stressed object is not a general precondition for a stressless verb in German. Similar patterns of leftmost stress within the VP in Persian are reported in Kahnemuyipour (2004). 2. The account of the phase-based theory of phrasal stress by ...
... Notice that this suggests that adjacency of the verb to the stressed object is not a general precondition for a stressless verb in German. Similar patterns of leftmost stress within the VP in Persian are reported in Kahnemuyipour (2004). 2. The account of the phase-based theory of phrasal stress by ...
Document
... Yami verbs divide into indicative and non-indicative forms. All verbs are either dynamic or stative (See Section 6.3). The indicative verbs are either neutral or perfective. Perfective verbs, marked with the prefix ni-, have past time reference and are anterior. Unlike most of the languages of the N ...
... Yami verbs divide into indicative and non-indicative forms. All verbs are either dynamic or stative (See Section 6.3). The indicative verbs are either neutral or perfective. Perfective verbs, marked with the prefix ni-, have past time reference and are anterior. Unlike most of the languages of the N ...
The ergative features of Papuan and Austronesian languages
... 1 However, a group of Australian languages from south-east Queensland (Galali, Wangkumara…), or Dhalanji (Western Australia) also have distinct marking for S, A and O. ...
... 1 However, a group of Australian languages from south-east Queensland (Galali, Wangkumara…), or Dhalanji (Western Australia) also have distinct marking for S, A and O. ...
Case and Event Structure
... information about the manner in which an activity is carried out (cf. Hale and Keyser 1993, Hale and Keyser 1999 and Krifka 1995). The complement of v may be a root (cf. Marantz 1997) which introduces the internal argument and may specify information about what happens to the internal argument. If t ...
... information about the manner in which an activity is carried out (cf. Hale and Keyser 1993, Hale and Keyser 1999 and Krifka 1995). The complement of v may be a root (cf. Marantz 1997) which introduces the internal argument and may specify information about what happens to the internal argument. If t ...
Post-syntactic movement and the Old Irish Verb
... Putting these two sets of facts together, it appears that finite and non-finite clauses can receive a unified account if the verb initially combines with the object, forming a verbal constituent in both cases. The difference between the VS orders and the SV orders is that the verb raises past the su ...
... Putting these two sets of facts together, it appears that finite and non-finite clauses can receive a unified account if the verb initially combines with the object, forming a verbal constituent in both cases. The difference between the VS orders and the SV orders is that the verb raises past the su ...
simple and complex predicates
... In this chapter, the constructions which involve verbs and/or coverbs in predicative function are discussed. Verbs alone may function as simple predicates (§3.1). The combination of a verb and one or two unmarked coverbs in a single intonation unit will be referred to as ‘canonical complex verb’ (§3 ...
... In this chapter, the constructions which involve verbs and/or coverbs in predicative function are discussed. Verbs alone may function as simple predicates (§3.1). The combination of a verb and one or two unmarked coverbs in a single intonation unit will be referred to as ‘canonical complex verb’ (§3 ...
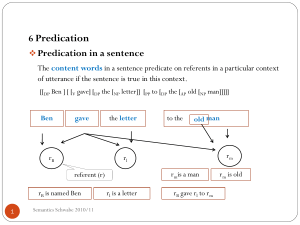
referential argument
... Predicative use of nouns and adjectives − Adjectives and nouns can be used predicatively. − They are complements of the copula syntactically. − Semantically, they are predicate terms the subject is an argument of. − Predicative predication terms are parasitic, for their first argument, on the ...
... Predicative use of nouns and adjectives − Adjectives and nouns can be used predicatively. − They are complements of the copula syntactically. − Semantically, they are predicate terms the subject is an argument of. − Predicative predication terms are parasitic, for their first argument, on the ...
Clause Structure: the three layers
... native speakers occurs, it provides evidence that at least some speakers use the construction. The main corpora used are Mark Davies’ Corpus of Contemporary American English (COCA) and the British National Corpus (BNC). I also use the World Atlas of Linguistic Structure (WALS) database, mainly to pr ...
... native speakers occurs, it provides evidence that at least some speakers use the construction. The main corpora used are Mark Davies’ Corpus of Contemporary American English (COCA) and the British National Corpus (BNC). I also use the World Atlas of Linguistic Structure (WALS) database, mainly to pr ...
The Syntax of Valuation in Auxiliary–participle
... require valuation by an AUX. Furthermore, since only AUX involves an interpretable T-feature (iT: perf), ParPars are not interpreted as perfect/participles, but only morphologically realized as PARTs. Lastly, regarding the word order differences between Scandinavian and Frisian, I assume that the he ...
... require valuation by an AUX. Furthermore, since only AUX involves an interpretable T-feature (iT: perf), ParPars are not interpreted as perfect/participles, but only morphologically realized as PARTs. Lastly, regarding the word order differences between Scandinavian and Frisian, I assume that the he ...
1 On the Identity of Roots Heidi Harley, University of - LingBuzz
... Morphology model are reviewed, and its original concept of an un-‐individuated acategorial root node is introduced. In section 2.1 arguments are presented which point to the conclusion that roots are in f ...
... Morphology model are reviewed, and its original concept of an un-‐individuated acategorial root node is introduced. In section 2.1 arguments are presented which point to the conclusion that roots are in f ...
Lexical and Viewpoint Aspect in Kubeo
... construction that can be analyzed exclusively as a perfective or imperfective marker. Hence, they are not a grammatical category in the way described by Dahl (1985). They are rather a conceptual category that can be inferred from the meaning of predicates. (ii) More recently in the theoretical liter ...
... construction that can be analyzed exclusively as a perfective or imperfective marker. Hence, they are not a grammatical category in the way described by Dahl (1985). They are rather a conceptual category that can be inferred from the meaning of predicates. (ii) More recently in the theoretical liter ...
Chapter 8 The verb complex
... Reduplication derives intransitive verbs from transitive roots. In some instances a verb may also be derived from a verb root giving a habitual, ongoing or diminutive verbs, or with semantically unpredictable results. In addition a handful of verbs are derived by reduplication from noun roots. These ...
... Reduplication derives intransitive verbs from transitive roots. In some instances a verb may also be derived from a verb root giving a habitual, ongoing or diminutive verbs, or with semantically unpredictable results. In addition a handful of verbs are derived by reduplication from noun roots. These ...
Journal of Linguistics Bare nominals and incorporating verbs in
... languages have shown that they are in fact well-attested and rather productive in Romanian, Italian, and European and Brazilian Portuguese, among others. This fact raises the following basic alternative: either Chierchia’s (1998) parameterization of Romance BNs is incorrect or we have to consider th ...
... languages have shown that they are in fact well-attested and rather productive in Romanian, Italian, and European and Brazilian Portuguese, among others. This fact raises the following basic alternative: either Chierchia’s (1998) parameterization of Romance BNs is incorrect or we have to consider th ...