24-Transistor
... The pnp transistor, shown in Fig. 1a) contains three distinct regions, a p-type "emitter", an ntype "base" and a p-type "collector", which together form two pn junctions. In a typical amplifier circuit, voltages are supplied so that the emitter-base junction is forward-biased and the collector-base ...
... The pnp transistor, shown in Fig. 1a) contains three distinct regions, a p-type "emitter", an ntype "base" and a p-type "collector", which together form two pn junctions. In a typical amplifier circuit, voltages are supplied so that the emitter-base junction is forward-biased and the collector-base ...
MSE-630 Lecture 4 Semiconductor theories
... material making it more positive, and holes in the p material, making it more negative. This creates a built-in electric field that discourages further transfer across the interface. ...
... material making it more positive, and holes in the p material, making it more negative. This creates a built-in electric field that discourages further transfer across the interface. ...
Ch 5 Homework - ECM
... 20. A(n) ____ is an electrical component that converts AC to DC by allowing voltage and current to move in only one direction. ...
... 20. A(n) ____ is an electrical component that converts AC to DC by allowing voltage and current to move in only one direction. ...
ECE 662 - George Mason University
... re emitter resistance of forward - biased Ce depletion layer capacitanc e across base - emitter ...
... re emitter resistance of forward - biased Ce depletion layer capacitanc e across base - emitter ...
File - N@Y@
... Derive an expression for the stability factor of a collector –to –base bias circuit. Mention the disadvantage of collector –to-base bias. Can they be overcome? Draw a circuit diagram of CE transistor amplifier using emitter biasing .Describe qualitatively the stability action of the circuit. Draw a ...
... Derive an expression for the stability factor of a collector –to –base bias circuit. Mention the disadvantage of collector –to-base bias. Can they be overcome? Draw a circuit diagram of CE transistor amplifier using emitter biasing .Describe qualitatively the stability action of the circuit. Draw a ...
4 - Rutgers Physics
... Next connect the full wave rectifier circuit shown in Figure 2. Use a symmetric transformer (e.g. TC016), where the impedance of the primary equals the impedance of the secondary windings. The transformer has a center tap (i.e. a line connected to the center of the coil). Try to characterize the tra ...
... Next connect the full wave rectifier circuit shown in Figure 2. Use a symmetric transformer (e.g. TC016), where the impedance of the primary equals the impedance of the secondary windings. The transformer has a center tap (i.e. a line connected to the center of the coil). Try to characterize the tra ...
H – Parameter model :-
... = reverse voltage transfer ratio with input part open circuited. h21 = [i2 / i1] with V2 = 0 = Forward current gain with output part short circuited. ...
... = reverse voltage transfer ratio with input part open circuited. h21 = [i2 / i1] with V2 = 0 = Forward current gain with output part short circuited. ...
Class B Output
... * No DC current is used to bias this configuration. *Activated when the input voltage is greater than the Vbe for the transistors. * npn Transistor operates when positive, pnp when negative. * At a zero input voltage, we get no output voltage. ...
... * No DC current is used to bias this configuration. *Activated when the input voltage is greater than the Vbe for the transistors. * npn Transistor operates when positive, pnp when negative. * At a zero input voltage, we get no output voltage. ...
Input Components
... Transistors require a base voltage of at least 0.6V with respect to the emitter to "turn on". (Darlington Pair transistors require 1.2 V). A limiting resistor - typically 1K is required in the base circuit of the transistor stage to prevent overrunning and hence overheating and destruction of the tr ...
... Transistors require a base voltage of at least 0.6V with respect to the emitter to "turn on". (Darlington Pair transistors require 1.2 V). A limiting resistor - typically 1K is required in the base circuit of the transistor stage to prevent overrunning and hence overheating and destruction of the tr ...
Ballistic Devices
... • Operation: The ability of a measured system to control the transport of some particles between the two reservoirs • Most direct form - Quantum Point Contact • Output is the electric current I due to ballistic electrons driven by the voltage difference V between the electrodes • Current depends on ...
... • Operation: The ability of a measured system to control the transport of some particles between the two reservoirs • Most direct form - Quantum Point Contact • Output is the electric current I due to ballistic electrons driven by the voltage difference V between the electrodes • Current depends on ...
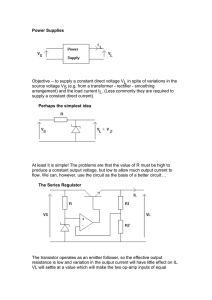
1. The simple version
... advantage of much higher efficiency than the series regulator -- the switch is either fully on (so there is no voltage drop across it) or fully off (so no current flows in it) and, since power = VI, no power is dissipated in the switch. (In fact, it will not be totally ideal and some power will be d ...
... advantage of much higher efficiency than the series regulator -- the switch is either fully on (so there is no voltage drop across it) or fully off (so no current flows in it) and, since power = VI, no power is dissipated in the switch. (In fact, it will not be totally ideal and some power will be d ...
DTDG14GP
... otherwise dispose of the same, no express or implied right or license to practice or commercially exploit any intellectual property rights or other proprietary rights owned or controlled by ROHM CO., LTD. is granted to any such buyer. Products listed in this document are no antiradiation design. ...
... otherwise dispose of the same, no express or implied right or license to practice or commercially exploit any intellectual property rights or other proprietary rights owned or controlled by ROHM CO., LTD. is granted to any such buyer. Products listed in this document are no antiradiation design. ...
Power Point Slides
... and the current resumes (Forward biased diode) • Applying positive to the N type removes more electrons and increases the depletion. Almost no current flows. (Reverse biased diode) ...
... and the current resumes (Forward biased diode) • Applying positive to the N type removes more electrons and increases the depletion. Almost no current flows. (Reverse biased diode) ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... Answer all questions. All questions carry equal marks. ...
... Answer all questions. All questions carry equal marks. ...
Tunnel Diode small ( )
... - the input signal power is then amplified at constant current by the large base collector reverse bias voltage to a larger output power - a limitation of the npn transistor amplifier is its low input impedance (or low input resistance), also its power consumption and integration density are not the ...
... - the input signal power is then amplified at constant current by the large base collector reverse bias voltage to a larger output power - a limitation of the npn transistor amplifier is its low input impedance (or low input resistance), also its power consumption and integration density are not the ...
Transistor
.jpg?width=300)
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify and switch electronic signals and electrical power. It is composed of semiconductor material with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals changes the current through another pair of terminals. Because the controlled (output) power can be higher than the controlling (input) power, a transistor can amplify a signal. Today, some transistors are packaged individually, but many more are found embedded in integrated circuits.The transistor is the fundamental building block of modern electronic devices, and is ubiquitous in modern electronic systems. Following its development in 1947 by American physicists John Bardeen, Walter Brattain, and William Shockley, the transistor revolutionized the field of electronics, and paved the way for smaller and cheaper radios, calculators, and computers, among other things. The transistor is on the list of IEEE milestones in electronics, and the inventors were jointly awarded the 1956 Nobel Prize in Physics for their achievement.