- Catalyst
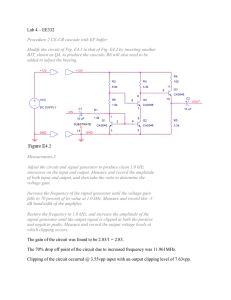
... b) Explain what determines the bias current level of Q4. c) Explain what advantage the addition of Q4 provides over the amplifier of procedure 1. Repsponses-2 a) The conversion to decibels would be 20Log(Vout/Vin) = 20Log(2.83/1) = 9.036dB b) Vth is applied to the base and Rth is the effective resis ...
... b) Explain what determines the bias current level of Q4. c) Explain what advantage the addition of Q4 provides over the amplifier of procedure 1. Repsponses-2 a) The conversion to decibels would be 20Log(Vout/Vin) = 20Log(2.83/1) = 9.036dB b) Vth is applied to the base and Rth is the effective resis ...
Building a Simple Circuit
... proportional to each other. • V=I x R. • Voltage = current x resistance. ...
... proportional to each other. • V=I x R. • Voltage = current x resistance. ...
TAN150
... The TAN150 is a high powered COMMON BASE bipolar transistor. It is designed for pulsed systems in the frequency band 960-1215 MHz. The device has gold thin-film metallization and diffused ballasting for proven highest MTTF. The transistor includes input and output prematch for broadband capability. ...
... The TAN150 is a high powered COMMON BASE bipolar transistor. It is designed for pulsed systems in the frequency band 960-1215 MHz. The device has gold thin-film metallization and diffused ballasting for proven highest MTTF. The transistor includes input and output prematch for broadband capability. ...
IMX8
... otherwise dispose of the same, no express or implied right or license to practice or commercially exploit any intellectual property rights or other proprietary rights owned or controlled by ROHM CO., LTD. is granted to any such buyer. Products listed in this document are no antiradiation design. ...
... otherwise dispose of the same, no express or implied right or license to practice or commercially exploit any intellectual property rights or other proprietary rights owned or controlled by ROHM CO., LTD. is granted to any such buyer. Products listed in this document are no antiradiation design. ...
7 Segment Display Driver
... see that the LED has provided an alternative route for this energy to continue flowing. One simple example is the ram water pump. This pump uses water from lets say 10m above to create a stream in a pipe, once this stream has reached a specific speed the valve closes due to the forces applied to it. ...
... see that the LED has provided an alternative route for this energy to continue flowing. One simple example is the ram water pump. This pump uses water from lets say 10m above to create a stream in a pipe, once this stream has reached a specific speed the valve closes due to the forces applied to it. ...
Bias Circuit Design for Low-Voltage Cascode Transistors
... The bias circuit should fix the gate voltage of the cascode transistor in such a way that the transistor connected at its source works in saturation. However, since this could cause a serious reduction in the dynamic range, there is a trade-off on the value of the gate voltage. The most simple circu ...
... The bias circuit should fix the gate voltage of the cascode transistor in such a way that the transistor connected at its source works in saturation. However, since this could cause a serious reduction in the dynamic range, there is a trade-off on the value of the gate voltage. The most simple circu ...
4. Colpitts Oscillator - The Designer`s Guide Community
... at a Colpitts oscillator with automatic gain control. ...
... at a Colpitts oscillator with automatic gain control. ...
Chapter 3 Special-Purpose Diodes
... Analysis of this transistor circuit to predict the dc voltages and currents requires use of Ohm’s law, Kirchhoff’s voltage law and the beta for the transistor. Application of these laws begins with the base circuit to determine the amount of base current. Using Kichhoff’s voltage law, subtract the . ...
... Analysis of this transistor circuit to predict the dc voltages and currents requires use of Ohm’s law, Kirchhoff’s voltage law and the beta for the transistor. Application of these laws begins with the base circuit to determine the amount of base current. Using Kichhoff’s voltage law, subtract the . ...
npn pnp - Portland State University
... For increasing, but small, values of the drain-source voltage VDS, the current increases increases, similar to the case of a simple resistor (ohmic region.) As VDS increases further, the current begins to level off because the channel narrows at the drain end (see Fig.3.) When the drain-source volta ...
... For increasing, but small, values of the drain-source voltage VDS, the current increases increases, similar to the case of a simple resistor (ohmic region.) As VDS increases further, the current begins to level off because the channel narrows at the drain end (see Fig.3.) When the drain-source volta ...
Current-Mode Logic
... negligible, now have become a factor in design. The problems we will focus on are to either reduce or utilize leakage current and to lower power consumption. Our proposed area of research is to this is instead of doing logic with voltages, using current mode logic. Current mode based circuits offer ...
... negligible, now have become a factor in design. The problems we will focus on are to either reduce or utilize leakage current and to lower power consumption. Our proposed area of research is to this is instead of doing logic with voltages, using current mode logic. Current mode based circuits offer ...
NEW COMPLEMENTARY BiCMOS DIGITAL GATES FOR LOW
... determined by the feedback CMOS inverter, INV. For the pull up transition, a low (zero) output voltage would feedback a high voltage to the gate of the input stage thereby triggering N1 ON. A low transition applied to the input causes N1 to conduct, drawing its current from the conducting Q1. The ri ...
... determined by the feedback CMOS inverter, INV. For the pull up transition, a low (zero) output voltage would feedback a high voltage to the gate of the input stage thereby triggering N1 ON. A low transition applied to the input causes N1 to conduct, drawing its current from the conducting Q1. The ri ...
5.4.4. Base spreading resistance and emitter current crowding
... density, especially since the emitter current density depends exponentially on the local baseemitter voltage. This effect is minimal in the center of the emitter-base diode and strongly increases toward the edges. In extreme cases, this effect causes the emitter current to occur only at the very edg ...
... density, especially since the emitter current density depends exponentially on the local baseemitter voltage. This effect is minimal in the center of the emitter-base diode and strongly increases toward the edges. In extreme cases, this effect causes the emitter current to occur only at the very edg ...
A cmos bandgap reference without resistors - Solid
... Index Terms—Analog circuits, analog integrated circuits, CMOS analog integrated circuits, reference circuits, temperature. ...
... Index Terms—Analog circuits, analog integrated circuits, CMOS analog integrated circuits, reference circuits, temperature. ...
Transistor
.jpg?width=300)
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify and switch electronic signals and electrical power. It is composed of semiconductor material with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals changes the current through another pair of terminals. Because the controlled (output) power can be higher than the controlling (input) power, a transistor can amplify a signal. Today, some transistors are packaged individually, but many more are found embedded in integrated circuits.The transistor is the fundamental building block of modern electronic devices, and is ubiquitous in modern electronic systems. Following its development in 1947 by American physicists John Bardeen, Walter Brattain, and William Shockley, the transistor revolutionized the field of electronics, and paved the way for smaller and cheaper radios, calculators, and computers, among other things. The transistor is on the list of IEEE milestones in electronics, and the inventors were jointly awarded the 1956 Nobel Prize in Physics for their achievement.