The Urea Cycle - Rose
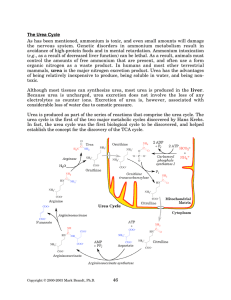
... releases free amino acids into circulation to act as energy sources for the body, and to act as substrates for gluconeogenesis in the liver. As has been mentioned, the toxicity of free ammonium means that, whenever possible, ammonium is maintained in an organic form. In most tissues, excess ammonium ...
... releases free amino acids into circulation to act as energy sources for the body, and to act as substrates for gluconeogenesis in the liver. As has been mentioned, the toxicity of free ammonium means that, whenever possible, ammonium is maintained in an organic form. In most tissues, excess ammonium ...
The Regulation of Energy Metabolism Pathways
... Mildronate is known to be an inhibitor of L-carnitine biosynthesis (Simkhovich et al., 1988), its transport into tissues and its reabsorption in the kidney (Kuwajima et al., 1999). The Ki for GBB hydroxylase enzyme inhibition by mildronate has been determined to be 19 μM (enzyme prepared as describe ...
... Mildronate is known to be an inhibitor of L-carnitine biosynthesis (Simkhovich et al., 1988), its transport into tissues and its reabsorption in the kidney (Kuwajima et al., 1999). The Ki for GBB hydroxylase enzyme inhibition by mildronate has been determined to be 19 μM (enzyme prepared as describe ...
Chapter 7 General Principles of Exercise Prescription
... expended during an activity to the rate of energy expended at rest. . . . (One) MET is the rate of EE while sitting at rest . . . by convention, [1 MET is equal to] an oxygen uptake of 3.5 [mL ∙ kg−1 ∙ min−1]” (38). MET-min: An index of EE that quantifies the total amount of physical activity perfor ...
... expended during an activity to the rate of energy expended at rest. . . . (One) MET is the rate of EE while sitting at rest . . . by convention, [1 MET is equal to] an oxygen uptake of 3.5 [mL ∙ kg−1 ∙ min−1]” (38). MET-min: An index of EE that quantifies the total amount of physical activity perfor ...
Metabolism of lipids
... units in the elongation step is malonyl-ACP (a three-carbon unit) but during the elongation, CO2 is released. This drives the reaction • The reducing agent is NADPH. • Elongation by FA synthase complex stops upon formation of C16 palmitate. Further elongation and the insertion of double bonds (by de ...
... units in the elongation step is malonyl-ACP (a three-carbon unit) but during the elongation, CO2 is released. This drives the reaction • The reducing agent is NADPH. • Elongation by FA synthase complex stops upon formation of C16 palmitate. Further elongation and the insertion of double bonds (by de ...
video slide
... – Is an energy-coupling mechanism that uses energy in the form of a H+ gradient across a membrane to drive cellular work Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... – Is an energy-coupling mechanism that uses energy in the form of a H+ gradient across a membrane to drive cellular work Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
LIPID MOBILIZATION
... The NADH+H+ and FADH2 produced are oxidized further by the mitochondrial respiratory chain to establish an electrochemical gradient of protons, which is finally used by the F1F0-ATP synthase (complex V) to produce ATP, the only form of energy used by the cell. ...
... The NADH+H+ and FADH2 produced are oxidized further by the mitochondrial respiratory chain to establish an electrochemical gradient of protons, which is finally used by the F1F0-ATP synthase (complex V) to produce ATP, the only form of energy used by the cell. ...
A Study of Free Amino Acids and of Glutamine
... from dietary sources alone. As a result, a portion of the nitrogen needed for tumor growth is drawn from the protein stores of the host (10). Under these circumstances, it would seem likely that the amino acid metabolism of the host would be dis turbed. Information on this point, however, has not be ...
... from dietary sources alone. As a result, a portion of the nitrogen needed for tumor growth is drawn from the protein stores of the host (10). Under these circumstances, it would seem likely that the amino acid metabolism of the host would be dis turbed. Information on this point, however, has not be ...
Human Physiology - Orange Coast College
... Lactic acid produced by anaerobic respiration delivered to the liver. LDH converts lactic acid to pyruvic acid. Pyruvic acid converted to glucose-6phosphate: Intermediate for glycogen. Converted to free glucose. Gluconeogenesis: conversion to noncarbohydrate molecules through pyruvic acid to glu ...
... Lactic acid produced by anaerobic respiration delivered to the liver. LDH converts lactic acid to pyruvic acid. Pyruvic acid converted to glucose-6phosphate: Intermediate for glycogen. Converted to free glucose. Gluconeogenesis: conversion to noncarbohydrate molecules through pyruvic acid to glu ...
PDF
... Insulin is; a polypeptide hormone, composed of two amino acid chains (A chain: 21 amino acids; B chain 30 amino acids). The chains are connected to each other by disulfide linkage; those chains contain 51 amino acids with a molecular weight of 6,000. It is secreted by the β cells of the pancreas whe ...
... Insulin is; a polypeptide hormone, composed of two amino acid chains (A chain: 21 amino acids; B chain 30 amino acids). The chains are connected to each other by disulfide linkage; those chains contain 51 amino acids with a molecular weight of 6,000. It is secreted by the β cells of the pancreas whe ...
Metabolism of Xenobiotics
... "The nomenclature system is based solely on the sequence similarity among P450s and does not indicate the properties or function of individual P450s" In the current nomenclature system [ ], the cytochrome "P450s are named using the root symbol CYP ..., followed by an Arabic numeral designating the f ...
... "The nomenclature system is based solely on the sequence similarity among P450s and does not indicate the properties or function of individual P450s" In the current nomenclature system [ ], the cytochrome "P450s are named using the root symbol CYP ..., followed by an Arabic numeral designating the f ...
PDF
... and others, such as acetylcholine. Neurotransmitter imbalances caused by disturbances in the monoamine ...
... and others, such as acetylcholine. Neurotransmitter imbalances caused by disturbances in the monoamine ...
Insulin and Glucagon
... glucose taken up from blood by working muscles, the level of blood glucose is not altered. Decreased secretion of insulin and a marked increase in glucagon secretion prompt the liver to break down glycogen and start gluconeogenesis. These actions provide the glucose required to balance glucose uptak ...
... glucose taken up from blood by working muscles, the level of blood glucose is not altered. Decreased secretion of insulin and a marked increase in glucagon secretion prompt the liver to break down glycogen and start gluconeogenesis. These actions provide the glucose required to balance glucose uptak ...
ATP Synthesis
... ∆ε° = +0.085V => ∆G° = -16 kJ/mol - This reaction does not generate sufficient free energy to pump protons across the IMM via the transmembrane domain of Complex II—this step is however important in that it injects electrons directly into CoQ so that the energy carried by electrons can be utilized b ...
... ∆ε° = +0.085V => ∆G° = -16 kJ/mol - This reaction does not generate sufficient free energy to pump protons across the IMM via the transmembrane domain of Complex II—this step is however important in that it injects electrons directly into CoQ so that the energy carried by electrons can be utilized b ...
as a PDF
... marlin, striped marlin and Mediterranean spearfish), xiphiid billfishes (Pacific and Mediterranean stocks) and a scombrid fish (butterfly mackerel) were included in the analysis. Our main objectives were (1) to assess the maximum possible substrate flux in heater tissue, and (2) to determine what me ...
... marlin, striped marlin and Mediterranean spearfish), xiphiid billfishes (Pacific and Mediterranean stocks) and a scombrid fish (butterfly mackerel) were included in the analysis. Our main objectives were (1) to assess the maximum possible substrate flux in heater tissue, and (2) to determine what me ...
Lecture 008, Tissue - SuperPage for Joel R. Gober, PhD.
... >> Yeah, sure. Because that’s why it turned in to Carbon Dioxide and water. Yeah, by itself it will do it how? It will do it very slowly. Okay? Because there’s an activation energy barrier but if we put in the energy to that dust we can get all of these dust to turn into carbon dioxide and water ver ...
... >> Yeah, sure. Because that’s why it turned in to Carbon Dioxide and water. Yeah, by itself it will do it how? It will do it very slowly. Okay? Because there’s an activation energy barrier but if we put in the energy to that dust we can get all of these dust to turn into carbon dioxide and water ver ...
video slide - Ionia Public Schools
... anaerobic respiration but is often used to refer to aerobic respiration • Although carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are all consumed as fuel, it is helpful to trace cellular respiration with the sugar glucose: C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy (ATP + heat) ...
... anaerobic respiration but is often used to refer to aerobic respiration • Although carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are all consumed as fuel, it is helpful to trace cellular respiration with the sugar glucose: C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy (ATP + heat) ...
Aalborg Universitet Occurrence and in situ physiology of uncultured putative alphaproteobacterial
... removal (EBPR) wastewater treatment plants has been proposed as one cause of deterioration of EBPR. Putative GAOs from the Alphaproteobacteria, Defluviicoccus spp. (including D. vanus), were studied in full-scale EBPR plants to determine their distribution, abundance and ecophysiology. Fluorescence ...
... removal (EBPR) wastewater treatment plants has been proposed as one cause of deterioration of EBPR. Putative GAOs from the Alphaproteobacteria, Defluviicoccus spp. (including D. vanus), were studied in full-scale EBPR plants to determine their distribution, abundance and ecophysiology. Fluorescence ...
Glycolysis - WordPress.com
... on how efficiently oxygen can be delivered to, and processed by, your muscles. A continuous supply of oxygen allows you to maintain a reduced intensity level for a long period of time. If you are able to extend an exercise activity beyond approximately two minutes in length it will be due to the fac ...
... on how efficiently oxygen can be delivered to, and processed by, your muscles. A continuous supply of oxygen allows you to maintain a reduced intensity level for a long period of time. If you are able to extend an exercise activity beyond approximately two minutes in length it will be due to the fac ...
Feodor Lynen - Nobel Lecture
... contains two carbon atoms less than the original acid, and which is immediately oxidised in the same manner in the next cycle. This reaction sequence can be repeated until the fatty acid has been entirely converted into acetylCoA. The substrate is regenerated in this repeated reaction sequence, whic ...
... contains two carbon atoms less than the original acid, and which is immediately oxidised in the same manner in the next cycle. This reaction sequence can be repeated until the fatty acid has been entirely converted into acetylCoA. The substrate is regenerated in this repeated reaction sequence, whic ...
enzymes lecture 1
... (C) Apoenzyme (D) Holoenzyme 3- Enzymes are largely ……………… in their chemical nature. (A) Lipids (B) Steroids (C) Protein (D) All A, B and C ...
... (C) Apoenzyme (D) Holoenzyme 3- Enzymes are largely ……………… in their chemical nature. (A) Lipids (B) Steroids (C) Protein (D) All A, B and C ...
carnitine deficiency??? - UCSF | Department of Medicine
... • Fatty acid transport enzyme deficiency, like carnitine acyl transferase, carnitine palmitoyltransferase (CPT) I and CPT II. No response to carnitine. • Beta-oxidation enzyme defects. No response to carnitine Carnitine Deficiency in Chronic Dialysis A relative carnitine deficiency can occur in dial ...
... • Fatty acid transport enzyme deficiency, like carnitine acyl transferase, carnitine palmitoyltransferase (CPT) I and CPT II. No response to carnitine. • Beta-oxidation enzyme defects. No response to carnitine Carnitine Deficiency in Chronic Dialysis A relative carnitine deficiency can occur in dial ...
227 integrated responses to exhaustive exercise and recovery in
... As a sprint swimmer with over 60 % of its body mass in white muscle (Johnston, 1980; Stevens, 1968), the rainbow trout provides an ideal model in which to study the exercise physiology of this tissue. Indeed, the acid–base, metabolic and fluid volume responses induced by short-term ‘anaerobic’ exhau ...
... As a sprint swimmer with over 60 % of its body mass in white muscle (Johnston, 1980; Stevens, 1968), the rainbow trout provides an ideal model in which to study the exercise physiology of this tissue. Indeed, the acid–base, metabolic and fluid volume responses induced by short-term ‘anaerobic’ exhau ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.























