ppt
... 1. Acetyl CoA onto ACP P-SH group 2. Acetyl CoA transfers to Cys –SH of other 3. This Acetyl CoA will become the w (last) C of the fatty acid (i.e. carbon 16 of palmitate) 4. Malonyl CoA attaches to ACP SH 5. Malonyl CoA releases CO2; 2-C unit condenses with the Acetyl CoA, and a 4-C product is prod ...
... 1. Acetyl CoA onto ACP P-SH group 2. Acetyl CoA transfers to Cys –SH of other 3. This Acetyl CoA will become the w (last) C of the fatty acid (i.e. carbon 16 of palmitate) 4. Malonyl CoA attaches to ACP SH 5. Malonyl CoA releases CO2; 2-C unit condenses with the Acetyl CoA, and a 4-C product is prod ...
Ch. 33 Synthesis of Fatty acids, Triacylglycerols, Membrane lipids
... Glucose to pyruvate in mitochondrion, forms Ac CoA, OAA, which form citrate Citrate in cytosol then to Ac CoA, malonyl CoA Fatty acid synthesis involve series 2-C additions from malonyl CoA to the ω-C of Ac CoA onto FA synthase. Costs 2 NADPH and 1 ATP per cycle addition ...
... Glucose to pyruvate in mitochondrion, forms Ac CoA, OAA, which form citrate Citrate in cytosol then to Ac CoA, malonyl CoA Fatty acid synthesis involve series 2-C additions from malonyl CoA to the ω-C of Ac CoA onto FA synthase. Costs 2 NADPH and 1 ATP per cycle addition ...
Document
... in the analysis of a wide variety of enantiomeric and diastereomeric guests. Recent work in our laboratory has shown that the intercalation of chiral cationic host molecules into R-zirconium phosphate, a lamellar cation exchanger, provides a useful medium for batchwise resolution of racemic mixtures ...
... in the analysis of a wide variety of enantiomeric and diastereomeric guests. Recent work in our laboratory has shown that the intercalation of chiral cationic host molecules into R-zirconium phosphate, a lamellar cation exchanger, provides a useful medium for batchwise resolution of racemic mixtures ...
Cholesterol And Sterol Metabolism
... Glucagon stimulates adenyl cyclase producing cAMP cAMP activates protein kinase A Inactivates HMG-CoA reductase ...
... Glucagon stimulates adenyl cyclase producing cAMP cAMP activates protein kinase A Inactivates HMG-CoA reductase ...
Requirements - Department of Medical Biochemistry, Semmelweis
... reason, the semester will not be acknowledged. The student in this case is not allowed to sit for the semifinal exam. Missed practicals can be completed only in the same week at another group; certificate from the host teacher should be presented by the student to the assigned teacher. Grading of th ...
... reason, the semester will not be acknowledged. The student in this case is not allowed to sit for the semifinal exam. Missed practicals can be completed only in the same week at another group; certificate from the host teacher should be presented by the student to the assigned teacher. Grading of th ...
Urea Cycle - MBBS Students Club
... • The ammonia produced by enteric bacteria and absorbedinto portal venous blood and the ammonia produced by tissues are rapidly removed from circulation by the liver and converted to urea. • Only traces (10–20μg/dL) thus normally are present in peripheral blood. • This is essential, since ammonia is ...
... • The ammonia produced by enteric bacteria and absorbedinto portal venous blood and the ammonia produced by tissues are rapidly removed from circulation by the liver and converted to urea. • Only traces (10–20μg/dL) thus normally are present in peripheral blood. • This is essential, since ammonia is ...
macromolecule foldable
... 1. Give 2 FUNCTIONS FOR NUCLEIC ACIDS 2. List 2 EXAMPLES OF NUCLEIC ACIDS ...
... 1. Give 2 FUNCTIONS FOR NUCLEIC ACIDS 2. List 2 EXAMPLES OF NUCLEIC ACIDS ...
AccessMedicine | Print: Cha
... The 5'-phosphoryl group of a mononucleotide can esterify a second hydroxyl group, forming a phosphodiester. Most commonly, this second hydroxyl group is the 3'-OH of the pentose of a second nucleotide. This forms a dinucleotide in which the pentose moieties are linked by a 3',5'-phosphodiester bond ...
... The 5'-phosphoryl group of a mononucleotide can esterify a second hydroxyl group, forming a phosphodiester. Most commonly, this second hydroxyl group is the 3'-OH of the pentose of a second nucleotide. This forms a dinucleotide in which the pentose moieties are linked by a 3',5'-phosphodiester bond ...
DESIGN AND SYNTHESIS OF TRIPHENYL-1H-PYRAZOLE DERIVATIVES AS ANTICANCER AGENTS
... commercialization of a drug is a tedious, time consuming and costintensive process. For these reasons, any tool or technique that increases the efficiency of any stage of the drug discovery process is highly desirable. As the main paradigm of medicinal chemistry is that the biological activity, as w ...
... commercialization of a drug is a tedious, time consuming and costintensive process. For these reasons, any tool or technique that increases the efficiency of any stage of the drug discovery process is highly desirable. As the main paradigm of medicinal chemistry is that the biological activity, as w ...
Peptide synthesis – chemistry and modifications
... Fischer’s pioneering work in the early 1900’s, synthesis methods have improved continually – especially with Merrifield’s development of solid-phase syntheses. Besides the classical synthesis in solution, solid-support synthesis is now the most widely used method to prepare synthetic peptides. The a ...
... Fischer’s pioneering work in the early 1900’s, synthesis methods have improved continually – especially with Merrifield’s development of solid-phase syntheses. Besides the classical synthesis in solution, solid-support synthesis is now the most widely used method to prepare synthetic peptides. The a ...
Early days of tRNA research: Discovery, function, purification and
... This result also supported the notion of amino acid transfer to RNA although the ribonuclease sensitive ATP-AMP exchange was observed only in the presence of alanine and not other amino acids. Zamecnik and his colleagues named the RNA in the pH 5 enzyme fraction soluble RNA3 (sRNA). This RNA is now ...
... This result also supported the notion of amino acid transfer to RNA although the ribonuclease sensitive ATP-AMP exchange was observed only in the presence of alanine and not other amino acids. Zamecnik and his colleagues named the RNA in the pH 5 enzyme fraction soluble RNA3 (sRNA). This RNA is now ...
2. Solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) - RSC Publishing
... amino acid and the carboxylic group of a second one, the so-called peptide bond. In Nature these interactions between the twenty natural L-amino acids finally produce the proteins. Fischer demonstrated that proteins are formed by amino acids and the peptide bond the interaction between them. He synt ...
... amino acid and the carboxylic group of a second one, the so-called peptide bond. In Nature these interactions between the twenty natural L-amino acids finally produce the proteins. Fischer demonstrated that proteins are formed by amino acids and the peptide bond the interaction between them. He synt ...
PDF Full-text
... Benzyloxycarbonyl is a standard group used for N-protection, but other carbamates are compatible with the phospha-Michael addition conditions, particularly with the mild TMSCl/tertiary amine version. These other carbomates commonly include t-butyloxycarbonyl (Boc) [23] and 9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl ...
... Benzyloxycarbonyl is a standard group used for N-protection, but other carbamates are compatible with the phospha-Michael addition conditions, particularly with the mild TMSCl/tertiary amine version. These other carbomates commonly include t-butyloxycarbonyl (Boc) [23] and 9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl ...
- Wiley Online Library
... and co-workers instead used magnesium monohydrate phosphate dispersed in water (saturated solution) in their syntheses, whereas Kongshaug and co-workers obtained low water activity by the use of phosphoric acid. Hermes-Lima & Vieyra (1992) were successful in condensing pyrophosphate (PPi) from ortho ...
... and co-workers instead used magnesium monohydrate phosphate dispersed in water (saturated solution) in their syntheses, whereas Kongshaug and co-workers obtained low water activity by the use of phosphoric acid. Hermes-Lima & Vieyra (1992) were successful in condensing pyrophosphate (PPi) from ortho ...
Special aspects of renal metabolism
... Removing α-amino group is obligatory in the catabolism of all amino acids Once removed, nitrogen can be incorporated into other compounds or excreted, with the carbon skeletons metabolized Transamination and oxidative deamination will provide ammonia and aspartate (sources of urea nitrogen) ...
... Removing α-amino group is obligatory in the catabolism of all amino acids Once removed, nitrogen can be incorporated into other compounds or excreted, with the carbon skeletons metabolized Transamination and oxidative deamination will provide ammonia and aspartate (sources of urea nitrogen) ...
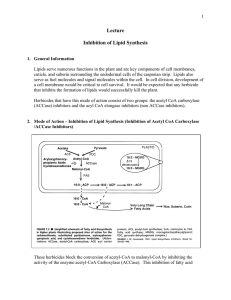
Lecture Inhibition of Lipid Synthesis
... Sethoxydim was discovered by Nippon Soda Co. and was developed by BASF in the U.S. where it was first tested in 1978. Clethodim was not discovered until 1987. 7. Mode of Action – Inhibition of Lipid Synthesis (Inhibition of Elongases / non ACCase Inhibitors) ...
... Sethoxydim was discovered by Nippon Soda Co. and was developed by BASF in the U.S. where it was first tested in 1978. Clethodim was not discovered until 1987. 7. Mode of Action – Inhibition of Lipid Synthesis (Inhibition of Elongases / non ACCase Inhibitors) ...
Summary of Chapter 24
... • Glutamine synthetase is a central control point in the nitrogen metabolism, since Gln is an amino group donor and a storage of ammonia. 1. Feedback inhibition: His, Tyr, carbamoyl phosphate, AMP, CTP, glucosamine-6phosphate (all end products from Gln) are allosteric inhibitors. Ala, Ser and Gly al ...
... • Glutamine synthetase is a central control point in the nitrogen metabolism, since Gln is an amino group donor and a storage of ammonia. 1. Feedback inhibition: His, Tyr, carbamoyl phosphate, AMP, CTP, glucosamine-6phosphate (all end products from Gln) are allosteric inhibitors. Ala, Ser and Gly al ...
The ins and outs of sphingolipid synthesis
... a-oxoamine synthases, and is composed of a heterodimer of two similar, but non-identical, subunits, named Lcb1p (long chain base 1) and Lcb2p, which were first identified in yeast by genetic methods [7,8]. Eukaryotic SPTs are membrane bound, with the active site facing the cytoplasm (Figure 2). Stud ...
... a-oxoamine synthases, and is composed of a heterodimer of two similar, but non-identical, subunits, named Lcb1p (long chain base 1) and Lcb2p, which were first identified in yeast by genetic methods [7,8]. Eukaryotic SPTs are membrane bound, with the active site facing the cytoplasm (Figure 2). Stud ...
CHOLESTEROL SYNTHESIS
... epoxide lanosterolcyclase to form the first steroidal intermediate LANOSTEROL. ...
... epoxide lanosterolcyclase to form the first steroidal intermediate LANOSTEROL. ...
Document
... pyrimidine nucleotides from low molecular weight precursors in amounts sufficient for their own needs. The de novo pathways are almost identical in all organisms. ...
... pyrimidine nucleotides from low molecular weight precursors in amounts sufficient for their own needs. The de novo pathways are almost identical in all organisms. ...
The origin of the RNA world: Co-evolution of genes and metabolism
... fashion, many extant metabolic pathways likely resulted from reinforcement of pre-existing pathways, with gradual replacement of primordial catalysts by more efficient catalysts, beginning with metal ions and small molecules and progressing to macromolecular RNA and/or protein catalysts. Thus, extant ...
... fashion, many extant metabolic pathways likely resulted from reinforcement of pre-existing pathways, with gradual replacement of primordial catalysts by more efficient catalysts, beginning with metal ions and small molecules and progressing to macromolecular RNA and/or protein catalysts. Thus, extant ...
Essentials of Glycobiology Lecture 42 June 9, 1998 Jeff Esko
... ManNH2-Man-GlcN-PI is a poor substrate for the a2mannosyltransferase Trypanosomes selectively take up and exchange fatty acid analogs (10-(propoxy)decanoic acid) for acyl chains on glycosylphosphatidylinositol O O HO ...
... ManNH2-Man-GlcN-PI is a poor substrate for the a2mannosyltransferase Trypanosomes selectively take up and exchange fatty acid analogs (10-(propoxy)decanoic acid) for acyl chains on glycosylphosphatidylinositol O O HO ...
Oligonucleotide synthesis

Oligonucleotide synthesis is the chemical synthesis of relatively short fragments of nucleic acids with defined chemical structure (sequence). The technique is extremely useful in current laboratory practice because it provides a rapid and inexpensive access to custom-made oligonucleotides of the desired sequence. Whereas enzymes synthesize DNA and RNA only in a 5' to 3' direction, chemical oligonucleotide synthesis does not suffer from this limitation, although it is, most often, carried out in the opposite, 3' to 5' direction. Currently, the process is implemented as solid-phase synthesis using phosphoramidite method and phosphoramidite building blocks derived from protected 2'-deoxynucleosides (dA, dC, dG, and T), ribonucleosides (A, C, G, and U), or chemically modified nucleosides, e.g. LNA, BNA.To obtain the desired oligonucleotide, the building blocks are sequentially coupled to the growing oligonucleotide chain in the order required by the sequence of the product (see Synthetic cycle below). The process has been fully automated since the late 1970s. Upon the completion of the chain assembly, the product is released from the solid phase to solution, deprotected, and collected. The occurrence of side reactions sets practical limits for the length of synthetic oligonucleotides (up to about 200 nucleotide residues) because the number of errors accumulates with the length of the oligonucleotide being synthesized. Products are often isolated by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) to obtain the desired oligonucleotides in high purity. Typically, synthetic oligonucleotides are single-stranded DNA or RNA molecules around 15–25 bases in length.Oligonucleotides find a variety of applications in molecular biology and medicine. They are most commonly used as antisense oligonucleotides, small interfering RNA, primers for DNA sequencing and amplification, probes for detecting complementary DNA or RNA via molecular hybridization, tools for the targeted introduction of mutations and restriction sites, and for the synthesis of artificial genes.