An Introduction to Invertebrates I Chapter 33A: 1. Porifera 2. Cnidaria
... called a proctostome (“anal mouth”) through which food enters the ...
... called a proctostome (“anal mouth”) through which food enters the ...
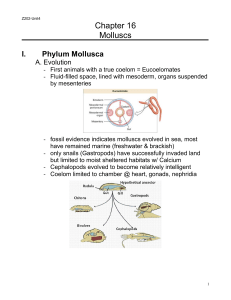
Chapter 16 Molluscs
... sensory & locomotor organs 2. Visceral mass portion contains digestive, circulatory, respiratory, & reproductive organs 3. Mantle forms a protective covering ...
... sensory & locomotor organs 2. Visceral mass portion contains digestive, circulatory, respiratory, & reproductive organs 3. Mantle forms a protective covering ...
Bilateral symmetry - Cal State LA
... studies indicate both groups evolved from an ancestor that did have a coelom (because all their relatives have one) - indicates secondary loss of an ancestral trait, likely an adaptation to their environment and mode of hunting ...
... studies indicate both groups evolved from an ancestor that did have a coelom (because all their relatives have one) - indicates secondary loss of an ancestral trait, likely an adaptation to their environment and mode of hunting ...
Week 9 Follow-Along Sheet File
... Contain anterior/posterior, ventral/dorsal areas of the body _____________________ has evolved Resulting in use of their head for orientation ______________________: 3 germ layers (Ecto-, Meso-, Endoderm) We will talk about: Phylum Platyhelminthes Phylum Rotifera Phylum Nematoda ...
... Contain anterior/posterior, ventral/dorsal areas of the body _____________________ has evolved Resulting in use of their head for orientation ______________________: 3 germ layers (Ecto-, Meso-, Endoderm) We will talk about: Phylum Platyhelminthes Phylum Rotifera Phylum Nematoda ...
First Lab Practical
... - body cavities originally for locomotion using hydrostatic skeleton - pseudocoelom made from blastocoel and not completely lined with mesoderm; true coeloms not made from blastocoel and completely lined with mesoderm diseases: Trematodes (snail, fish, human), Nematode (elephantiasis and trichinosis ...
... - body cavities originally for locomotion using hydrostatic skeleton - pseudocoelom made from blastocoel and not completely lined with mesoderm; true coeloms not made from blastocoel and completely lined with mesoderm diseases: Trematodes (snail, fish, human), Nematode (elephantiasis and trichinosis ...
Lecture 22 - Taft College
... blocks from larger molecules to smaller ones that may be absorbed and used by the body. – a. mechanical or physical digestion - ex. - chewing – b. chemical digestion – ex. Digestive enzymes (catalysts) 3. Absorption - taking in the nutrients that have been broken down. 4. Defecation or egestion elim ...
... blocks from larger molecules to smaller ones that may be absorbed and used by the body. – a. mechanical or physical digestion - ex. - chewing – b. chemical digestion – ex. Digestive enzymes (catalysts) 3. Absorption - taking in the nutrients that have been broken down. 4. Defecation or egestion elim ...
Ch. 25
... the system consists of a network of fine tubules that run through the body enlarged flame cells (cilia-lined bulbs) are located on the side branches of the tubules the cilia move water and excretory substances into the tubules and then into exit pores the primary function of the flame cells ...
... the system consists of a network of fine tubules that run through the body enlarged flame cells (cilia-lined bulbs) are located on the side branches of the tubules the cilia move water and excretory substances into the tubules and then into exit pores the primary function of the flame cells ...
Biology 213, Lab 4
... Annelida) you will sketch a cross section (except for the sponge, in which you will sketch a longitudinal section) and label the following. Note the most simpler animals will have fewer structures to label. ...
... Annelida) you will sketch a cross section (except for the sponge, in which you will sketch a longitudinal section) and label the following. Note the most simpler animals will have fewer structures to label. ...
Kingdom Animalia – Cnidaria corals, sea anemones, jelly fish, box
... Have tissue level of organization, with three tissue layers (triploblastic – with endoderm, ectoderm, and mesoderm) Have bilateral symmetry Have only one opening to the body cavity / digestive cavity Have cephalization (and at least at some stage of their lives, so will all the animals that we’ll di ...
... Have tissue level of organization, with three tissue layers (triploblastic – with endoderm, ectoderm, and mesoderm) Have bilateral symmetry Have only one opening to the body cavity / digestive cavity Have cephalization (and at least at some stage of their lives, so will all the animals that we’ll di ...
Topic 21: Animal Kingdom - University of Maine System
... Better breathing, legs, teeth, and brain. ...
... Better breathing, legs, teeth, and brain. ...
Taxonomy and Systematics: Seeking Order Amidst Diversity
... Jointed appendages Open circulatory system Hemolymph (the open-circulation system equivalent of blood) carries dissolved gases through short vessels and the hemocoel (main body cavity in adults, since coelom is reduced) As in much of modern systematics, classes are in flux; nevertheless, here are 5 ...
... Jointed appendages Open circulatory system Hemolymph (the open-circulation system equivalent of blood) carries dissolved gases through short vessels and the hemocoel (main body cavity in adults, since coelom is reduced) As in much of modern systematics, classes are in flux; nevertheless, here are 5 ...
Phylum Cnidaria (Coelenterata)
... • First true nerve cells in K. Anamalia – Nerve net sends impulses in all directions – Cells of epidermis and gastrodermis arranged into contractile fibers ...
... • First true nerve cells in K. Anamalia – Nerve net sends impulses in all directions – Cells of epidermis and gastrodermis arranged into contractile fibers ...
Lecture Chpt. 32 Intro Animals
... no body cavity between digestive cavity & outer body wall no tube outside of a tube ...
... no body cavity between digestive cavity & outer body wall no tube outside of a tube ...
Earthworm Dissection
... Title the second half Earthworm Dissection. If your earthworm is not dissected using the power point presentation, your entire group receives a zero! ...
... Title the second half Earthworm Dissection. If your earthworm is not dissected using the power point presentation, your entire group receives a zero! ...
chapter 4 animal kingdom
... OnlyCrocodiles have four chambered heart Respirationisby lungs. Fertilization is internal. Oviparous andeggiscovered by hard calcareoue shells Ex. Snake, Tortoise, Turtle, Viper, Lizard ...
... OnlyCrocodiles have four chambered heart Respirationisby lungs. Fertilization is internal. Oviparous andeggiscovered by hard calcareoue shells Ex. Snake, Tortoise, Turtle, Viper, Lizard ...
19.4 Molluscs, Annelids, and Arthropods
... (seven pairs) No jaws or paired fins Hagfish are scavengers. Some lampreys are ...
... (seven pairs) No jaws or paired fins Hagfish are scavengers. Some lampreys are ...
MIAMI-DADE COLLEGE
... function. 10.2 Differentiating arteries, capillaries, and veins under the microscope. 10.3 Explaining the function of arteries, capillaries, and veins. 10.4 Locating the major arteries and veins of the systemic, hepatic portal, pulmonary, and cerebral circulation using appropriate models and charts. ...
... function. 10.2 Differentiating arteries, capillaries, and veins under the microscope. 10.3 Explaining the function of arteries, capillaries, and veins. 10.4 Locating the major arteries and veins of the systemic, hepatic portal, pulmonary, and cerebral circulation using appropriate models and charts. ...
Key Terms
... body. The carbohydrates, proteins and fats that we ingest in food supply energy, as well as building materials the body uses for growth and maintenance. Each of these resources is vital to human survival. But how long can your body last when one of these resources reaches a critical low? Stories of ...
... body. The carbohydrates, proteins and fats that we ingest in food supply energy, as well as building materials the body uses for growth and maintenance. Each of these resources is vital to human survival. But how long can your body last when one of these resources reaches a critical low? Stories of ...
biology - HCC Learning Web
... relatives, live in almost every terrestrial habitat and in fresh water The internal anatomy of an insect includes several complex organ systems ...
... relatives, live in almost every terrestrial habitat and in fresh water The internal anatomy of an insect includes several complex organ systems ...
Document
... 1. Which of the following is not a characteristic of most members of the phylum Annelida? a. hydrostatic skeleton b. segmentation c. pseudocoelom d. closed circulatory system e. all of the above are characteristics of Annelida 2. Which phylum is characterized by animals that have a segmented body? a ...
... 1. Which of the following is not a characteristic of most members of the phylum Annelida? a. hydrostatic skeleton b. segmentation c. pseudocoelom d. closed circulatory system e. all of the above are characteristics of Annelida 2. Which phylum is characterized by animals that have a segmented body? a ...
Phylum Annelida The phylum Annelida is constructed on a tube
... >>Insert a 12.5-cm piece of filter paper in the bottom of an l50 mm Petri dish. Wet it completely with spring water and remove any excess water. Invert the bottom half of a 60 mm Petri dish (upside down) on top of the filter paper, in the middle of the dish. Tape two washers on top of the smaller di ...
... >>Insert a 12.5-cm piece of filter paper in the bottom of an l50 mm Petri dish. Wet it completely with spring water and remove any excess water. Invert the bottom half of a 60 mm Petri dish (upside down) on top of the filter paper, in the middle of the dish. Tape two washers on top of the smaller di ...
Insect physiology
Insect physiology includes the physiology and biochemistry of insect organ systems.Although diverse, insects are quite indifferent in overall design, internally and externally. The insect is made up of three main body regions (tagmata), the head, thorax and abdomen.The head comprises six fused segments with compound eyes, ocelli, antennae and mouthparts, which differ according to the insect’s particular diet, e.g. grinding, sucking, lapping and chewing. The thorax is made up of three segments: the pro, meso and meta thorax, each supporting a pair of legs which may also differ, depending on function, e.g. jumping, digging, swimming and running. Usually the middle and the last segment of the thorax have paired wings. The abdomen generally comprises eleven segments and contains the digestive and reproductive organs.A general overview of the internal structure and physiology of the insect is presented, including digestive, circulatory, respiratory, muscular, endocrine and nervous systems, as well as sensory organs, temperature control, flight and molting.